New Insights into Venus’ Formation and Evolution
During the early stages of the Solar System, chaos reigned as rocks hurtled through space, colliding with the newly formed planets and leaving behind a trail of impact craters and basins. While Mercury, Mars, and the Moon bear the scars of these violent collisions, Venus has long puzzled scientists with its lack of large impact basins.
Recent research has uncovered a new type of impact structure on Venus known as tessera terrain. This unique feature, found on the surface of Venus, spans approximately 1,500 kilometers and is believed to have been formed by two consecutive giant impacts that occurred around 3.5 billion years ago. Geologist Vicki Hansen of the Planetary Science Institute suggests that this discovery could provide valuable insights into Venus’ early history and shed light on the processes that shaped the planet.
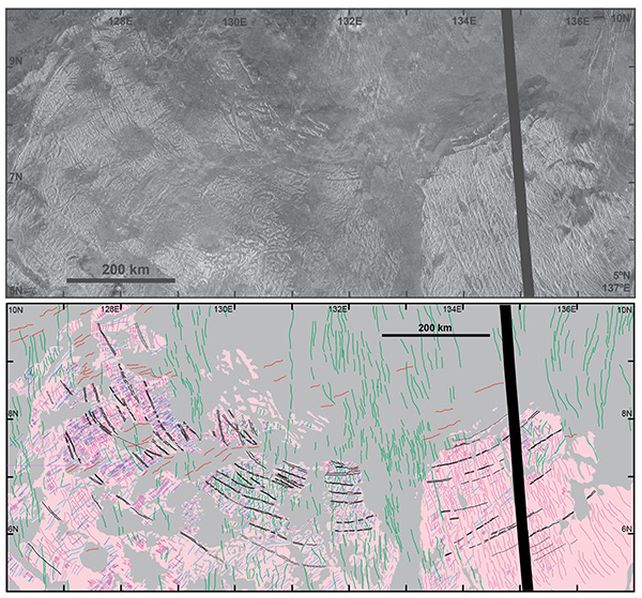
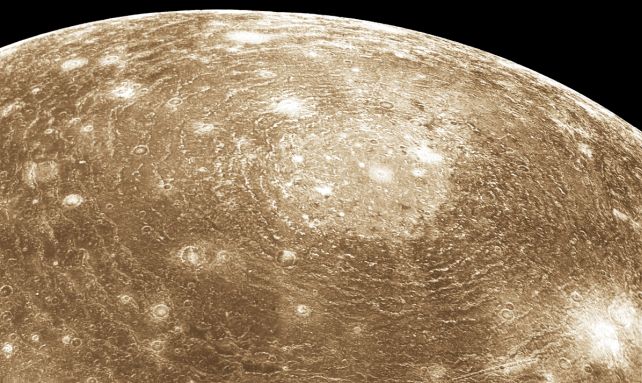
The modeling suggests that these impacts, each approximately 75 kilometers in size, penetrated Venus’ thin crust and triggered the upwelling of magma, resulting in the formation of the tessera pattern. This process is reminiscent of the formation of multi-ring impact structures observed on Jupiter’s moon Callisto, such as Valhalla.
What sets the Haastte-Baad Tessera apart is the presence of solid residuum, which results from the upwelling of magma and plays a crucial role in the elevation of the terrain. This phenomenon challenges traditional notions of impact crater formation and highlights the complexity of planetary processes.
By unraveling the mysteries of Venus’ past, scientists hope to gain a deeper understanding of the early dynamics that shaped our Solar System. The study, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, underscores the importance of reevaluating existing paradigms and embracing the unexpected in our quest to decipher the secrets of our celestial neighbors.





