Healthcare systems are experiencing unprecedented challenges with increasing costs, clinician burnout, and disjointed patient data undermining both efficiency and quality of care.
This is where AI in healthcare, particularly AI Agents, is becoming increasingly important. AI agent solutions are transforming how healthcare organizations operate and enhancing patient care.
According to projections, the Agentic AI sector in healthcare is expected to reach $4.96 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 45.56% from 2025 to 2030. As a significant component, AI Agents offer substantial advantages to the healthcare sector.
Wondering how to utilize AI Agents to align with current healthcare software trends? This article covers everything you need to know about AI Agents in healthcare, including types, benefits, use cases, and real-world examples.
Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways
- AI agents are autonomous software that utilizes artificial intelligence to analyze data, make decisions, and learn to fulfill specific objectives on behalf of users.
- In the healthcare context, AI agents interpret medical information, influence decisions, and execute actions to enhance patient outcomes, support healthcare providers, and streamline operations.
- Implementing AI agents in healthcare enables organizations to achieve quicker, more precise diagnoses, create personalized treatment plans, improve patient engagement, and enhance overall outcomes.
- Healthcare facilities can employ AI agents for diagnosis support, tailored treatment plans, drug discovery, workflow automation, and to combat fraud.
- Prominent examples of AI agents in healthcare include Sully AI, Innovaccer, and Notable.
What Are AI Agents in Healthcare?
AI agents are software platforms capable of autonomously executing tasks, making decisions, and interacting with data or users with minimal human intervention.
Within the healthcare field, AI agents are sophisticated systems that analyze medical data, make informed decisions, and take actions aimed at improving healthcare processes. Their focus includes enhancing patient outcomes, aiding providers, and optimizing administrative workflows.
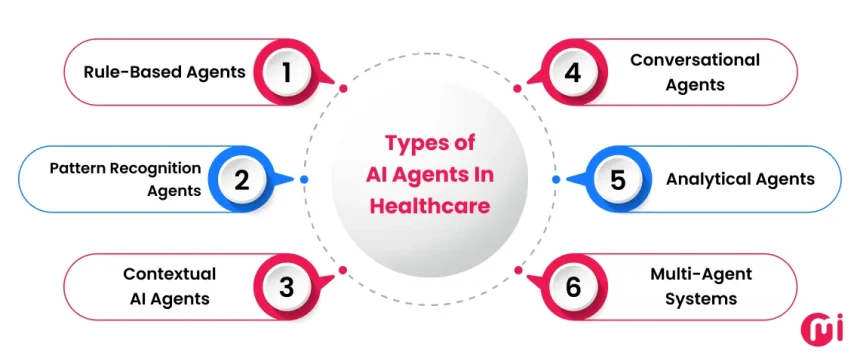
Types of AI Agents In Healthcare
The principal categories of AI agents used in healthcare consist of rule-based agents, ML-based pattern recognition agents, contextual AI agents, conversational agents, analytical agents, and multi-agent systems.
Let’s explore these various types of AI agents in the healthcare sector:
</figure>
1. Rule-Based Agents
These agents follow set rules to complete designated tasks. In healthcare, they can manage straightforward tasks such as sending alerts, reminders, or responding to frequently asked questions.
2. Pattern Recognition Agents (ML-Based)
These ML-enhanced agents identify trends, correlations, and anomalies in extensive data sets. Healthcare organizations can utilize pattern recognition agents for early disease detection, monitoring patient vitals, or identifying unusual billing practices.
3. Contextual AI Agents
Contextual AI agents make decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of patient data and operational context. Healthcare facilities can use them to recommend treatment plans or adjust workflows by factoring in multiple aspects simultaneously.
4. Conversational Agents
Conversational agents operate as natural language interfaces, like chatbots or voice assistants, facilitating interactions between patients and staff. They create an experience akin to communicating with a professional to resolve queries. Healthcare institutions can implement these agents for appointment scheduling, patient inquiries, follow-ups, and basic triage.
