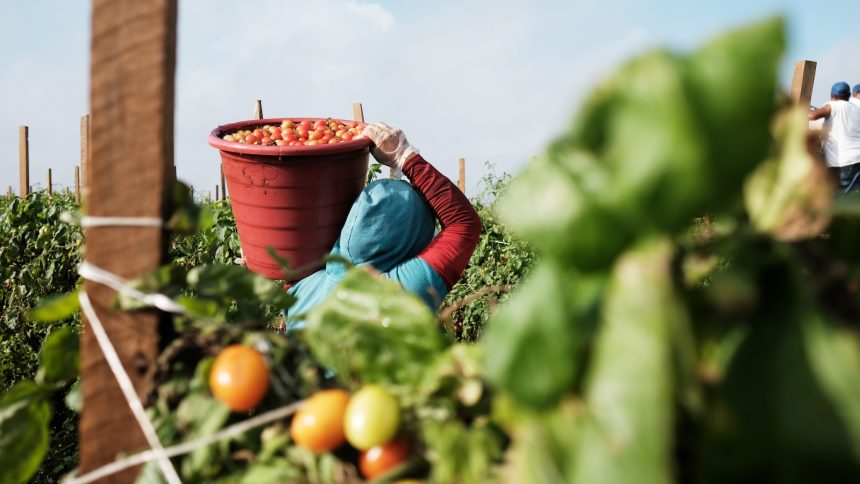
The Trump administration’s recent decision to discontinue the survey used to set minimum wages for migrant farmworkers on temporary visas has sparked controversy among various stakeholders in the agricultural industry. This move, announced by the Department of Agriculture, has raised concerns about the potential impact on farmworkers, farm employers, and the overall food system in the United States.
The H-2A visa program, which allows farmers to hire seasonal workers from abroad, relies on the Adverse Effect Wage Rate (AEWR) to determine wages for these workers. The AEWR is based on the previous year’s Agricultural Labor Survey, which is used to establish a wage floor for all farm laborers. By ending the use of this survey, the USDA has effectively removed the mechanism that sets minimum wages for farmworkers, leading experts to predict a decrease in wages for both legal and undocumented workers in the agricultural sector.
While some farm groups have welcomed this decision, arguing that AEWRs have become burdensome for their businesses, labor groups have raised concerns about the impact on farmworkers’ livelihoods. The move to lower wages for farmworkers, coupled with the Trump administration’s immigration policies focused on deporting undocumented workers, could exacerbate financial insecurity for workers in the agricultural industry.
Jose Oliva, campaigns director at the HEAL Food Alliance, highlighted the broader implications of the administration’s decision, noting that it could further destabilize an already precarious industry. Farmworkers, who are already at a heightened risk of heat-related illnesses and other climate impacts, may face increased challenges as a result of the changing wage landscape in agriculture.
Researchers have found that farmworkers are significantly more likely to die from heat-related illnesses compared to workers in other industries. With the added risks of wildfires, flash flooding, and other climate-related events, farmworkers are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. The Trump administration’s decision to cut wages for H-2A workers could further exacerbate these challenges, placing additional strain on an already at-risk workforce.
As stakeholders in the agricultural industry grapple with the implications of the USDA’s decision, the future of farm labor and food production in the United States remains uncertain. The debate over wages for farmworkers and the broader impact on the agricultural sector underscores the complex interplay between immigration policy, labor rights, and the climate crisis in the realm of food production. The H-2A visa program has seen a steady increase in demand over the years, as farm employers struggle to fill jobs with U.S. citizens. Many farmers view the program as their best option for hiring migrant workers, especially in the current political climate where the government is focused on deporting undocumented workers. Immigration raids on farms under the Trump administration’s mass deportation strategy will likely further drive farmers to rely on the H-2A visa program, according to labor experts.
Brooke Rollins, the Trump administration’s agriculture secretary, has expressed a desire to create a farm workforce that is “100 percent American.” However, the minimum wages for farmworkers are so low that they do not attract many U.S.-born workers to the agriculture industry. Edgar Franks, political director for Familias Unidas por la Justicia, a farmworker labor union, pointed out that the Adverse Effect Wage Rate (AEWR) is too low to entice local workers to take on farm jobs.
Oliva, from the HEAL Food Alliance, warned that further lowering wages for farm work could result in a decline in the number of able and willing workers. He emphasized that if wages decrease, workers may feel pressured to work longer hours to make ends meet. This added physical exertion is particularly concerning given the impacts of climate change driving up temperatures.
Despite the challenges and dangers faced by farmworkers, the H-2A visa program continues to be in high demand. The program, which allows agricultural employers to hire temporary or seasonal workers from abroad, has grown significantly over the years. Last year alone, nearly 400,000 visas were issued, according to the Farm Bureau.
The Department of Labor’s recent interim final rule adjusting the AEWR methodology has raised concerns about how wages for farmworkers will be impacted. This move follows previous attempts by federal agencies, under the Trump administration, to change how seasonal migrant farm laborers are paid. The United Farm Workers union has vowed to fight against exploitation and deportation, but it remains to be seen if they will take legal action against the USDA’s decision to end the FLS once again.
In conclusion, the implications of lowering wages for H-2A workers extend beyond the workers themselves. It could also undercut the wages of local farmworkers, including U.S. citizens, further exacerbating the challenges faced by those in the agriculture industry. The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and advancements being made every day. One of the most exciting areas of technological development is artificial intelligence (AI). AI is a branch of computer science that aims to create machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
One of the key areas where AI is making a significant impact is in the field of healthcare. AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by improving patient outcomes, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency. One way AI is being used in healthcare is through the development of diagnostic tools. AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to help doctors quickly and accurately diagnose diseases. This can lead to earlier detection of illnesses and better treatment options for patients.
AI is also being used to personalize treatment plans for patients. By analyzing a patient’s medical history, genetic information, and lifestyle factors, AI can help doctors develop tailored treatment plans that are more effective and have fewer side effects. This personalized approach to healthcare can lead to better outcomes for patients and reduce the burden on healthcare systems.
Another area where AI is transforming healthcare is in drug discovery. Developing new drugs is a time-consuming and expensive process, but AI has the potential to streamline this process by analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying potential drug candidates more quickly. This could lead to the development of new treatments for diseases that currently have limited treatment options.
AI is also being used to improve the efficiency of healthcare systems. By automating routine tasks, such as scheduling appointments and processing paperwork, AI can free up healthcare professionals to focus on providing quality care to patients. AI-powered chatbots are also being used to provide patients with information and support, reducing the need for human intervention.
While the potential benefits of AI in healthcare are vast, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. One of the main concerns is the ethical implications of using AI in healthcare. Issues such as patient privacy, data security, and bias in AI algorithms need to be carefully considered to ensure that AI is used responsibly and ethically.
Overall, AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by improving patient outcomes, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency. By harnessing the power of AI, healthcare professionals can provide better care to patients and develop new treatments for diseases. As technology continues to advance, the future of healthcare looks brighter than ever before.