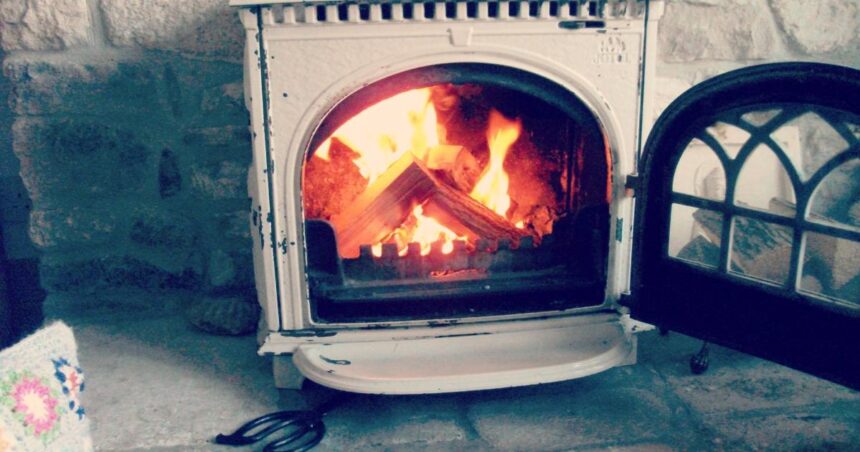
Wood burners in urban family homes should be phased out to protect children’s health, leading paediatricians have said.
A new position statement from the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health (RCPCH) calls for tougher Government action to curb air pollution.
One key new recommendation is to “phase out domestic wood-burning in urban areas, assist rural residents to transition away from wood as a primary heating source, and support those in fuel poverty with fuel cost assistance.”
Dangerous
Other measures to protect children include monitoring air quality around schools and giving councils new powers to act when pollution exceeds safe limits.
The RCPCH said it also wants to see Ella’s law brought in, and for the Government to commit to World Health Organisation (WHO) air quality guidelines.
Ella’s law is named after Ella Roberta Adoo Kissi Debrah, who died in 2013 aged nine as a result of asthma, contributed to by exposure to excessive air pollution in London.
She was the first person in England to have air pollution named as a cause of death by a coroner.
The RCPCH also wants to see Awaab’s law implemented and expanded, to protect private renters from dangerous living conditions, such as those with damp and mould.
Irreversibly
It is named after two-year-old Awaab Ishak, who died in 2020 from a respiratory condition caused by “extensive” mould in the one-bedroom flat where he lived.
The RCPCH said the UK Government must also work to ensure half of urban journeys can be walked or cycled by 2030, alongside accessible public transport.
RCPCH vice president for policy and a paediatric respiratory consultant, Dr Mike McKean, said: “This year, air pollution has officially overtaken high blood pressure and smoking as the leading contributor to global disease.
“Exposure to air pollution is now the second leading risk factor for death in children under five, both globally and in the UK.
“As a consultant in respiratory paediatrics, I am especially concerned about the impact of air pollution on a child’s developing lungs.
“Breathing dirty air as a child irreversibly stunts lung growth and continues to affect lung capacity in adulthood, in some cases it can even result in death.
Particulate
“As paediatricians, we want to ensure that no child should suffer as Ella and Awaab did.”
Dr Emily Parker, RCPCH clinical fellow, said: “As a doctor working in paediatric A&E, I see the impacts of air pollution on children during almost every shift.
“I want to protect them from this avoidable harm, but there is a limit to what I or any clinician can do through clinical work.
“That’s why we’re calling on the government to prioritise taking national action and tackle the top causes of (particulate matter) PM2.5 and nitrogen dioxide, the two air pollutants that are most harmful to children’s health.
Conditions
“In 2021, the World Health Organisation outlined new, evidence-based targets for these pollutants, yet the Government has not yet committed to meeting these guidelines, which are aimed at protecting human health.
“Air pollution limits across the UK are currently set dangerously high, often at four times WHO guidelines. As of yet, no government plan is in place to reduce these levels.”
According to the RCPCH, PM2.5 is one of the most harmful air pollutants and can be breathed deep into the lungs and absorbed into the bloodstream.
This affects children’s developing organs and increases the chance of developing long-term health conditions in adulthood.
Prevent
It said children are especially vulnerable to air pollution because they inhale more air than adults in proportion to their body weight, breathe in air pollution that is closer to ground level such as vehicle exhaust fumes, and are less able to control their exposure than adults.
Professor Sir Stephen Holgate, the Royal College of Physician’s special adviser on air quality, said: “The economic burden of air pollution, including its avoidable strain on the NHS, and the harms caused by poor indoor air quality are further evidence that decisive steps must be taken.
“We’re particularly supportive of RCPCH’s call for a Clean Air Act and the expansion of Awaab’s law, both of which are vital to protecting the most vulnerable and ensuring healthier environments for all…
“There can be no question that cleaning up the air we all depend upon for life would prevent many diseases and save countless lives.”
This Author
Jane Kirby is the PA health editor.