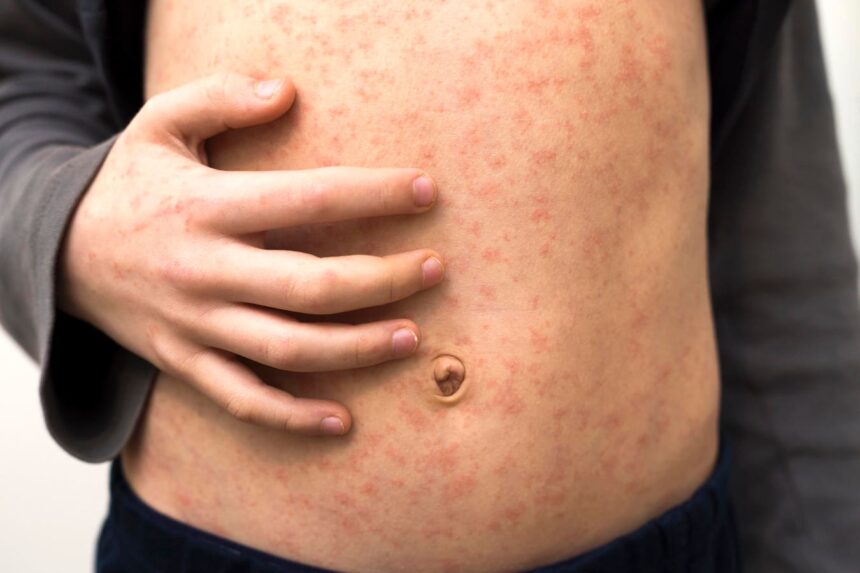
Measles is a highly contagious and potentially fatal disease that is currently surging around the world. According to the World Health Organization, there were approximately 10.3 million reported cases of measles last year, representing a 20% increase from the previous year. The main reason for this rise in cases is attributed to inadequate vaccine coverage.
Measles primarily affects young children, with an estimated 107,500 deaths reported in 2023, most of whom were under the age of 5. To prevent outbreaks and safeguard the population, the WHO recommends that almost all children (95%) receive two doses of the measles vaccine. However, in 2023, only 74% of children had received both doses, while 87% had received at least one dose.
Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the Director-General of the WHO, emphasized the importance of immunization in preventing the spread of measles, stating that the measles vaccine has saved more lives than any other vaccine in the past 50 years. He urged countries to invest in immunization for every individual to protect the most vulnerable populations.
Measles is transmitted through the air when infected individuals cough, sneeze, or breathe. Common symptoms include a high fever, cough, runny nose, and a distinctive rash that covers the entire body. In severe cases, measles can lead to complications such as blindness, brain swelling, ear infections, severe diarrhea, and pneumonia.
Vaccines play a crucial role in training the body to fight off the measles virus, making it more difficult for the disease to take hold. While there is no specific treatment for measles, caregivers can help alleviate symptoms and provide comfort to patients.
In the United States, measles cases are relatively rare due to longstanding childhood vaccination programs. However, outbreaks still occur, with 277 cases reported so far this year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rise in measles rates is often attributed to vaccine skepticism, fueled in part by a fraudulent study published in the medical journal The Lancet in the 1990s. The study falsely claimed a link between the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and autism, leading to widespread distrust of vaccines. Despite overwhelming scientific evidence refuting this claim, the misinformation continues to circulate, contributing to lower vaccine uptake rates.
Prominent figures, such as Robert F Kennedy Jr, have perpetuated the false narrative linking vaccines to autism. Kennedy, who has long promoted this view, is associated with an anti-vaccine activist organization called the Children’s Health Defense, known for spreading misinformation about health issues, including measles immunization, on social media platforms.
In conclusion, measles remains a significant public health concern globally, necessitating increased efforts to improve vaccine coverage and combat misinformation surrounding vaccination. By prioritizing immunization and raising awareness about the importance of vaccines, we can work towards eliminating measles and protecting vulnerable populations from this deadly disease.