A Natural Yeast on Your Skin Could Help Fight Deadly Staph Infections
A deadly superbug that claims the lives of more than a million people globally a year may have a surprising nemesis that lives right under your nose – quite literally. This unlikely hero dominates your skin microbiome, where it appears to keep staph infections at bay.
The unsung hero in question is a species of natural yeast known as Malassezia sympodialis, one of the most common microorganisms found on healthy human skin. Recent research indicates that as this yeast cleans oil and fat from your skin, it produces a fatty acid that inhibits the development and growth of staph infections.
Lab experiments led by scientists at the University of Oregon (UO) have shown that M. sympodialis can combat Staphylococcus aureus bacteria through its acidic byproducts.
The yeast-produced acid, commonly found on healthy skin, is believed to prevent S. aureus from over-colonizing the microbiome. While S. aureus is a normal part of the skin microbiome, it can lead to dangerous infections if it becomes dominant or penetrates deeper tissues.
Skin and soft tissue infections involving S. aureus result in approximately 500,000 hospitalizations annually in the United States, and the bacterium has shown resistance to every class of antibiotics currently available.
Lead author Caitlin Kowalski, an evolutionary biologist at UO, emphasized the importance of exploring natural defenses against staph infections, stating, “There are lots of studies that identify new antibiotic structures, but what was fun and interesting about ours is that we identified a compound that is well-known and has been studied before.”
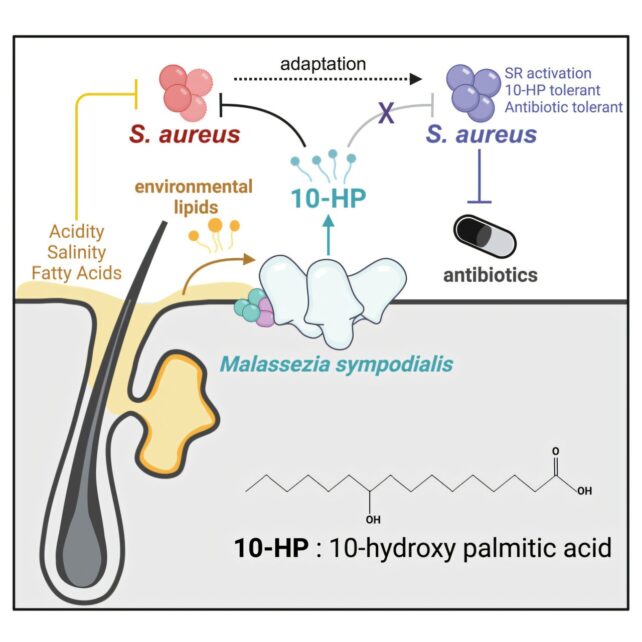
The compound responsible for this antimicrobial activity is called 10-hydroxy palmitic acid (10-HP), which was previously overlooked due to its toxic effects in a low pH environment like the skin, rather than under normal lab conditions.
Through experiments with human skin biopsies, Kowalski and her team discovered that the acid was produced by resident Malassezia yeast.
Biologist Matthew Barber, Kowalski’s adviser, described the discovery as “like finding a needle in a haystack but with molecules you can’t see.”
In laboratory tests, the M. sympodialis yeast significantly reduced the viability of various S. aureus strains after just two hours of treatment. However, over time, the bacteria developed some resistance to the yeast’s 10-HP, similar to how they adapt to clinical antibiotics.
Interestingly, researchers found that other species of Staphylococcus bacteria, which are less threatening than S. aureus, had already developed similar mechanisms to coexist with M. sympodialis yeast.
The authors of the study highlighted the need to further explore the roles of Malassezia in shaping microbial interactions and resistance in the skin microbiome.
Kowalski plans to delve deeper into the genetic mechanisms of antibiotic-resistant staph infections to understand how the bacteria evolve to evade various antimicrobial agents.
Barber emphasized the ongoing need for research to find new ways to treat or prevent infections, stating, “We still have a lot of work to do in understanding the microorganisms and discovering new strategies.”
The findings of this study were published in Current Biology.





