Alcohol Consumption Linked to Long-Term Brain Health Issues, Study Shows
Alcohol is well-known for its detrimental effects on health, and a recent study conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo in Brazil suggests that it may also have long-term implications for brain health. The study analyzed brain autopsy data from 1,781 individuals to investigate the impact of regular drinking habits on neurological health.
After adjusting for various sociodemographic and clinical variables, such as smoking and physical activity, the researchers found that heavy drinkers had a 133 percent higher risk of developing vascular brain lesions compared to non-drinkers. Former heavy drinkers also had an 89 percent higher risk, while moderate drinkers had a 60 percent higher risk.
Furthermore, heavy and former heavy drinkers were found to have increased odds of other neurological damage. Heavy drinkers had a 41 percent higher risk of tau protein tangles, a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease, while former heavy drinkers had a 31 percent higher risk. On average, heavy drinkers were found to die 13 years earlier than non-drinkers.
It is important to note that the study only establishes an association between heavy drinking and brain damage, and does not definitively prove causation.
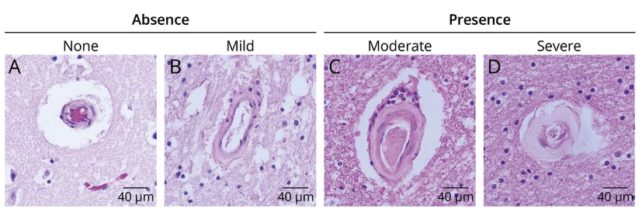
The data for the study was collected as part of Brazil’s Biobank for Aging Studies project, where post-mortem brain examinations were conducted. Participants’ drinking habits were assessed through detailed questionnaires completed by their next of kin.
The researchers categorized the participants into four groups based on their weekly alcohol consumption, with one drink equivalent to 14 grams of alcohol. The groups included never-drinkers, moderate drinkers (seven or fewer drinks per week), heavy drinkers (eight or more drinks per week), and former heavy drinkers.
Lead researcher Alberto Fernando Oliveira Justo emphasized the direct link between heavy drinking and brain injury, highlighting the potential long-term impact on memory and cognitive function. Public health awareness and preventive measures to reduce heavy drinking are crucial in light of these findings.
In addition to the increased risks of brain lesions and tau tangles, former heavy drinkers exhibited lower brain mass-to-body height ratios and impaired cognitive abilities. However, these associations were not observed in moderate or heavy drinkers.
While the study has its limitations, such as its cross-sectional design and inability to track changes in drinking habits over time, it underscores the potential health risks associated with alcohol consumption, even in moderation. Alcohol consumption has already been linked to various health issues, including heart problems, cancer, and delayed healing.
The findings of the study were published in the journal Neurology.





