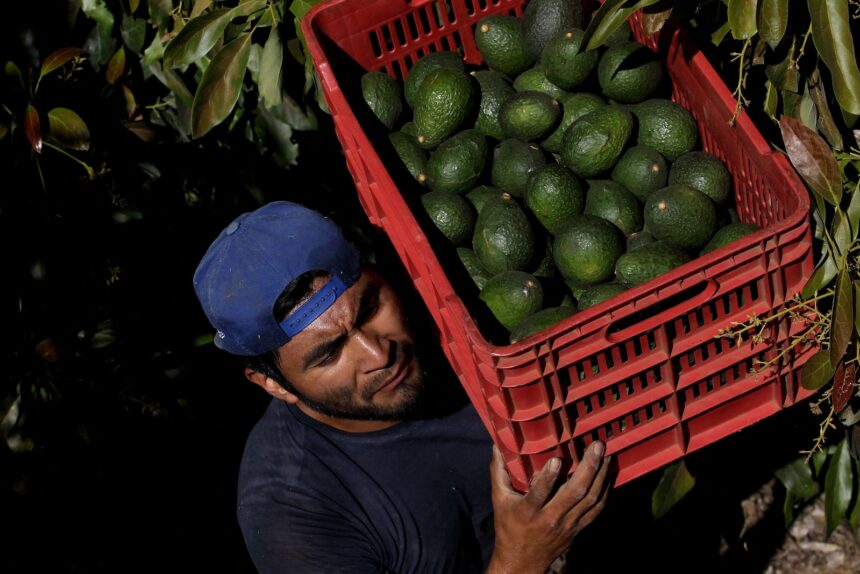
Avocados have become a staple in American cuisine, with their creamy texture and versatile uses making them a favorite ingredient. However, the surge in demand for avocados has come at a steep environmental cost, particularly in Michoacán, Mexico, where vast tracts of land are illegally cleared for avocado production.
Alejandro Méndez López, the secretary of the environment in Michoacán, has been leading efforts to address the ecological impact of the avocado industry. One such initiative is the Pro-Forest Avocado certification program, which aims to ensure that packinghouses shipping avocados internationally are sourcing sustainably grown fruit. This program has faced resistance from some avocado growers who fear it will impact their economic interests.
Despite facing threats and backlash from those opposed to the certification program, López remains committed to addressing the environmental challenges posed by the avocado industry. He believes that the use of satellite monitoring to track orchards for signs of deforestation is a critical step in ensuring the industry’s sustainability.
Michoacán’s Avocado Belt, with its fertile soils and favorable climate, has become a hub for avocado production, supplying a significant portion of the world’s avocados. The region’s avocado industry experienced exponential growth following the opening of the U.S. market through NAFTA, leading to a surge in exports to the United States.
While the avocado industry has brought economic opportunities to disadvantaged areas in Michoacán, it has also been associated with violence and environmental degradation. Local cartels and militias have sought to control the industry through coercion and violence, leading to widespread deforestation and illegal land use practices.
Despite these challenges, there are farmers like Juan Gabriel Pedraza, an Indigenous Purépecha farmer, who are working to protect the forests and promote sustainable avocado farming practices. Pedraza sees himself as a guardian of the forest, recognizing the importance of maintaining a balance between agriculture and environmental conservation.
As the avocado industry grapples with issues of violence, corruption, and environmental degradation, initiatives like the Pro-Forest Avocado certification program offer a glimmer of hope for a more sustainable future. While the road ahead may be challenging, individuals like Alejandro Méndez López remain committed to ensuring that the avocado industry evolves in a way that benefits both people and the planet. Avocado consumption has skyrocketed in recent years, leading to increased demand for the fruit and, consequently, deforestation in avocado-growing regions. A recent study found that major U.S. supermarket chains, such as Costco, Target, and Walmart, purchased avocados from packinghouses that sourced their fruit from orchards on recently deforested land in Michoacán, Mexico.
Antonio González-Rodríguez, a forest conservation scientist at the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, expressed concern over the conversion of forests into avocado orchards in Michoacán. His team estimated that by 2050, an additional 100,000 hectares of avocado orchards could be established in the region, leading to significant forest loss, including in protected reserves that are home to endangered species like the eastern Monarch butterfly.
The environmental impact of deforestation for avocado cultivation is staggering. Forests serve as vital carbon sinks, and their destruction diminishes the ecosystem’s ability to store carbon. Additionally, clearing forests contributes to water scarcity by increasing soil erosion and disrupting natural filtration processes, ultimately affecting communities’ access to clean drinking water.
