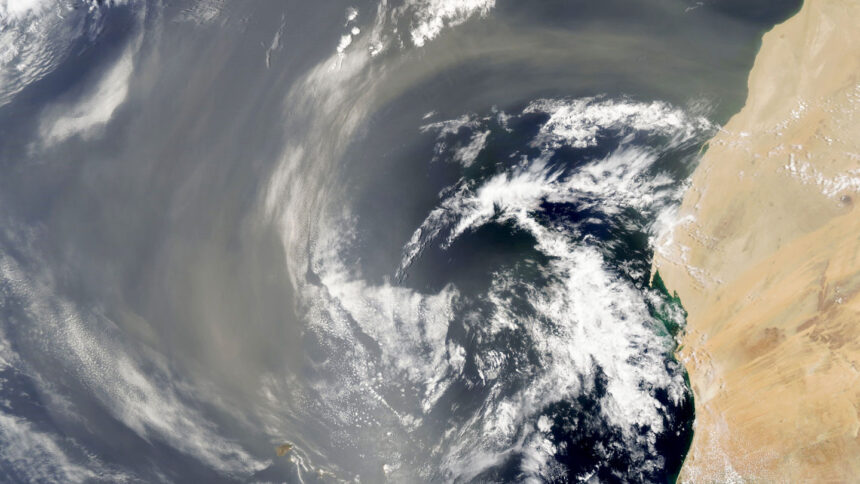
This process of iron alteration in Saharan dust as it travels across the Atlantic Ocean has significant implications for marine ecosystems. The study, published in Frontiers in Marine Science, reveals that chemical reactions in the atmosphere play a crucial role in making iron minerals in the dust more water-soluble. This transformation creates a valuable nutrient source for iron-starved seas, supporting the growth of phytoplankton.
Timothy Lyons, a biogeochemist at the University of California, Riverside, emphasizes the importance of iron for marine life. Phytoplankton, the foundation of marine food chains, require iron to carry out photosynthesis and convert carbon dioxide into sugars.
Each year, more than 240 million metric tons of Saharan dust is carried over the Atlantic Ocean, contributing to the red soils of islands like Bermuda and the Bahamas. However, a significant portion of this dust settles on the ocean surface, providing a vital source of iron to areas that are too remote to receive it from rivers.
Through their research, Lyons and marine geologist Jeremy Owens discovered a surprising change in the composition of dust-derived minerals settling in the Atlantic over the past 120,000 years. They found that the reactive iron content in the dust minerals had undergone a significant transformation during its transatlantic journey.
Typically, around 40% of iron in dust and soil is present in reactive minerals that can be utilized by organisms. However, in core samples collected from the Atlantic seabed, the dust minerals from farther west contained only about 9% of reactive iron minerals, compared to 18% in samples from closer to Africa.
The researchers concluded that as the dust particles travel across the ocean, they undergo photochemical reactions and are exposed to acids and ultraviolet radiation. These processes break down the minerals and increase the solubility of iron, making it more accessible to marine life.
Ultimately, the altered iron in the dust acts as a vital nutrient source for phytoplankton in iron-deficient regions of the ocean, supporting the growth of these microscopic organisms that form the basis of marine ecosystems.
Further exploration of dust transport and chemical reactions in the atmosphere could lead to a deeper understanding of the role of Saharan dust in shaping marine environments and sustaining oceanic life.
Iron is a crucial element in nourishing phytoplankton blooms, which in turn support a wide range of marine life in the ocean. Recent studies have shown that dust-derived iron, particularly from the Sahara desert, plays a significant role in providing this essential nutrient to the marine ecosystem. However, researchers have found that not all iron from desert dust makes it to the seafloor intact.
The study conducted by Owens and Lyons revealed that the reactive iron that reaches the seafloor is the portion that remains unaltered during air transport and is not consumed by other processes. Interestingly, the farther the desert dust travels, the less iron is left to reach the seafloor. This finding highlights the complex journey of iron particles from the desert to the ocean depths.
