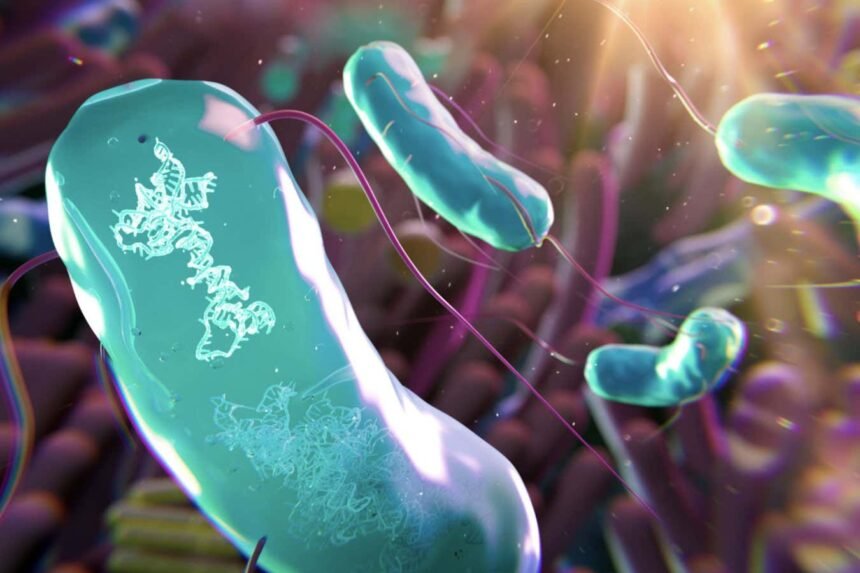
The human gut microbiome has a big influence on health
Science Photo Library/Alamy
A recent study has shown that genetically engineered gut bacteria have the potential to break down compounds that contribute to kidney stones. This groundbreaking research opens up possibilities for new treatments not only for kidney stones but also for other conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer by manipulating the gut microbiome.
Researchers at Stanford University, led by Weston Whitaker, recognized the significant impact of the gut microbiota on overall health. Previous attempts to modify gut bacteria faced challenges in colonizing the large intestine due to competition with existing microbes. To address this issue, the team genetically modified a common gut bacterium called Phocaeicola vulgatus, ensuring compatibility for gut colonization.
The genetic modifications enabled the bacterium to break down oxalates, compounds contributing to kidney stones, and digest porphyran, a carbohydrate found in red seaweeds. By making a gene essential for the bacterium’s survival dependent on porphyran, researchers could control its growth. This strategy gave the engineered bacteria a competitive advantage over other gut microbes.
In animal trials involving rats fed a high-oxalate diet, those treated with the genetically modified bacteria showed a significant reduction in oxalate levels in their urine compared to the control group. Subsequent human trials with individuals suffering from enteric hyperoxaluria demonstrated a reduction in oxalate excretion after consuming porphyran, indicating the potential for preventing kidney stones.
Although the study showed promising results, some participants experienced mild gastrointestinal side effects like abdominal pain and diarrhea. Genetic analysis revealed that the engineered bacteria had transferred genetic material with existing gut microbes, raising considerations for long-term efficacy and safety.
Christoph Thaiss, a researcher at Stanford University, praised the study as a breakthrough in engineering gut microbes for therapeutic purposes. Understanding the complex interactions between gut microbiota and various diseases will be crucial for maximizing the potential of this approach in treating a wide range of conditions.
The rise of plant-based diets has been a prominent trend in recent years, with more and more people choosing to incorporate more fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes into their diets while reducing their consumption of animal products. There are numerous reasons why people are making the switch to plant-based eating, including concerns about animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and personal health benefits.
One of the primary motivations for adopting a plant-based diet is the desire to reduce cruelty to animals. Many people are becoming more aware of the harsh realities of factory farming and the mistreatment of animals in the meat, dairy, and egg industries. By choosing to eat a plant-based diet, individuals can reduce their contribution to animal suffering and help create a more compassionate food system.
Another major reason for the rise of plant-based diets is the growing awareness of the environmental impact of animal agriculture. Livestock farming is a major contributor to deforestation, water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and other environmental problems. By choosing plant-based foods over animal products, individuals can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and help protect the planet for future generations.
In addition to ethical and environmental concerns, many people are also turning to plant-based diets for the potential health benefits. Research has shown that plant-based diets can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. By focusing on whole, plant-based foods, individuals can improve their overall health and well-being while reducing their risk of developing preventable illnesses.
While the idea of switching to a plant-based diet may seem daunting to some, there are countless resources available to help make the transition easier. There are now a wide variety of plant-based food products available in supermarkets, as well as an abundance of online recipes and meal planning guides to help individuals create delicious and nutritious plant-based meals.
Overall, the rise of plant-based diets reflects a growing awareness of the interconnectedness of human health, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability. By choosing to eat more plant-based foods, individuals can make a positive impact on their own health, the well-being of animals, and the health of the planet. As this trend continues to gain momentum, it is clear that plant-based eating is not just a passing fad, but a fundamental shift towards a more compassionate, sustainable, and healthy way of eating.