5. Analytical Agents
Unlike basic predictive analytics dashboards, analytical agents analyze complex datasets to generate insights and predictions. In healthcare, these agents assist with clinical decisions, population health surveillance, and resource allocation.
6. Multi-Agent Systems
Also known as agentic AI systems, these enable collaboration among multiple AI agents to solve intricate problems and achieve shared objectives. Healthcare organizations can leverage multi-agent systems for comprehensive solutions combining imaging analysis, patient data, and workflow automation.
For more clarity, read about AI agents vs Agentic AI.
Why Healthcare Organizations Need AI Agents
A majority of healthcare organizations adopt AI agents to tackle operational challenges and escalating costs, enhance productivity, improve diagnostic decision-making accuracy, provide proactive patient experiences, and unlock valuable insights from isolated data sources.
To Combat Operational Inefficiencies & Rising Costs
Healthcare personnel are often inundated with administrative responsibilities like manual data entry, repetitive processes, and lengthy approval chains. By deploying AI agents, providers can automate standard tasks involving claims processing, scheduling, and reporting. This automation enhances hospital staff focus on patient care while reducing operational expenditures and labor time.
To Empower Healthcare Professionals with Enhanced Diagnostic Precision
AI agents function as digital assistants for healthcare providers, enabling them to analyze patient histories, lab results, and imaging data to uncover critical insights more quickly. They help ease cognitive load and burnout for medical teams, fostering confident evidence-based decisions and improved diagnostic accuracy.
To Promote Proactive Patient Experiences
Patients expect healthcare applications to meet the level of convenience associated with consumer apps. AI agents fulfill this need through personalized notifications, chat-based symptom assessments, and proactive follow-ups.
As a result, healthcare providers achieve better adherence, improved clinical forecasts, and advancements in value-based care initiatives.
To Unlock Insights from Disparate Data
Data within healthcare organizations is often scattered across various platforms, including EHRs, billing software, and wearable technology. This dispersal can complicate decision-making.
AI agents help unify and interpret real-time data, establishing a coherent source of truth that enhances population health insights, clinical forecasts, and value-based care initiatives.
To Navigate Complex Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
The healthcare sector is heavily regulated, necessitating AI agents to assist in navigating intricate compliance and ethical frameworks. They aid in automating adherence to rigorous regulations such as HIPAA and HITECH, ensuring the protection of patient data.
Additionally, AI agents promote explainable AI practices, establishing accountability and building trust with both clinicians and patients.
Also Read: AI Agents for Business: Definition, Benefits, and More
Benefits of AI Agents in Healthcare
By integrating AI agents into their processes, healthcare organizations gain advanced diagnostic support, automated administrative operations, personalized patient experiences, regulatory compliance, and reduced patient care costs.
Here are some key benefits of implementing AI agents in healthcare:
1. Advanced Diagnostic Support
An AI agent connected to systems within radiology, laboratories, and EHR/EMR can access comprehensive patient data. These extensively trained agents can analyze medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs alongside pathology and patient information with high accuracy, identifying patterns that are often invisible to the human eye.
This capability aids providers in making quicker and more accurate diagnoses, particularly in complex or data-intensive scenarios.
2. Automated Administrative Processes
AI agents can streamline workflows for hospital administration by automating patient intake, appointment scheduling, referral management, and processing billing and insurance claims. This leads to a significant reduction in administrative costs and accelerates processing timelines.
3. Tailored Patient Experiences
AI agents analyze patient data, such as medical histories, genetic profiles, and lifestyle factors, to suggest individualized treatment plans and anticipate how a patient responds to various therapies.
4. Continuous Monitoring
By integrating with wearable and connected medical devices, AI agents can serve as dedicated monitors, tracking vital signs. They alert care teams to potential health risks when abnormalities are detected, enabling early intervention, especially for chronic disease management.
