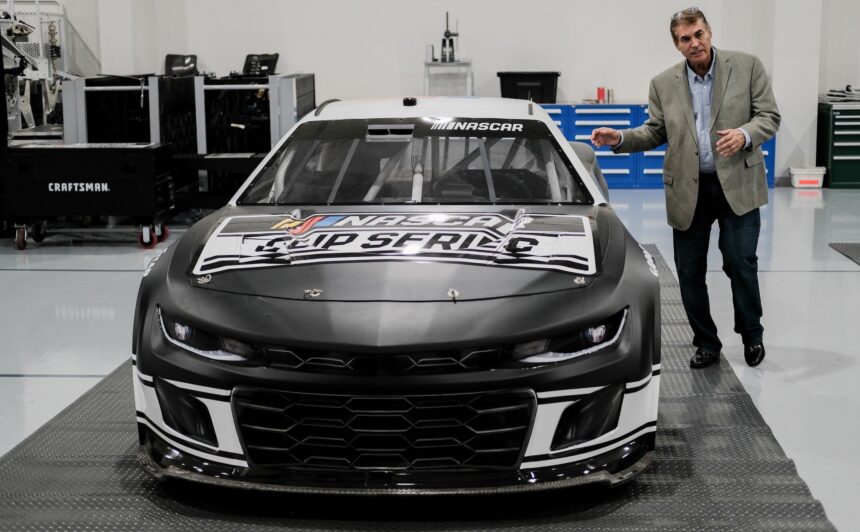
With advancements in materials, 3D printing is now able to produce parts that can withstand the harsh conditions of NASCAR racing. In the past, parts may have been too brittle or not strong enough to handle the stresses of high-speed racing. But now, with materials like carbon fiber and advanced composites, 3D-printed parts are becoming more common in the sport.
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing in NASCAR is the ability to quickly prototype and test new parts. Instead of waiting weeks for a part to be manufactured using traditional methods, teams can now design a part in CAD software, print it out, and test it on the track all within a matter of days. This rapid iteration process allows teams to fine-tune their setups and gain a competitive edge over their rivals.
Another benefit of 3D printing is the ability to create complex geometries that would be impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. This opens up new possibilities for aerodynamic components, cooling systems, and other parts that can improve a car’s performance on the track. With the tight competition in NASCAR, every little bit of performance gain can make a difference.
As NASCAR teams continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with 3D printing, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of the technology in the future. From custom-designed parts to fully 3D-printed cars, the future of NASCAR is looking more high-tech than ever before.
With the partnership between Stratasys and NASCAR growing stronger, it’s clear that 3D printing will play a significant role in the future of the sport. As technology continues to evolve, we can only imagine the incredible advancements that will come from the marriage of racing and additive manufacturing.
So, the next time you watch a NASCAR race and see those cars speeding around the track, remember that behind the scenes, 3D printing technology is helping to drive innovation and push the sport to new heights. The future of NASCAR is here, and it’s being built layer by layer.
The world of 3D printing is constantly evolving, with new materials pushing the boundaries of what is possible. According to experts in the field, the latest materials are truly incredible in terms of their heat resistance and strength-to-weight ratio. This opens up a world of possibilities for industries looking to create lightweight yet durable components.
One area of focus for the future of 3D printing is throughput, or how quickly a printer can produce parts. Instead of having multiple printers working simultaneously, the goal is to increase the speed at which each printer can operate. This will allow for faster production of parts without compromising on quality or strength.
NASCAR, known for its emphasis on speed, has embraced 3D printing as a tool for rapid prototyping and testing. One example cited is a custom fixture printed by Stratasys for a tubing component on a Joe Gibbs Racing car. This quick turnaround allowed the team to identify and address a potential issue before it became a problem on the track.
In the past, fitting parts that didn’t quite match required manual adjustments or costly machining processes. With 3D printing, teams can quickly iterate and test designs without the need for extensive rework. This not only saves time and money but also allows for more efficient production processes.
Joe Gibbs Racing has found success using 3D-printed ducts in their cars, where airflow direction is crucial for performance. By leveraging 3D printing technology, the team can create custom ducts that optimize airflow and cooling, leading to better on-track performance.
Overall, the benefits of 3D printing in the world of racing are clear: faster production, lower costs, and greater design flexibility. As materials continue to advance and printers become more efficient, the possibilities for innovation in the industry are endless. It’s a testament to the power of technology in driving progress and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in motorsports. The COVID-19 pandemic has brought significant challenges to healthcare systems worldwide, putting immense strain on hospitals, healthcare workers, and resources. As countries continue to battle the virus, the need for innovative and efficient solutions to manage patient care has become more critical than ever.
One such solution that has emerged in response to the pandemic is telemedicine. Telemedicine, also known as telehealth, involves the use of technology to deliver healthcare services remotely, allowing patients to receive medical care from the comfort of their own homes. This method of care has become increasingly popular during the pandemic, as it helps to reduce the risk of virus transmission and allows healthcare providers to treat patients without needing to be physically present.
Telemedicine offers a wide range of benefits for both patients and healthcare providers. For patients, telemedicine provides convenient access to medical care, especially for those who are unable to visit a healthcare facility in person. It also eliminates the need for travel and waiting times, making it a time-saving and cost-effective option for many individuals. Additionally, telemedicine can help to improve patient outcomes by enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients more closely and provide timely interventions when needed.
For healthcare providers, telemedicine offers greater flexibility in managing patient care, particularly during times of high demand or when resources are limited. It also allows providers to expand their reach and serve patients who may not have access to traditional healthcare services. Telemedicine can also help to reduce the workload of healthcare workers by streamlining administrative tasks and reducing the need for in-person consultations.
Despite its many benefits, telemedicine also presents some challenges that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is ensuring the security and privacy of patient information, as telemedicine involves the use of electronic devices and communication platforms that may be vulnerable to cyber attacks. Healthcare providers must implement robust security measures to protect patient data and comply with regulatory requirements.
Another challenge is the digital divide, which refers to the disparities in access to technology and internet connectivity among different populations. This can pose a barrier to accessing telemedicine services for individuals who do not have access to reliable internet or smartphones. Healthcare providers must work to bridge this gap by providing alternative options for patients who may not have access to digital devices.
Overall, telemedicine has emerged as a valuable tool in managing patient care during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. By leveraging technology to deliver healthcare services remotely, telemedicine offers a convenient and efficient way to provide medical care to patients while minimizing the risk of virus transmission. As healthcare systems continue to adapt to the challenges posed by the pandemic, telemedicine is likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery.