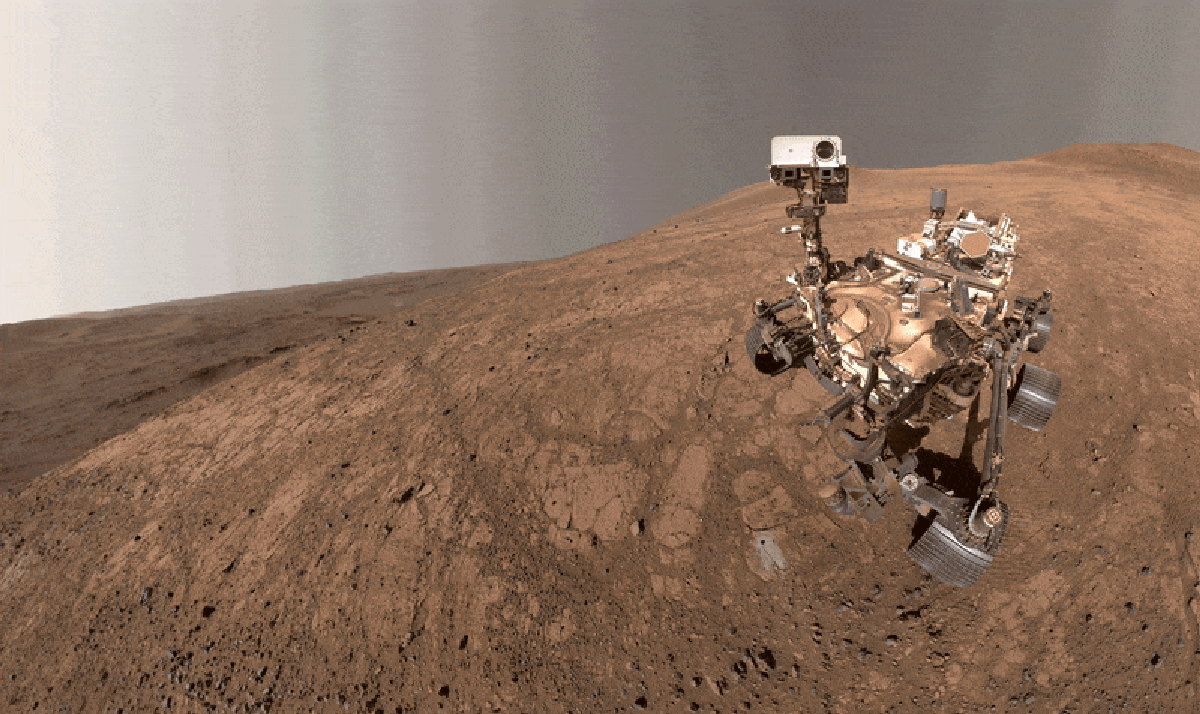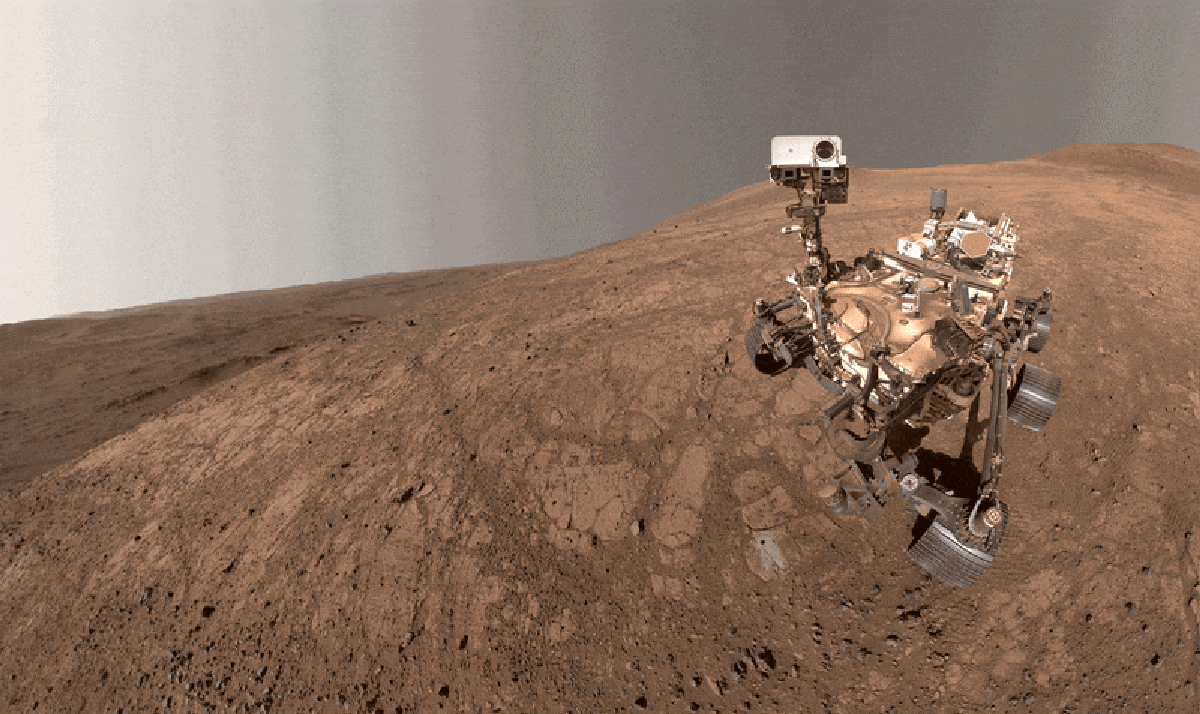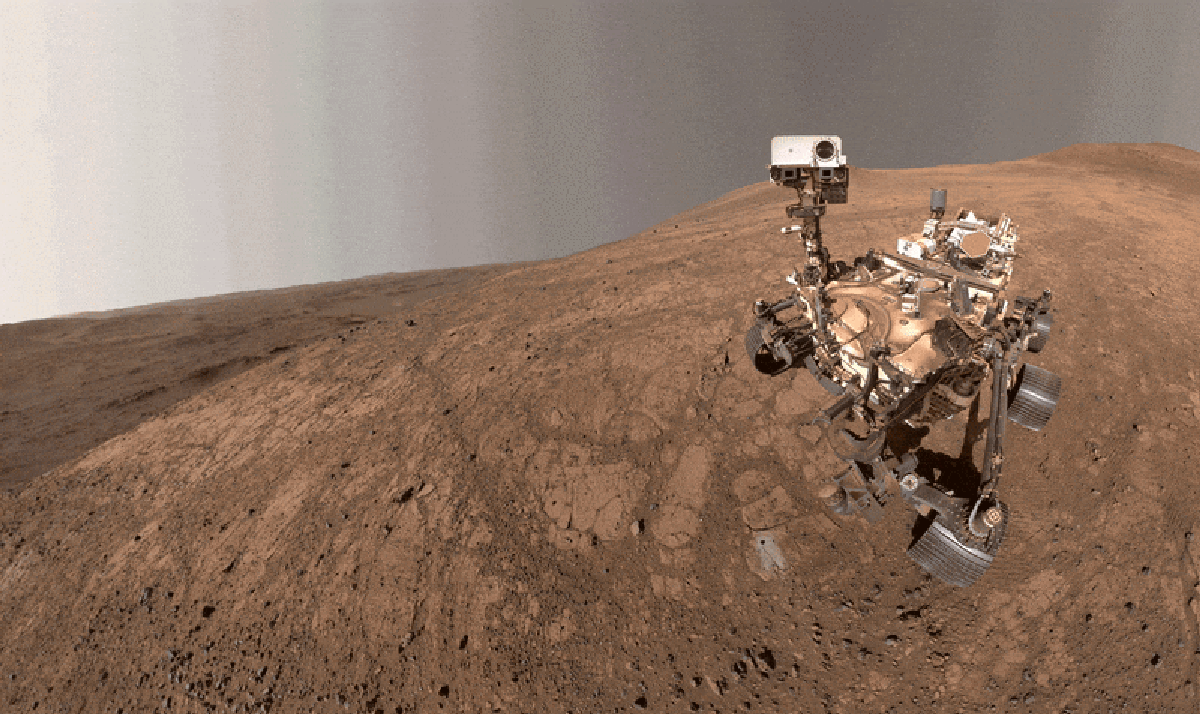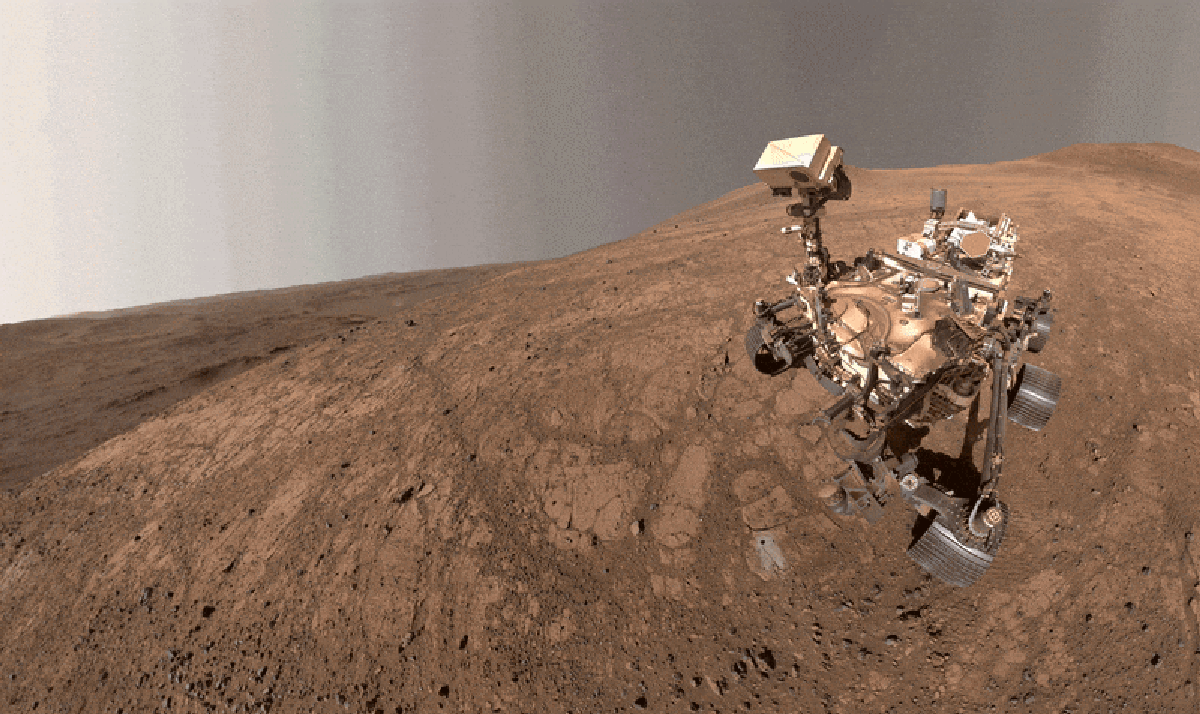
The discovery of Cheyava Falls, a school-desk-sized chunk of mudstone on Mars, has sent shockwaves through the scientific community. Formed billions of years ago in a long-lost lake on Mars, this rock is a treasure trove of information about the planet’s past. Covered in strange speckles and ring-shaped blobs, scientists have dubbed these features as poppy seeds and leopard spots. What makes Cheyava Falls even more intriguing is the presence of organic matter, suggesting the possibility of ancient alien microbes.
While the Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission aims to bring back samples of Cheyava Falls to Earth for further study, the project is facing challenges. In response, a group of scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) has come up with an innovative plan to study the rock’s mysterious features. By creating simulated mudstones in a lab environment that mimic the conditions on early Mars, they hope to unravel the secrets of Cheyava Falls.
The key to understanding Cheyava Falls lies in redox reactions, a fundamental process driven by electrons. These reactions play a crucial role in the chemistry of living organisms, allowing them to obtain energy and carry out essential functions. By studying the poppy seeds and leopard spots on Cheyava Falls, scientists can gain insights into the past environment of Mars and the possibility of microbial life.
