Wastewater surveillance has emerged as a crucial tool in monitoring regional infection trends, especially in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. In a recent development in Japan, the National Action Plan for Novel Influenza has mandated the regular implementation of wastewater surveillance to track infection rates in the community.
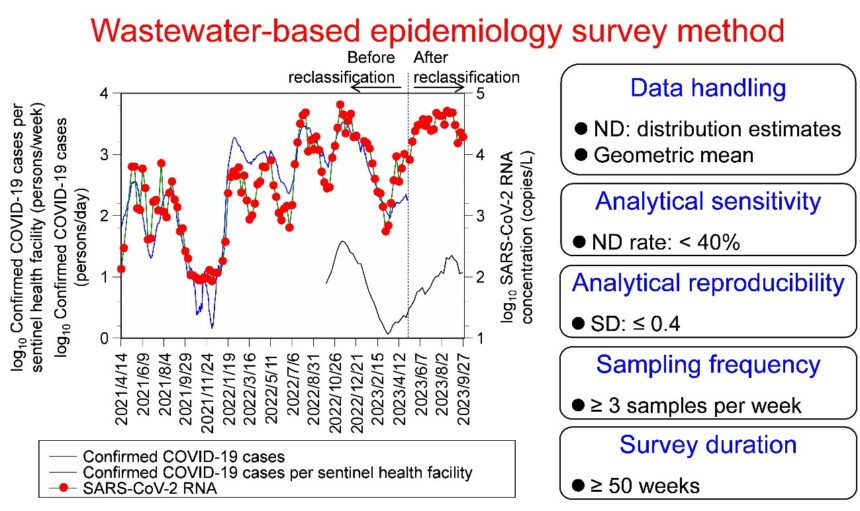
However, the effectiveness of this surveillance method depends on the accuracy of measuring viral concentrations in wastewater. A research team in Japan analyzed data from the city of Sapporo between April 2021 and September 2023 to identify the most effective methods for monitoring COVID-19 infection patterns. The dataset they utilized was highly sensitive and reproducible, with a substantial sample size and survey period.
The study, published in the journal Science of The Total Environment, revealed a strong correlation between viral concentrations in wastewater and the number of infected individuals in the community. The research team emphasized the importance of survey frequency, recommending at least three to five samples per week for accurate monitoring.
Lead author Michio Murakami highlighted the significance of this research in demonstrating the efficacy of wastewater surveillance for tracking infection trends. The study provides detailed guidance on methodologies for understanding infection patterns, including data processing, analytical sensitivity, and survey frequency.
As wastewater surveillance becomes more prevalent and its results are disseminated, the findings of this study are expected to be valuable for decision-making processes. By utilizing COVID-19 as a case study, the research team has set a precedent for effective wastewater surveillance methods that can be applied in future public health crises.
For more information on this study, readers can refer to the publication in Science of The Total Environment with DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.176702. The research was conducted by a team from Osaka University, further solidifying the credibility and importance of the findings in the field of public health.
In conclusion, the study underscores the importance of implementing robust wastewater surveillance methods to accurately monitor infection trends in the community. By adhering to recommended survey techniques and frequency, public health officials can leverage this innovative approach to enhance their understanding of regional infection patterns and make informed decisions to combat infectious diseases effectively.