5. Compliance Assurance
AI agents access connected healthcare databases to track data usage patterns and billing codes to ensure compliance with laws like HIPAA and GDPR. They can also enforce adherence to these regulations, protecting patient information.
Moreover, AI agents help maintain audit trails and secure patient data while ensuring all procedures comply with healthcare standards.
6. Streamlined Revenue Cycle
AI agents automate processes like claim handling, verification, and billing, reducing errors and expediting revenue collection.
7. Cost Savings
By combining automation, predictive analytics, and better resource management, AI agents greatly decrease administrative and operational expenses. This supports healthcare organizations in achieving financial sustainability while enhancing the quality of care.
Also Read: AI Agents for Enterprises: Practical Use Cases, Examples, and Implementation Strategies
Top Use Cases of AI Agents in Healthcare
AI agents can be employed in healthcare to strengthen processes including diagnostic support, clinical documentation, personalized treatment strategies, remote patient monitoring, and revenue cycle management.
Let’s delve deeper into the principal applications of AI agents in healthcare for optimal results:
1. Diagnostic Support
Every year, diagnostic mistakes affect about 12 million Americans. Factors contributing to this may include cognitive overload, insufficient tracking of patient health, incomplete information, or lack of familiarity with rare conditions.
AI agents in healthcare can be programmed to analyze vast amounts of patient data, swiftly identifying health risks with precision. They also compare symptoms with medical databases and clinical findings to highlight potential diagnoses that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Unlike traditional clinical decision support tools that depend on fixed rule systems, AI agents apply pattern recognition drawn from millions of clinical instances, detecting subtle correlations across diverse data sources.
For example, connecting a slight lab value change with medication history and genetic background might take clinicians hours to piece together manually. Further, these AI agents continuously update their knowledge base, ensuring evidence-based recommendations as medical science evolves.
Through these applications, AI agents improve diagnostic accuracy, expedite diagnosis, bolster clinician confidence, and prevent unnecessary costs.
2. Clinical Documentation with AI Scribe
Doctors spend close to 2 hours documenting (performing EHR tasks) for every hour spent on direct patient care. This often contributes to work-life imbalance, dissatisfaction, elevated attrition rates, and burnout exceeding 50%. Such burden can also lead to diagnostic errors.
Healthcare decision-makers can incorporate AI agents with their telehealth platforms to automatically transcribe patient-physician conversations while learning individual physician preferences regarding note style and automatically integrating relevant patient data from EHR.
This results in reduced documentation times, increased face time for clinicians with patients, enhanced physician satisfaction, and improved financial outcomes.
3. Customized Treatment Plans
As noted by a AAMC news article, many cancer patients and their clinicians have come to realize that the conventional “one-size-fits-all” approach often overlooks individual responses to treatment. Advances in genomics and pharmacogenomics show that individual genetic makeup, along with lifestyle and environmental factors, profoundly influences drug efficacy and safety.
This principle extends beyond cancer to various chronic conditions. Healthcare institutions can deploy AI agents to analyze unique patient characteristics, including genetic information, biomarkers, medical backgrounds, lifestyle choices, and responses to prior treatments, in order to offer personalized therapy recommendations.
These agents synthesize current clinical research, treatment protocols, and real-world outcome data to propose interventions that align with each patient’s distinctive profile.
If integrated efficiently, AI agents can elevate treatment effectiveness, lower the chance of adverse reactions, and decrease the time to therapeutic effectiveness as well as overall costs per patient.
4. Remote Patient Monitoring
The U.S. healthcare system incurs a cost of approximately $26 billion annually due to hospital readmissions within 30 days, with Medicare imposing penalties on hospitals for excessive readmissions. Many of these complications are preventable if addressed early. Traditional care models often rely on infrequent assessments during office visits, missing out on dynamic physiological changes that indicate developing issues.
In this context, the deployment of AI agents is particularly meaningful, especially in critical care settings. AI agents can be programmed to constantly analyze data from connected medical devices, home monitoring systems, and patient-reported symptoms, tracking health status consistently between clinical visits.
