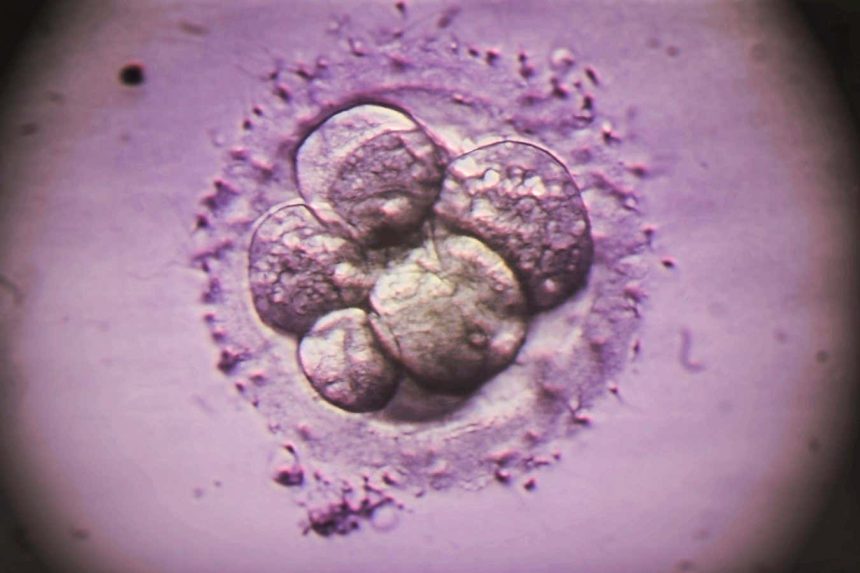
In the world of in vitro fertilisation (IVF), the process of genetic testing of embryos before implantation is crucial. However, a recent study has shed light on the limitations of a widely used test called preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A). This test, which checks for extra or missing chromosomes in embryos, may not be able to detect genetic abnormalities that form just before implantation, raising questions about its effectiveness in selecting healthy embryos for transfer to the uterus.
Researchers, led by Ahmed Abdelbaki at the University of Cambridge, conducted a study to monitor the development of human embryos for 46 hours after thawing, replicating the timeline between testing and implantation. Using a light-sheet microscope, which minimises light exposure and allows longer observation, they injected fluorescent dye into 13 embryos to track the formation of genetic abnormalities in real time. The study revealed that 8% of cells experienced chromosome misalignment, a phenomenon that can lead to extra or missing chromosomes and increase the risk of miscarriage or genetic conditions like Down syndrome.
Interestingly, these errors were found to occur in the outer layer of cells, which eventually form the placenta, and not in the cells at the centre of the embryos that develop into the fetus. Previous research has shown that embryos with some genetic abnormalities in the outer cells can still result in successful pregnancies, suggesting that these errors may not necessarily impact embryo viability.
However, the study emphasises the need for further research in screening embryos for genetic abnormalities, especially considering the potential genetic changes that may occur between testing and implantation. Dr. Lilli Zimmerman from Northwell Health in New York state highlights the importance of understanding how these genetic errors may affect embryo viability and the need for larger studies to validate these findings.
In conclusion, while PGT-A remains a valuable tool in the IVF process, this study underscores the complexity of embryo development and the need for more comprehensive screening methods. As technology advances and research continues, the goal is to improve the selection of healthy embryos for successful pregnancies through a deeper understanding of genetic abnormalities and their impact on embryo viability.