One of the implications of dust-derived iron reaching the seafloor is its role in spawning phytoplankton blooms, which form the basis of the marine food chain. Small fish and other organisms that feed on plankton benefit from this influx of nutrients, ultimately supporting larger predators in the ecosystem. For example, Atlantic skipjack tuna have been observed to be attracted to areas where Saharan dust settles, indicating the importance of this iron source for marine life.
While the study focused on identifying the source of iron in sediment samples from the Atlantic, it is worth noting that other sources, such as smoke from wildfires in North America, could also contribute to the iron content. By analyzing the ratios of iron to aluminum and light iron atoms to heavy iron atoms in the samples, researchers were able to trace the potential origin of the dust to the Sahara desert.
In the future, further research involving sediment analysis from various sites in the Atlantic could provide a more comprehensive understanding of how dust travels across the ocean and undergoes chemical transformations. This information is crucial for unraveling the intricate relationship between desert dust, iron deposition, and marine productivity in the oceans.
Overall, the study sheds light on the complex dynamics of iron transport from deserts to the seafloor and its implications for marine ecosystems. Understanding the role of dust-derived iron in marine productivity is essential for conservation efforts and sustainable management of ocean resources. The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and advancements being made every day. One of the most exciting developments in recent years is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is a branch of computer science that aims to create machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
AI has the potential to revolutionize industries across the board, from healthcare to finance to transportation. It has already been implemented in a wide range of applications, such as virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, self-driving cars, and recommendation systems on streaming services like Netflix and Spotify.
One of the key advantages of AI is its ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data at incredible speeds. This allows AI systems to make decisions based on data-driven insights, leading to more accurate and efficient outcomes. For example, AI-powered medical diagnostic tools can help doctors identify diseases earlier and more accurately than traditional methods, potentially saving lives in the process.
Another benefit of AI is its ability to automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative work. This can lead to increased productivity and cost savings for businesses, as well as improved job satisfaction for employees.
However, the rise of AI also raises important ethical and societal questions. Some experts warn that AI could lead to widespread job displacement, as machines increasingly take over tasks that were once performed by humans. There are also concerns about the potential for AI systems to perpetuate bias and discrimination, as they are trained on data that may be biased or incomplete.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of AI are too great to ignore. As long as we approach the development and deployment of AI with caution and a strong ethical framework, we can harness its power to improve our lives in countless ways. The future of AI is bright, and it is up to us to ensure that it is used responsibly and ethically for the benefit of all. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the way we communicate has also evolved. With the rise of digital technology, communication has become faster, more convenient, and more accessible than ever before. From social media platforms to instant messaging apps, there are countless ways for people to stay in touch with one another, regardless of their location.
One of the most significant developments in communication technology in recent years has been the advent of video calling. Video calling allows individuals to have face-to-face conversations in real-time, no matter where they are in the world. This technology has revolutionized the way we communicate, making it easier than ever to connect with friends, family, and colleagues.
Video calling offers a range of benefits that traditional phone calls or text messages simply cannot match. For starters, being able to see the person you are speaking to adds a personal touch to the conversation. Facial expressions, body language, and other non-verbal cues all play a crucial role in communication, and video calling allows for these nuances to be conveyed effectively.
Furthermore, video calling is particularly useful for those who are separated by long distances. Whether it’s a loved one living abroad or a colleague working remotely, video calling helps bridge the gap and maintain strong relationships despite the physical distance. It enables people to stay connected in a way that feels more personal and intimate than a simple phone call.
In addition to its personal benefits, video calling has also proven to be a valuable tool for businesses. With the rise of remote work and virtual meetings, video calling has become an essential means of communication for many companies. It allows teams to collaborate effectively, regardless of where their members are located, and facilitates real-time discussions that can lead to quicker decision-making and problem-solving.
Of course, like any technology, video calling also has its drawbacks. Connectivity issues, technical glitches, and privacy concerns can all pose challenges when using video calling platforms. However, as technology continues to advance, these issues are likely to be addressed, making video calling an even more seamless and reliable form of communication in the future.
Overall, video calling has fundamentally changed the way we communicate, bringing people closer together and enabling more meaningful connections. Whether used for personal or professional purposes, video calling has become an indispensable tool in today’s digital age. As technology continues to evolve, it will be exciting to see how video calling continues to shape the way we interact with one another in the years to come.