These agents can identify troubling trends, forecast deteriorations, and initiate interventions before conditions worsen, thereby supporting proactive care strategies for chronic illnesses and post-discharge patients.
Over time, healthcare facilities are likely to see improvements in readmission rates, early intervention metrics, patient engagement levels, and cost savings attributable to AI agent applications.
5. Revenue Cycle & Claims Management
Approximately 10% of claims filed by hospitals experience rejection or denial, leading to an average revenue loss of $5 million per year. Moreover, hospitals face additional administrative expenses amounting to $8.6 billion annually, according to a study from Becker’s Hospital Review.
Healthcare institutions can mitigate this revenue reduction by employing AI agents to streamline the end-to-end revenue cycle encompassing patient registration, insurance validations, payment processing, and follow-up on accounts receivable. These agents can adeptly manage the intricate rules governing payer requirements, maintain coding accuracy, and optimize reimbursements.
The outcome is an enhancement in the clean claim rate, reduced days in accounts receivable, minimized denial rates, and increases in staff efficiency.
6. Medical Coding & Billing Assistance
Coding mistakes result in billions in losses for healthcare providers yearly due to under-coding (missing potential revenue) and over-coding (which may lead to compliance breaches, audits, or fraud accusations). The transition to ICD-10 introduced over 73,000 diagnosis codes requiring specialized expertise to navigate.
Healthcare organizations can employ AI agents to scrutinize clinical documentation and recommend appropriate medical codes, such as ICD-10 diagnosis codes, CPT procedure codes, and HCPCS supply codes, ensuring accurate billing and optimal reimbursement.
Additionally, these agents can enhance clinical documentation by pinpointing missing elements that would allow for more precise coding or better patient acuity capture.
7. Fraud Detection & Compliance Oversight
Healthcare fraud costs the industry tens of billions annually. Even using conservative estimates to gauge losses, around 3% of total healthcare expenditures, the implications are substantial. Some government sources estimate this figure could escalate to nearly 10%, equating to over $300 billion each year. A single violation of the False Claims Act could result in fines ranging from $14,308 to $28,619 for each claim.
Amid the prevailing examples of AI in healthcare, leveraging AI agents offers promise for addressing these issues. They can analyze billing practices, clinical documentation, and provider activities to detect potential fraud, waste, abuse, and compliance breaches. These agents identify discrepancies that may signal either deliberate fraudulent activities (e.g., overbilling) or unintentional mistakes before they precipitate audits, penalties, or legal troubles.
When implemented, AI agents can boost fraud detection rates, minimize false positives, mitigate audit risks, and provide financial safeguards.
8. Virtual Health Assistants & Enhancing Patient Engagement
Healthcare call centers typically manage thousands of inquiries daily regarding appointment scheduling, prescription refills, billing queries, or basic health information. Each call could cost around $4 to $8. It’s noteworthy that during these calls, staff frequently require time to gather information, causing 30% of patients to abandon calls after just one minute, according to Simbo AI.
As a superior solution, healthcare organizations can incorporate AI agents within patient portals. These can engage with patients using chatbots, voice assistants, and SMS to address health-related inquiries, schedule appointments, send medication reminders, conduct symptom assessments, and assist patients throughout their healthcare journeys. Such proactive AI agents operate continuously, managing routine inquiries that would otherwise demand staff time or risk going unaddressed.
Consequently, hospitals can see reduced call center workloads, enhanced patient satisfaction, fewer no-shows, and increased employee productivity.
9. Chronic Disease Management
Chronic conditions account for approximately 90% of the U.S.’s total $4.9 trillion healthcare expenditure. Furthermore, annually, 1.8 million people in the U.S. receive cancer diagnoses, and 600,000 die from the disease.
