A recent study led by Dr. Junqing Xie, based on the UK Biobank cohort of over 68,000 individuals, has shed light on the impact of various lifestyle factors on post-COVID complications, hospitalization, and death. This study, published in Nature Communications, highlighted the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle in reducing the risk of severe outcomes following a COVID-19 infection.
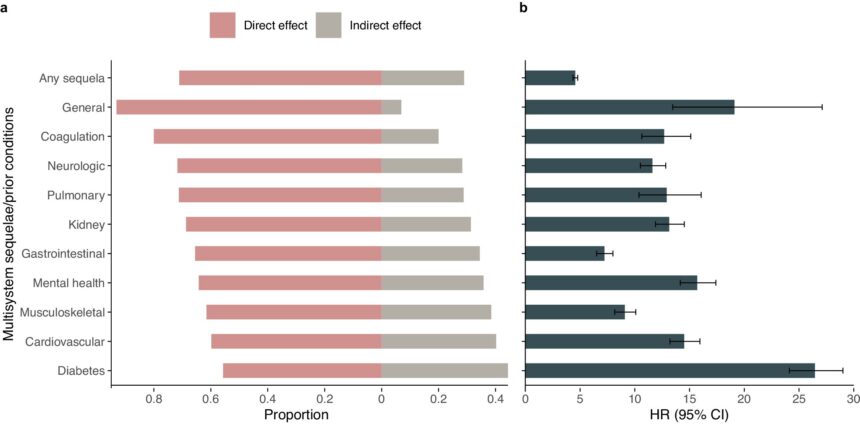
The research found that individuals with favorable lifestyle habits, including factors such as smoking, alcohol intake, BMI, physical activity, sedentary time, sleep duration, and dietary habits, had a lower risk of hospitalization, long-term health issues affecting multiple organs, and post-COVID death compared to those with unfavorable lifestyle habits. The benefits of a healthy lifestyle were observed across all 10 organs, including cardiovascular, metabolic, gastrointestinal, and mental health disorders, among others.
One of the key findings of the study was that adopting a healthy lifestyle can provide direct protection against post-COVID complications, beyond just reducing the risk of severe disease during the initial infection. These benefits were consistent across different disease severities, vaccination statuses, hospitalization experiences, and SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Dr. Junqing Xie emphasized the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle as a means of building resilience against chronic illnesses and coping with stresses such as COVID-19. The study’s results not only reinforce the known benefits of a healthy lifestyle on chronic disease prevention and life expectancy but also provide valuable insights for future pandemic preparedness.
The findings underscore the need for patients, clinicians, and policymakers to prioritize preventive strategies focused on modifiable lifestyle factors. By incorporating healthy habits into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of post-COVID complications and improve their overall health outcomes.
For more information, the study titled “Modifiable lifestyle factors and the risk of post-COVID-19 multisystem sequelae, hospitalization, and death” can be found in Nature Communications (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50495-7).
This research was conducted by the University of Oxford and highlights the significant impact of lifestyle choices on post-COVID health outcomes. It serves as a reminder of the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle for overall well-being and resilience in the face of future health challenges.