Who Actually Pays for Tariffs?
Many people engage in discussions about who actually bears the cost of tariffs, with some claiming that consumers are the sole bearers of this financial burden. Even renowned economists, like co-blogger Pierre Lemieux, have expressed similar views. However, it’s crucial to delve deeper into the assumptions underlying this claim.
Reflecting on my article “Tariffs Will Hurt Canadians and Americans Alike” published in Defining Ideas on December 19, 2024, I emphasized the complexity of determining the true cost distribution of tariffs:
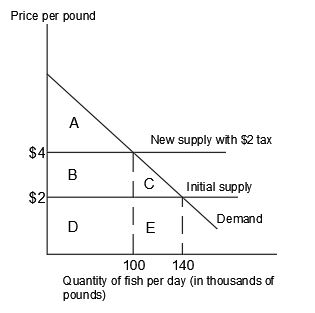
While it’s true that Americans write the checks for tariffs paid to US Customs and Border Protection on Chinese imports, this doesn’t necessarily imply that they bear the entire burden of the tax. Understanding the incidence of a tax requires considering the relative elasticities of supply and demand between producers (exporters) and consumers (importers).
There are extreme scenarios where importers shoulder the full weight of tariffs. One such case is when importers exhibit a completely inelastic demand for the taxed good, resulting in a price hike equivalent to the tariff amount but no change in quantity demanded. However, this scenario is highly unlikely given the presence of some level of demand elasticity even in the most rigid markets.
Another instance where importers may bear the entire tax burden is when the supply is infinitely elastic, causing the pre-tariff price to rise by the full tariff amount. This condition is more plausible and could occur if exporters have viable alternative markets for their goods.
Considering the ongoing tensions surrounding tariffs in Canada due to President Trump’s policies, it’s intriguing to note that Canadians’ reactions may not align with the economic implications. If Canadian exports face either perfectly inelastic demand or perfectly elastic supply, the impact of a 25% tariff might not significantly alter their revenues.
However, assuming a more realistic scenario where both demand and supply curves exhibit some elasticity, the burden of tariffs would likely be shared between Canadian exporters and American importers. While Americans may bear a larger portion of the cost, the disparity in population sizes between the two countries could result in higher per capita and per household losses for Canadians.
As highlighted in my previous article, even with a skewed burden distribution favoring American consumers, the per-person and per-household cost in Canada would be substantially higher due to the country’s smaller population.
The $95 billion loss anticipated for US consumers would translate to a per capita loss of $279 and a per household loss of $699, considering an average household size of 2.5 individuals. In contrast, Canada’s projected $23.75 billion loss would lead to a per capita loss of $579 and a per household loss of $1,448.