Upon being diagnosed, patients often incur visits with multiple specialists who may not effectively communicate, leading to redundant tests, conflicting treatment guidelines, and care gaps. During the often 3- to 6-month intervals between appointments, patients struggle with adhering to medications, lifestyle changes, and determining whether symptoms necessitate medical attention or can be self-managed.
Healthcare authorities can mitigate this serious challenge by adopting AI agents. These agents provide continuous support between clinical visits, maintaining continuity that episodic care models typically lack. They monitor patient-generated health data from glucose meters, blood pressure devices, and symptom logs to spot trends indicating deteriorating health.
In addition, these AI agents offer personalized education based on individual trends; for instance, if a diabetic patient’s glucose levels rise each morning, the agent may provide relevant insights about the dawn phenomenon and suitable breakfast options. If necessary, they facilitate coordination among providers by sustaining a comprehensive care plan, identifying overdue specialist referrals, and ensuring that test results are communicated effectively across care teams.
10. Operational Optimization Efforts
Patient experience can suffer due to suboptimal operations. Factors like prolonged emergency room wait times, surgical hold-ups, and hurried discharges negatively affect satisfaction ratings tied to reimbursement models. Traditional operational management relies on historical averages and manual coordination, potentially overlooking real-time data optimization.
By deploying AI agents, hospitals can enhance operational efficiency by forecasting demand, effectively managing resources, coordinating workflows, and pinpointing operational inefficiencies.
AI agents are capable of processing real-time data from patient arrivals, bed occupancy rates, staff availability, surgical schedules, supply usage, and even external variables such as weather fluctuations and community events to forecast demand and optimize resource allocation.
As a result, organizations improve capacity utilization, OR efficiency, reduce supply costs, and optimize labor expenditures.
| Category | AI Agent Use Case |
| Diagnostic Support | Analyzes patient data to detect patterns, surface likely diagnoses, and reduce diagnostic errors. |
| Clinical Documentation | Transcribes consultations, auto-fills EHRs, and cuts physician documentation time. |
| Personalized Treatment Plans | Uses genomics and patient data to recommend tailored, evidence-based therapies. |
| Remote Patient Monitoring | Tracks real-time health data to predict deterioration and prevent readmissions. |
| Revenue & Claim Management | Automates billing workflows, verifies payers’ rules, and minimizes claim denials. |
| Medical Coding & Billing | Suggests accurate ICD/CPT codes and improves documentation for reimbursement. |
| Fraud & Compliance Monitoring | Flags billing anomalies and detects fraud or compliance violations early. |
| Virtual Health Assistants | Engages patients via chat or voice for scheduling, reminders, and self-care support. |
| Chronic Disease Management | Monitors ongoing health data and coordinates care across multiple providers. |
| Operational Optimization | Forecasts demand, optimizes staffing, and streamlines hospital workflows. |
Real-World Examples of Top AI Agents in Healthcare
As healthcare providers transition from theory to practical implementation, several AI agent platforms, such as Sully AI, Innovaccer, and Notable, are setting high standards for automation, precision, and clinical efficiency.
Let’s examine these real-world examples of AI agents in healthcare that are reshaping care delivery:
1. Sully AI
Sully AI is an AI Agent platform supported by Y Combinator, offering a diverse range of healthcare functionalities, including:
- An AI Receptionist that handles patient calls, schedules appointments, and manages front office communications.
- An AI Scribe that automatically transcribes and organizes discussions between patients and doctors, alleviating the burden of manual documentation.
- An AI Medical Coder that reviews visit notes to provide precise medical coding (ICD-10 and CPT) to accelerate and ensure compliant billing.
- An AI Nurse that assists with patient intake, symptom screening, and triage prior to scheduled appointments. They also manage tasks like medication ordering, follow-ups, and referrals.
- An AI Medical Assistant that supports clinicians by addressing clinical inquiries and conducting rapid medical research.
This suite of functionalities reduces paperwork, speeds up charting, and affords providers more direct interaction with patients.
