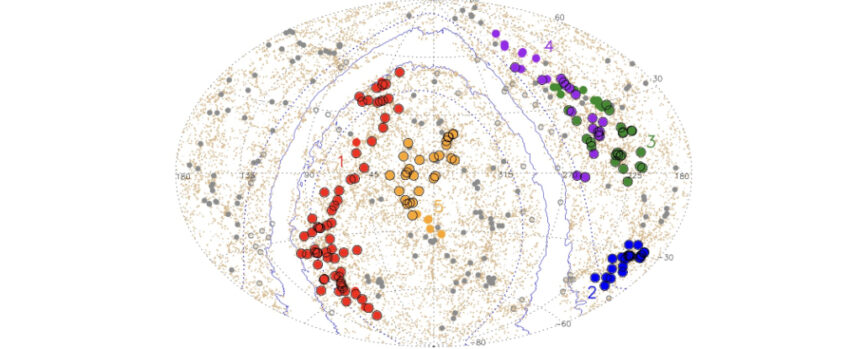
Exploring the Largest Structure in the Universe: Quipu
Understanding the Universe requires a deep dive into its largest structures, such as the recently discovered Quipu. This superstructure, named after the Incan measuring system, is a behemoth with a staggering mass of 200 quadrillion solar masses.
Astronomy is a field where massive numbers are commonplace, but the sheer size of Quipu is truly exceptional. Stretching over 400 megaparsecs, which is equivalent to more than 1.3 billion light-years, this superstructure demands attention due to its immense scale.
Research on Quipu and similar superstructures is crucial for advancing our understanding of the cosmos. By studying these colossal entities, astronomers aim to unravel the mysteries of galaxy evolution, refine cosmological models, and enhance the accuracy of cosmological measurements.
The study, titled “Unveiling the largest structures in the nearby Universe: Discovery of the Quipu superstructure,” authored by Hans Bohringer from the Max Planck Institute, underscores the significance of comprehending the local large-scale structure’s effects on cosmic observations.
Superstructures like Quipu consist of galaxy clusters and superclusters on a massive scale, challenging existing theories of cosmic evolution. These structures play a pivotal role in shaping the cosmos, influencing everything from the distribution of matter to the expansion of the Universe.
Quipu, along with four other superstructures identified in the study, harbors a substantial portion of galaxy clusters, galaxies, and matter, occupying a significant volume fraction. The intricate structure of Quipu resembles the knotted cords of an Incan quipu, hence its name.
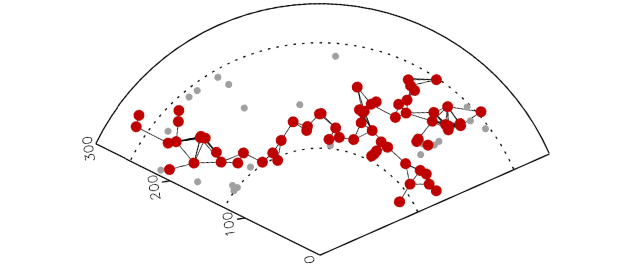
Using X-ray galaxy clusters for analysis, researchers identified Quipu and its counterparts within a distance range of 130 to 250 megaparsecs. X-ray emissions from galaxy clusters serve as indicators of mass distribution within these superstructures, enabling a detailed mapping of their structure.
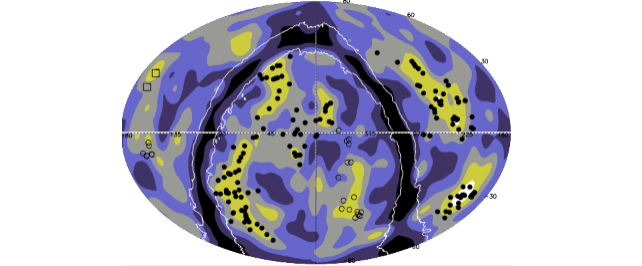
These colossal superstructures leave a profound impact on cosmological observations, affecting phenomena like the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) and the measurement of the Hubble constant. Their gravitational influence alters the CMB and distorts measurements, posing challenges for our understanding of the Universe’s early stages.

While these superstructures may eventually disintegrate into smaller units over cosmic time, their current existence holds profound implications for cosmological research. Understanding their properties and influence is crucial for unraveling the complexities of the Universe.
As astronomers delve deeper into the realm of superstructures like Quipu, new insights into galaxy evolution, cosmological models, and cosmic phenomena are poised to emerge. These colossal entities stand as testaments to the vastness and complexity of the Universe, beckoning us to explore further into the unknown.
This article was originally published by Universe Today. Read the original article.