One possible explanation for the formation of these features is nonbiological processes. Heating up the mudstone ingredients found in Cheyava Falls could trigger reactions that mimic the formation of poppy seeds and leopard spots. However, another intriguing possibility is the involvement of microbial activity. By introducing microbes into the lab-created mudstones, scientists can observe how these organisms interact with the minerals to produce similar features.
The experiments conducted by the JPL team aim to shed light on the origin of the poppy seeds and leopard spots on Cheyava Falls. While these studies may not provide definitive proof of past life on Mars, they offer valuable insights into the planet’s history and potential for supporting life. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of our neighboring planet, the discovery of Cheyava Falls stands as a testament to the enduring quest for knowledge in the field of astrobiology. The search for signs of ancient life on Mars has been a slow and painstaking process, according to Michael Tice, a geobiologist at Texas A&M College of Arts and Sciences and a member of the Perseverance science team. Tice explains that the formation of features like Cheyava Falls could have taken millions of years to develop, highlighting the intricate nature of Martian geology.
One key aspect of understanding the formation of Cheyava Falls is the comparison to sugar and oxygen reactions. Just like how sugar needs sustained heat to react with oxygen, the mudstones at Cheyava Falls may have required high temperatures of at least 150 degrees Celsius to form. However, the lack of evidence for such high-temperature conditions raises questions about alternative processes that could have led to the creation of these features.
One potential explanation is the involvement of microbial activity in the formation of Cheyava Falls. On Earth, microbes can consume organic matter and gain energy through reactions with Fe(III) and sulfates, processes that do not require high temperatures. Gupta, another member of the Perseverance science team, points out that the presence of these features in the mudstone is consistent with where microbes would likely thrive.
Despite the evidence pointing towards microbial involvement, distinguishing between geological and biological processes remains challenging. Morgan Cable, a research scientist at JPL and a member of the Perseverance science team, notes that the chemical pathways for both scenarios can start and end with similar reactants and products, making it difficult to determine the exact origin of the features.
To further investigate the potential role of microbes in the formation of Cheyava Falls, scientists are conducting laboratory experiments to recreate Martian conditions. By simulating different environmental factors and introducing microbes to Mars-like mudstones, researchers hope to observe similar patterns to those found in the Martian mudstone samples.
One method used to sterilize the mudstones for these experiments is dry heat microbial reduction (DHMR), a process that gradually warms the samples to deactivate any potential life forms. By inoculating the mudstones with microbes capable of reacting with Fe(III) and sulfates, researchers aim to replicate the poppy seeds and leopard spots seen in the Martian mudstone samples.
The experiments are expected to shed light on the specific microbial processes that could have occurred on Mars billions of years ago, providing valuable insights into the potential for ancient life on the red planet. The Perseverance science team is optimistic that their research will yield valuable results and potentially uncover more clues about the past habitability of Mars.
As the rover continues to explore Jezero Crater, the team remains hopeful that they will discover additional rocks with similar geochemical characteristics to further support their findings. The search for ancient Martian life is ongoing, and the scientists are dedicated to uncovering more evidence to paint a comprehensive picture of the planet’s past.
Now the hard work begins,
Hurowitz says.
After all the preparation and planning, the real work is just beginning. As Hurowitz stated, it’s time to roll up our sleeves and get to work on making our dreams a reality.
One of the key points Hurowitz emphasized is the importance of staying focused and dedicated to the task at hand. It’s easy to get caught up in the excitement of starting a new project, but it’s crucial to remain committed to putting in the hard work necessary for success.
Another important aspect Hurowitz touched on is the need for perseverance. Building something from the ground up is no easy feat, and there are bound to be obstacles along the way. The key is to stay resilient and keep pushing forward, no matter what challenges may arise.
Setting goals and creating a clear roadmap for achieving them is also essential. Hurowitz stressed the importance of having a plan in place to guide our efforts and keep us on track towards our ultimate objectives.
Ultimately, Hurowitz’s words serve as a reminder that the road to success is paved with hard work, dedication, and perseverance. Now is the time to put in the effort and make our dreams a reality.