Numerous healthcare institutions, including Tebra, Midi, Apogee, and AdvantageCare Physician, have placed their trust in Sully AI, achieving significant positive impacts.
2. Innovaccer
Innovaccer specializes in healthcare data activation and analytics, assisting providers, payers, and governmental bodies in unifying fragmented data to foster proactive decision-making and enhance patient care and operational efficiency.
Its AI agents facilitate ambient documentation, consultations, insights, and outcome forecasting, delivering insights that can be three times more accurate.
The platform provides pre-trained and customizable AI agents for specific healthcare tasks like:
- A Scheduling Agent aimed at automating appointment booking, rescheduling, and patient reminders.
- A Patient Intake Agent that simplifies onboarding and data collection.
- A Referral Agent managing care referrals effectively to close care loops.
- An Authorization Agent that oversees prior authorizations and tracks approvals.
- An ED Follow-up Agent for coordinating timely post-emergency department patient follow-ups.
- A Care Gap Closure Agent detecting care gaps and engaging patients for preventive care measures.
- A Risk Coding Agent optimized for maximizing reimbursement by identifying accurate risk codes.
- An FAQ Agent that promptly answers routine patient and staff queries.
Innovaccer’s solutions are empowering healthcare organizations including Kaiser Permanente, Dignity Health, Banner Health, and Baptist Health South Florida to foster better patient care, increase operational efficiency, and enhance financial performance.
3. Notable
Notable Health offers an AI platform designed to automate healthcare workflows, thus boosting operational efficiency and patient care quality. Its AI Agent Workforce allows organizations to manage rising workloads without needing additional staff, enabling growth in patient volume while controlling costs.
- It automates complete healthcare workflows including quality improvement, risk adjustment, patient access, revenue cycles, and more.
- It minimizes the necessity for manual administrative work, allowing healthcare providers to concentrate on higher-value care.
- The platform provides pre-built AI agents and a low-code interface to ensure custom solutions catered to specific needs.
- Analytics dashboards facilitate performance benchmarking and workflow optimization to demonstrate return on investment (ROI).
Notable is helping healthcare organizations such as Florida Health System, Sturdy Health, and Security Health Plan achieve improved efficiency, scalability, and enhanced patient care.
How MindInventory Empowers Healthcare Organizations With AI Agents
Recognizing the advantages AI agents offer in healthcare reveals opportunities for integration into workflows. However, successfully doing so requires input from an experienced AI/ML development company.
This is where MindInventory comes into play. Our dedicated AI developers for hire empower healthcare organizations by designing, building, and integrating AI agents that cater to their unique necessities.
Be it the automation of administrative tasks, enhancing diagnostic support for clinicians, or fostering personalized patient engagement, our AI solutions are crafted to yield significant results.
We achieve this by:
- Assessing workflows, data sources, and operational challenges to identify valuable opportunities for AI agent deployment.
- Designing AI agents that are in alignment with your clinical and operational objectives.
- Effortlessly integrating AI agents with EHRs, telehealth platforms, and administrative systems, ensuring a smooth interoperability of healthcare data and adoption.
- Ensuring compliance with industry standards such as HIPAA, HITECH, FHIR, and other regional healthcare regulations.
FAQs About AI Agent in Healthcare
How do AI Agents work in Healthcare?
AI Agents in healthcare function by analyzing data to automate tasks, assist in diagnoses, and enhance patient monitoring and engagement. Specifically, they operate as autonomous systems, processing information from patient records, medical images, and sensor data to take actions such as scheduling appointments, flagging health concerns, or recommending treatment options.
What is the process for developing AI agents for healthcare?
The development of AI agents for healthcare entails defining their purpose and scope, gathering and preparing relevant data, selecting appropriate AI technologies, designing the architecture, creating the core components of AI agents with necessary safeguards, testing and validating the construction, launching them in a production setting, and continuously monitoring and enhancing the agents’ performance.
What are the key challenges in implementing AI agents in healthcare?
