The human brain is a complex organ that plays a vital role in our daily functions. Recent research has uncovered a potential hidden network of vessels within the brain that could revolutionize our understanding of brain function and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. This discovery, if confirmed in future studies, has the potential to lead to new therapies and treatments for various brain conditions.
The brain has a unique way of cleaning itself by releasing metabolic waste into the glymphatic system, a network of channels surrounding the brain’s blood vessels that connect to the body’s lymphatic system. While previous imaging studies have not identified lymphatic vessels within the brain, a new study conducted by Chongzhao Ran and his team at Harvard University may have found a network of lymphatic-like structures inside the brain that are connected to the glymphatic system.
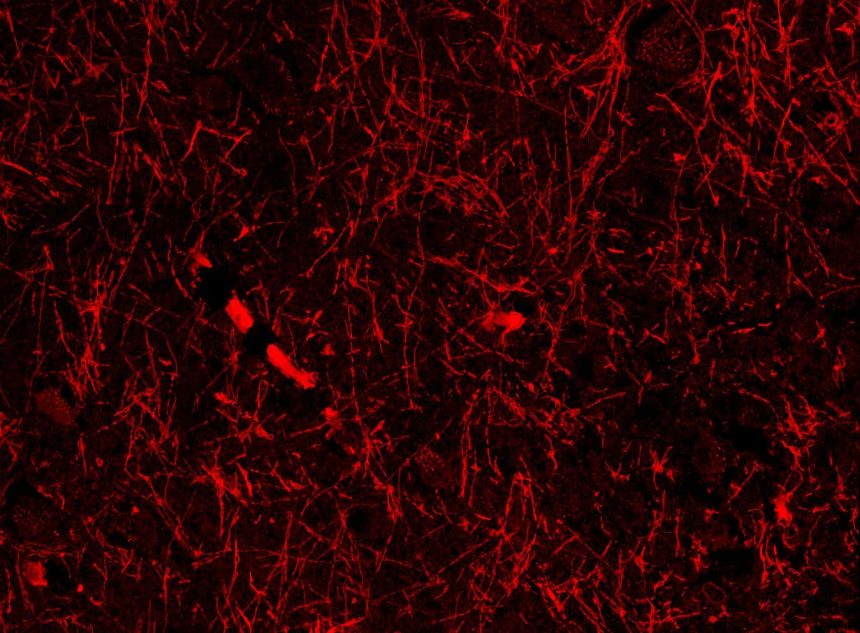
These structures were accidentally discovered by team member Shiju Gu while studying brain slices from mice with an Alzheimer’s-like disease. The researchers consistently found these vessel-like structures in various regions of the brain, including the cortex, hippocampus, and hypothalamus. They appear to wrap around the brain’s blood vessels and meningeal lymphatic vessels, indicating their role in waste drainage.
Importantly, these structures were also found in brain samples from individuals who had Alzheimer’s disease, suggesting a potential link between these structures and neurodegenerative conditions. The researchers hypothesize that these structures may be a form of lymphatic vessel or a type of protein that contributes to Alzheimer’s disease.
Further investigation is needed to confirm the nature of these structures, as some experts suggest they could be artifacts of the imaging technique used. The team plans to use electron microscopy to study the structures in more detail and determine their true identity. If confirmed, these findings could have significant implications for the development of treatments for conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Overall, this groundbreaking discovery sheds new light on the brain’s waste disposal system and opens up possibilities for innovative therapies and interventions in the field of neurodegenerative diseases. Further research is needed to fully understand the implications of these lymphatic-like structures within the brain and how they could be harnessed for therapeutic purposes.