On December 24, 2024, an interesting study was published that delved into the different styles of curiosity exhibited by individuals when exploring Wikipedia. The research identified three main types of inquisitiveness: the “busybody,” the “hunter,” and the “dancer.”
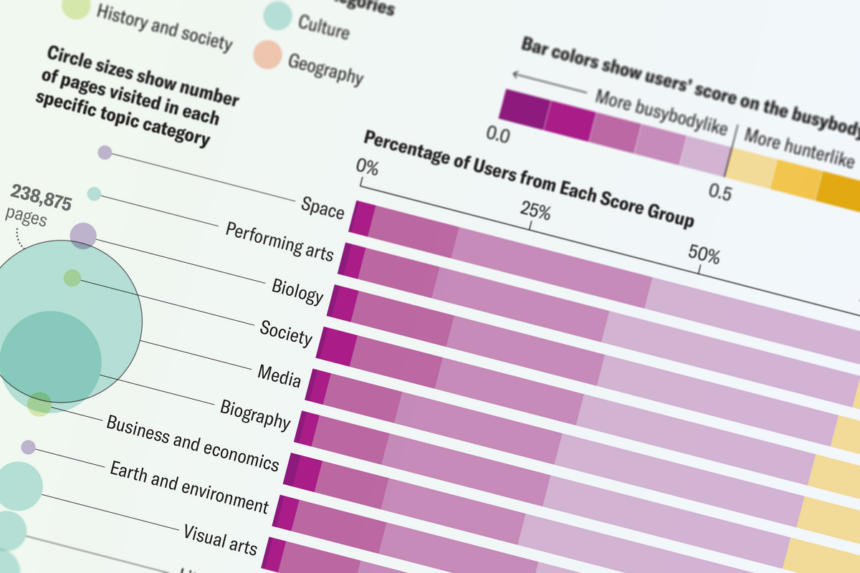
The term curiosity is often defined as a quality related to inquisitive thinking, exploration, investigation, and learning. However, the study conducted on Wikipedia users shed light on the diverse ways in which people approach information-seeking. The busybody type was characterized by a zigzagging path through various, sometimes unrelated topics. In contrast, the hunter maintained a focused search within a narrow range of closely related articles. The dancer, on the other hand, connected disparate topics to create new ideas and insights.
University of Pennsylvania network scientist Dani Bassett, one of the senior authors of the study, emphasized that curiosity is not just about acquiring information but also about connecting the pieces of information in meaningful ways. The researchers analyzed the browsing patterns of over 482,000 Wikipedia users across different countries and languages to map out these curiosity styles. They also linked these styles to location-based indicators such as education levels and gender equality.
Interestingly, the study found that in countries with higher education levels and greater gender equality, people tended to exhibit busybody-like browsing behavior. Conversely, in countries with lower scores on these indicators, individuals displayed more hunter-like behavior. This led to the hypothesis that societal structures and cultural norms play a significant role in shaping how people explore and engage with information.
The study also explored the topics of interest among busybodies and hunters, ranging from physics to visual arts. The researchers used knowledge networks to visualize how closely related different search topics were and how users navigated between them. The findings provided valuable insights into human behavior and information-seeking habits.
Princeton University psychologist Erik Nook commended the study for its interdisciplinary approach, bringing together expertise from various fields to understand human behavior better. The research team’s collaboration across disciplines like psychology, sociology, and computational modeling allowed for a comprehensive analysis of curiosity styles.
The origins of this study can be traced back to 2016 when Bassett and Perry Zurn, a professor of philosophy, noticed a gap in research on curiosity. Zurn’s deep dive into historical and philosophical literature unearthed descriptions of different curiosity styles, which were later confirmed and expanded upon in the recent study. The influence of philosophical thinkers like Heidegger and Nietzsche on the modern understanding of curiosity was highlighted through this research.
In conclusion, the study on Wikipedia searches and curiosity styles offers valuable insights into how people engage with information in the digital age. By understanding the different approaches to curiosity, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of human behavior and cognition. The integration of philosophy, psychology, and network science in this study exemplifies the interdisciplinary nature of modern research.