Avocado trees require significant amounts of water, and as temperatures rise due to climate change, their water needs are only increasing. This has led to water shortages in regions like Uruapan, where avocado orchards draw more water than is allocated for agriculture, exacerbating the water crisis in Mexico.
To address these environmental concerns, Michoacán implemented the Pro-Forest program, which focuses on sustainable avocado production in the region. The program requires orchards to adhere to strict guidelines, including no deforestation since 2018, no forest fires since 2012, and not operating on protected land. Participating growers must also pay for forest conservation to offset their water consumption and commit to buying from certified orchards.
While the Pro-Forest program aims to promote sustainable avocado production, challenges remain. Only a small percentage of the state’s packinghouses have signed on, and some growers are skeptical of government initiatives due to concerns about enforcement and potential disenfranchisement of smaller producers.
The future of avocado production in Michoacán hinges on the success of initiatives like the Pro-Forest program in balancing the economic benefits of avocado cultivation with environmental conservation efforts. As consumer awareness of the environmental impacts of avocado production grows, there is hope for a more sustainable avocado industry that protects forests and water resources for future generations. Politicians with avocado fields have long been a poorly kept secret. Many prominent figures in government have investments in avocado production, leading to concerns about the impact on the environment. One major issue is the lack of incentives for smaller producers to maintain the forests where avocados are grown, leading to deforestation in many regions.
As global demand for avocados continues to rise, countries like Colombia, Peru, and the Dominican Republic are increasing their production. Breeders are also developing new avocado varieties to meet consumer demands. However, this growth comes at a cost to the environment, as forests are cleared to make way for avocado orchards.
In response to the environmental impact of avocado production, regulators are taking action. The European Union plans to implement “deforestation-free” product regulations, while the United States has started addressing its role in driving deforestation through avocado imports. Former U.S. ambassador to Mexico, Ken Salazar, has called for avocados from illegally cleared orchards to be blocked from the market.
While President Donald Trump has not addressed the issue, there is a possibility that his administration may take action, especially considering the threat of tariffs on Mexico. Agricultural economists believe that the administration may be interested in addressing deforestation to limit overall imports from the country.
In Mexico, there are efforts to promote deforestation-free avocados through certification initiatives. Environmental activists like Julio Santoyo Guerrero see these programs as a step in the right direction, but more needs to be done to regulate the market and protect forests from destruction.
Corruption remains a significant challenge in the avocado industry, but activists like Guerrero believe that market demand, if regulated properly, could be the key to stopping deforestation. Without stricter regulations, forests will continue to be destroyed to meet the growing demand for avocados. It’s essential for politicians, regulators, and consumers to work together to protect the environment while satisfying the demand for this popular fruit. The Importance of Supporting Local Businesses
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on supporting local businesses and the impact it can have on communities. From small mom-and-pop shops to locally-owned restaurants, these businesses play a crucial role in driving economic growth, creating jobs, and fostering a sense of community pride.
One of the key reasons why supporting local businesses is so important is that it helps to stimulate the local economy. When you choose to shop at a local store rather than a big box retailer, more of your money stays within the community. This, in turn, helps to create a cycle of economic growth as local businesses are able to reinvest in their own communities, creating even more jobs and opportunities for residents.
Furthermore, supporting local businesses helps to preserve the unique character and charm of a community. These businesses often offer products and services that you can’t find anywhere else, adding to the overall vibrancy and diversity of the area. Whether it’s a boutique clothing store, a specialty coffee shop, or a family-owned bakery, local businesses help to give a community its own distinct flavor and personality.
Another important aspect of supporting local businesses is the environmental impact. When you shop locally, you are reducing the need for long-distance transportation of goods, which in turn helps to lower carbon emissions and reduce your carbon footprint. Local businesses also tend to source their products locally, further reducing their environmental impact and supporting sustainable practices.
In addition to the economic and environmental benefits, supporting local businesses also helps to build a stronger sense of community. When you shop at a local store, you are more likely to interact with the owners and employees, creating a personal connection that is often lacking in larger, impersonal corporations. This sense of community pride and connection can help to foster a more tight-knit and supportive environment for residents.
Ultimately, supporting local businesses is not just about shopping at a different store – it’s about investing in the future and well-being of your community. By choosing to support local businesses, you are helping to create a more vibrant, sustainable, and connected community for everyone. So next time you need to make a purchase, consider shopping local and see the positive impact it can have on your community.