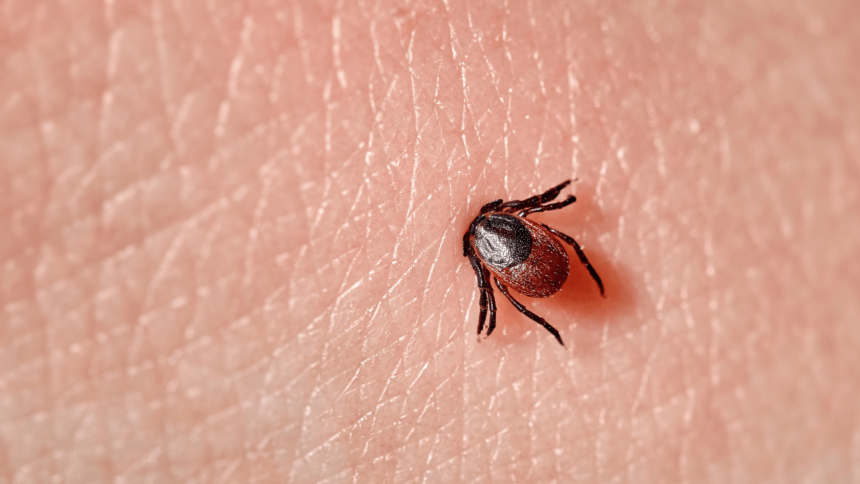
Ticks hitching a ride on migrating birds can pose a serious threat to public health, carrying diseases like Lyme disease, Anaplasmosis, and Powassan virus infection. A recent study published in the journal Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology highlights how climate change is making it easier for these ticks to spread and establish themselves in new areas.
According to University of Southern Mississippi biologist Shahid Karim, the changing climate may create more hospitable conditions for tropical tick species to thrive in regions where they were previously unable to survive. This could lead to the introduction of new diseases to these areas, posing a significant risk to both humans and animals.
Ticks are known to be efficient disease vectors, capable of transmitting pathogens between wildlife, domestic animals, and humans. With the help of migrating birds, ticks can travel long distances and spread to new locations. As global temperatures rise due to climate change, certain tick species are able to thrive in new environments and establish themselves as invasive species.
A prime example of this is the Asian long-horned tick, which was first detected in New Jersey in 2017 and has since spread to 14 additional states. This rapid geographic expansion of tick species is a cause for concern, as it increases the risk of disease transmission and establishment in new regions.
In a recent study, researchers investigated tick dispersal through migrating birds by setting up nets at various locations along the northern Gulf of Mexico. They categorized birds as residents, short-distance migrants, and long-distance migrants, and analyzed the ticks found on them to identify the species and pathogens they carried.
While the number of ticks collected was relatively low compared to the number of birds sampled, the study identified 18 different tick species, with four species accounting for the majority of ticks found. Short-distance migrants were found to carry more ticks than long-distance migrants, and some of the ticks discovered were neotropical species not native to the United States.
Further analysis of the bacteria carried by the ticks revealed the presence of Francisella and Rickettsia species, which can cause diseases like tularemia and spotted fevers in humans. These bacteria may help ticks cope with the energy demands of long-distance travel, but their potential impact on human health is still unknown.
More research is needed to fully understand the impact of bird-assisted tick dispersal and the potential risks to public health. In the meantime, it is important to take precautions when outdoors, such as wearing long sleeves, using bug repellent, and performing tick checks after being in tick-infested areas. By staying vigilant and informed, we can better protect ourselves from the threat of tick-borne illnesses in an evolving climate. The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
In today’s digital age, social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. From connecting with friends and family to staying updated on current events, social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have revolutionized the way we communicate and interact with others. However, while social media can have many benefits, it also has a dark side that is often overlooked – its impact on mental health.
Research has shown that prolonged use of social media can have negative effects on mental health, including increased feelings of loneliness, depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. One of the reasons for this is the constant comparison to others that social media encourages. People often only post the highlights of their lives on social media, creating a distorted view of reality that can leave others feeling inadequate or left out.
Moreover, the rise of cyberbullying on social media has also contributed to the decline in mental health among users. With the anonymity that social media provides, individuals are more likely to engage in hurtful behavior online, leading to increased feelings of stress and anxiety among victims.
Another factor contributing to the negative impact of social media on mental health is the addictive nature of these platforms. Studies have shown that the constant need to check notifications and updates on social media can lead to feelings of FOMO (fear of missing out) and an inability to disconnect from the online world, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and increased stress levels.
Despite these negative effects, there are ways to mitigate the impact of social media on mental health. Setting boundaries and limiting screen time, engaging in offline activities, and practicing mindfulness are all ways to reduce the negative effects of social media on mental health.
It is important for individuals to be mindful of their social media usage and its impact on their mental health. By being aware of the potential negative effects and taking steps to mitigate them, individuals can enjoy the benefits of social media while protecting their mental well-being.Ultimately, it is essential to strike a balance between staying connected online and taking care of one’s mental health offline.