Challenges in implementing AI agents within healthcare settings include addressing algorithmic bias, ensuring consistent transparency and explainability, adhering to regulatory frameworks, the necessity for clinical validation, resistance to change, a shortage of AI talent, and the potential costs associated with implementation.
How much does it cost to build an AI agent for healthcare?
The cost of constructing an AI agent for healthcare ranges from $50,000 to $250,000+. The overall price can fluctuate based on factors like data accessibility and preparation, compliance with regulations, system integration, advanced features, liability considerations, testing, and ongoing maintenance.
What’s the difference between AI agents and chatbots in healthcare?
In the healthcare realm, chatbots perform straightforward, predefined tasks like scheduling appointments and addressing basic questions, while AI agents are more sophisticated, autonomous systems capable of understanding context, executing complex multi-step procedures, making decisions, and offering personalized health advice.
How do AI agents improve patient care outcomes?
AI agents enhance patient care outcomes through various channels, providing clinicians with support to diagnose conditions quickly, developing customized treatment strategies, monitoring patients remotely, and identifying gaps in care before they escalate.
What is the future of AI Agents in healthcare?
The future of AI agents in healthcare points toward increased intelligence, connectivity, and predictability, transitioning from reactive to proactive roles in fields such as early disease detection, personalized treatment, and enhanced patient monitoring.
Are AI agents safe and compliant with healthcare regulations?
Yes, AI agents are generally secure and compliant with healthcare standards, provided that appropriate safeguards are implemented during their design and deployment by developers and healthcare partners. Robust governance and oversight are essential to mitigate risks related to data privacy, accuracy, bias, and accountability.
How do AI Agents work in Healthcare?
AI Agents in healthcare function by analyzing data to automate tasks, assist in diagnoses, and enhance patient monitoring and engagement. Specifically, they operate as autonomous systems, processing information from patient records, medical images, and sensor data to take actions such as scheduling appointments, flagging health concerns, or recommending treatment options.
What is the process for developing AI agents for healthcare?
The development of AI agents for healthcare entails defining their purpose and scope, gathering and preparing relevant data, selecting appropriate AI technologies, designing the architecture, creating the core components of AI agents with necessary safeguards, testing and validating the construction, launching them in a production setting, and continuously monitoring and enhancing the agents’ performance.
What are the key challenges in implementing AI agents in healthcare?
Challenges in implementing AI agents within healthcare settings include addressing algorithmic bias, ensuring consistent transparency and explainability, adhering to regulatory frameworks, the necessity for clinical validation, resistance to change, a shortage of AI talent, and the potential costs associated with implementation.
How much does it cost to build an AI agent for healthcare?
The cost of constructing an AI agent for healthcare ranges from $50,000 to $250,000+. The overall price can fluctuate based on factors like data accessibility and preparation, compliance with regulations, system integration, advanced features, liability considerations, testing, and ongoing maintenance.
What’s the difference between AI agents and chatbots in healthcare?
In the healthcare realm, chatbots perform straightforward, predefined tasks like scheduling appointments and addressing basic questions, while AI agents are more sophisticated, autonomous systems capable of understanding context, executing complex multi-step procedures, making decisions, and offering personalized health advice.
How do AI agents improve patient care outcomes?
AI agents enhance patient care outcomes through various channels, providing clinicians with support to diagnose conditions quickly, developing customized treatment strategies, monitoring patients remotely, and identifying gaps in care before they escalate.
What is the future of AI Agents in healthcare?
The future of AI agents in healthcare points toward increased intelligence, connectivity, and predictability, transitioning from reactive to proactive roles in fields such as early disease detection, personalized treatment, and enhanced patient monitoring.
Are AI agents safe and compliant with healthcare regulations?
Yes, AI agents are generally secure and compliant with healthcare standards, provided that appropriate safeguards are implemented during their design and deployment by developers and healthcare partners. Robust governance and oversight are essential to mitigate risks related to data privacy, accuracy, bias, and accountability.