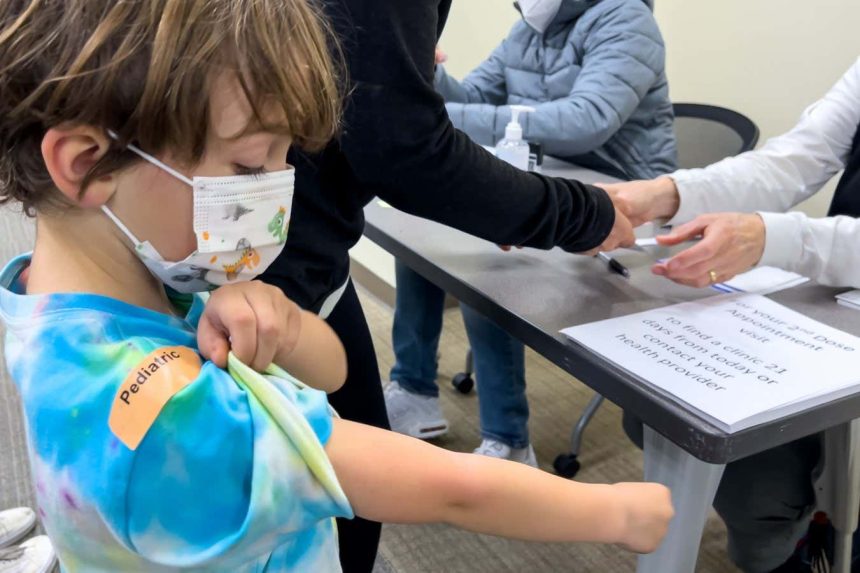
Getting vaccinated against covid-19 is safer than catching it
Juanmonino/Getty Images
The latest study on the impact of covid-19 vaccination in children has shed light on the risks associated with infection compared to vaccination. The study, which involved nearly 14 million children, revealed that the risk of serious side effects related to heart and blood vessel issues was significantly higher after infection than after vaccination.
Among children aged 5 to 18, the study found that there were over 17 additional cases per 100,000 of inflammatory conditions like Kawasaki disease in the six months following a SARS-CoV-2 infection. In contrast, children who received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine had nearly 2 fewer cases per 100,000.
Furthermore, the study highlighted that the risk of myocarditis, inflammation of the heart muscles, was more than twice as high after infection compared to vaccination. Reports of covid-19 infections causing myocarditis have been documented since April 2020, while cases of vaccines triggering myocarditis, albeit milder and with swift recovery, also emerged after vaccination campaigns began.
Despite concerns surrounding rare side effects of vaccines, the study reiterated that children who were vaccinated had a lower risk of myocarditis than unvaccinated individuals. The research team analyzed data from the National Health Service (NHS) in England, covering the period from January 2020 to December 2021.
Dr. Angela Wood from the Cambridge HDR UK Regional Network emphasized that while serious complications are rare in children, the study highlighted the higher risk associated with a covid-19 infection compared to vaccination. The comprehensive data analysis provided strong evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of vaccination in children.
However, experts like Dr. William Whiteley from the University of Edinburgh cautioned that the study’s findings may vary with different strains of the virus. Continuous monitoring and research are essential to understand the evolving landscape of covid-19 and vaccination strategies.
As the majority of the population now has some level of immunity to covid-19, the focus shifts towards booster shots and potential reinfections. Dr. Pia Hardelid from University College London emphasized the importance of ongoing studies to adapt to changing circumstances and optimize public health responses.
Topics: