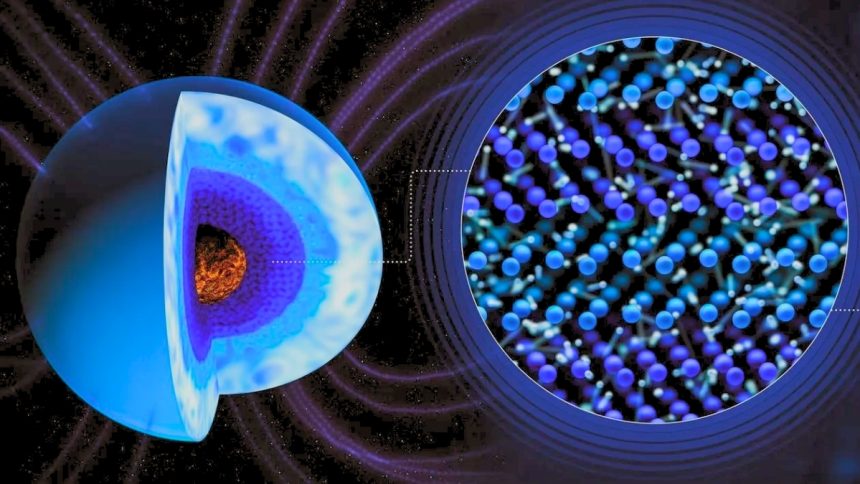
Ice giant planets like Neptune and Uranus have cores where the pressure and temperature are so extreme that water transitions into a phase completely unfamiliar under natural conditions on Earth. This form of water, known as ‘superionic water’, is a type of ice that is hot and black, unlike regular ice.
For years, scientists believed that the superionic water in the cores of these ice giants was responsible for the strange, unaligned magnetic fields observed by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. A recent study published in Nature Communications by researchers at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the Sorbonne provides experimental evidence of why this ice causes these unusual magnetic fields – because it is far messier than previously thought.
Under extreme pressures and temperatures, water can exist in a superionic phase where it looks like a solid but behaves like a crystal lattice. In this phase, oxygen atoms form the lattice while hydrogen atoms flow freely, conducting electricity in the process. Scientists had theorized that the lattice structure of superionic water was a ‘perfect’ crystal with atoms arranged in a body-centered cubic (BCC) or face-centered cubic (FCC) configuration.
To experimentally test this theory, researchers had to create superionic water, which is challenging due to its high-pressure and high-temperature requirements. Using diamond anvils to generate pressures of 1.8 million atmospheres and pulsed laser light to heat the water to 2500 Kelvin, the researchers successfully produced superionic water. However, the crystal structure disintegrated rapidly when pressure or temperature was lowered, requiring quick X-ray diffraction analysis to study its structure.
Contrary to expectations, the X-ray diffraction results revealed a messy lattice structure with blurred lines, combining FCC and hexagonal close-packed (HCP) configurations. Additional experiments showed overlapping lattices at higher pressures, challenging the idea of a clear transition between different structures.
The complex nature of superionic water suggests that it may play a role in the erratic magnetic fields observed in ice giant planets. While these experiments do not perfectly replicate the conditions in the planet cores, they offer valuable insights into the behavior of superionic water. This form of ice, which may be the most abundant type of water in the galaxy, is found in the interiors of Ice Giant planets like Neptune and Uranus.
Understanding the diverse forms of water in different environments expands our knowledge of this essential compound and its potential variations across the universe. Ice Giants, which are prevalent among known exoplanets, showcase the incredible diversity of water and its importance in planetary formation and evolution. Through ongoing research and exploration, scientists continue to uncover the mysteries of superionic water and its implications for planetary science. The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations being introduced every day. One of the most exciting developments in recent years is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. It has the ability to learn, reason, and make decisions like humans, making it a powerful tool for a wide range of applications.
One area where AI is making a significant impact is in healthcare. AI has the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered, by improving diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of medical data to identify patterns and trends that humans may not be able to detect. This can lead to more accurate and timely diagnoses, as well as personalized treatment plans for patients.
In addition to diagnosis and treatment, AI is also being used to streamline administrative tasks in healthcare settings. AI-powered chatbots can handle patient inquiries, schedule appointments, and even provide basic medical advice. This can free up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex tasks, while also improving the overall patient experience.
AI is also being used to develop new drugs and treatments for various medical conditions. By analyzing genetic data and other biological information, AI can help researchers identify potential drug targets and predict how different treatments will affect individual patients. This has the potential to revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry, by speeding up the drug development process and making treatments more personalized and effective.
Despite the many benefits of AI in healthcare, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. One of the biggest concerns is the potential for bias in AI algorithms, which can lead to inaccurate or discriminatory results. It is important for developers to ensure that AI systems are trained on diverse and representative data sets, in order to minimize bias and ensure fair and accurate outcomes.
Overall, the future of AI in healthcare looks bright. With continued advancements in technology and research, AI has the potential to transform the way healthcare is delivered, leading to better outcomes for patients and more efficient and effective care. By harnessing the power of AI, we can unlock new possibilities for improving health and well-being for people around the world.