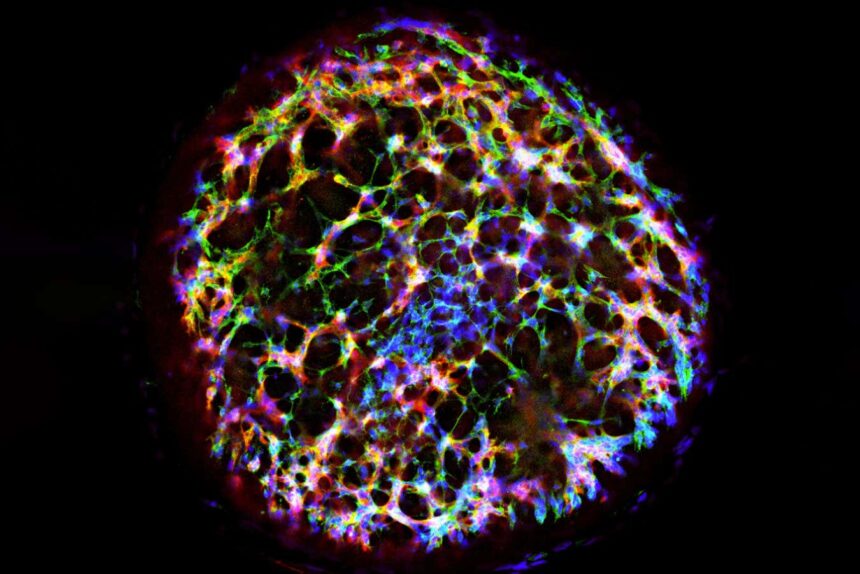
A human vascular organoid generated from stem cells
Melero-Martin Lab, Boston Children’s Hospital
A groundbreaking study has shown that tiny lab-grown blood vessels, known as organoids, could be the key to restoring blood flow to injured tissue in mice, ultimately reducing necrosis. This innovative approach holds promise for mitigating the damage caused by accidents or blood clots in the future.
Traditionally, researchers have created clusters of lab-grown blood vessels by exposing human stem cells to a combination of chemicals, a process that can take weeks and often yields vessels that do not accurately replicate those in the human body. However, a team led by Juan Melero-Martin at Harvard University took a different route. They genetically modified human stem cells derived from reprogrammed skin cells, giving them a genetic sequence that prompts the cells to develop into blood vessels when exposed to the antibiotic doxycycline. Remarkably, this approach resulted in the formation of fully functional blood vessel organoids in just five days, with protein and gene activity levels closely resembling those found in natural human vessels.
In a series of experiments on mice, the researchers demonstrated the efficacy of their organoids in treating tissue injuries. By surgically cutting off blood supply to one of the mice’s legs, reducing it to less than 10% of normal levels, and then implanting 1000 organoids at the injury site, they observed a significant restoration of blood supply to 50% of normal levels within two weeks. This successful vascular integration could have profound implications for reducing tissue damage in various medical scenarios, such as heart attacks.
According to Oscar Abilez from Stanford University, the ability to restore such a substantial amount of blood flow in damaged tissue could be instrumental in minimizing tissue necrosis. In the study, approximately 75% of the treated animals exhibited minimal levels of dead tissue, compared to nearly 90% in untreated individuals.
Furthermore, the researchers explored the potential of their organoids in treating mice with type 1 diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to pancreatic damage. By combining organoid implants with pancreatic tissue transplants, they significantly improved blood sugar control in the mice, showcasing the versatility and promise of this novel approach.
While the results are promising, further research in larger animals such as pigs is necessary before clinical trials in humans can commence, notes Abilez. Melero-Martin envisions human studies within the next five years, highlighting the potential impact of this technology on tissue repair and regeneration.
Besides its applications in tissue injury treatment, this breakthrough could pave the way for the development of lab-grown mini-organs that closely mimic human physiology. By incorporating blood vessels into organoids, researchers could create more accurate models for studying diseases and testing potential treatments, ultimately advancing medical research and personalized healthcare.