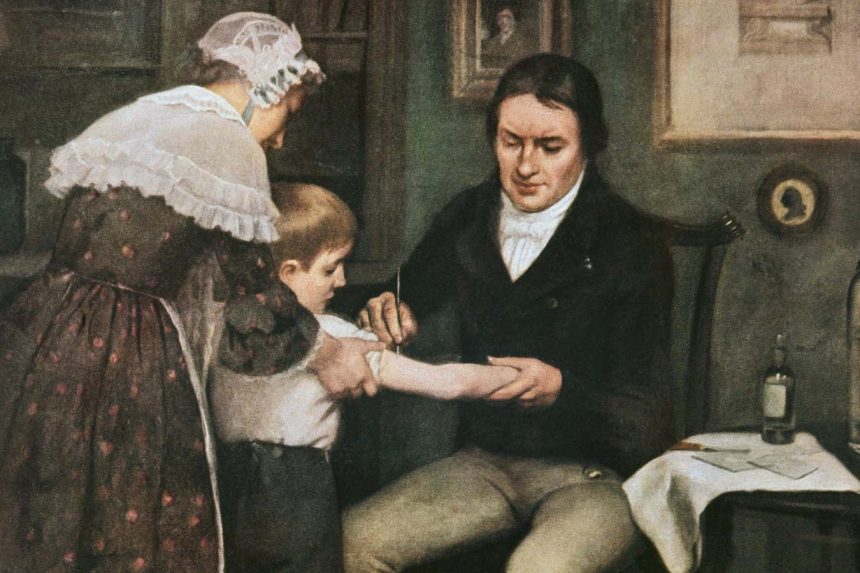
The successful smallpox vaccination campaign in Copenhagen in the early 1800s provides valuable lessons for boosting vaccine uptake in modern times. Smallpox, a deadly disease that claimed millions of lives, was eradicated globally in 1980 thanks to vaccination efforts.
In 1808, Copenhagen achieved one of the earliest local eradications of smallpox, with the help of the smallpox vaccine invented by Edward Jenner in 1796. The vaccine quickly gained attention and expectation among the Danish medical community and social elite. Doctors in Copenhagen began ordering the vaccine from England, and the results were astonishingly effective.
The King of Denmark established a vaccine commission in 1801 to oversee the rollout of the smallpox vaccine. By 1810, 90% of children in Copenhagen were vaccinated, making Denmark the most vaccinated country per capita in Europe. As a result, smallpox disappeared from the city just seven years after the vaccination campaign began.
Several factors contributed to the high vaccination rates in Copenhagen. The vaccine was offered free of charge to those who couldn’t afford it, and church leaders and school teachers helped promote and administer the vaccine. The commission also made the vaccine semi-mandatory by requiring it for children’s church confirmation.
Despite some initial resistance due to ignorance and prejudice, the majority of people embraced the vaccine. Denmark’s leaders presented a united front, instilling trust in the new vaccine among the population. This trust in government and medical authorities continues today, reflected in Denmark’s high childhood vaccination rates.
Denmark’s success in eradicating smallpox and maintaining high vaccination rates can be attributed to the collaboration between different authorities and the widespread trust in public institutions. This trust has led to continued high vaccination rates in Denmark, compared to countries with lower levels of public trust.
Overall, the Copenhagen smallpox vaccination campaign serves as a model for successful vaccine uptake, emphasizing the importance of collaboration, trust in authorities, and effective communication in public health initiatives. The world is changing rapidly, and with it, the way we interact with each other and with technology. As we continue to advance in the digital age, the importance of staying connected and informed has never been more crucial. With the rise of social media platforms and instant communication tools, the way we consume news and information is constantly evolving.
One of the most significant changes in recent years has been the shift towards digital journalism. Gone are the days of relying solely on newspapers and television for our news updates. Today, people turn to their smartphones, tablets, and computers to stay informed about current events. This shift has not only changed the way news is delivered, but also how it is consumed.
Digital journalism has made it easier for people to access news from around the world in real-time. With just a few clicks, readers can access breaking news updates, watch live streams of events, and engage with journalists and other readers through social media platforms. This level of connectivity has changed the way we engage with news, making it more interactive and personalized.
Another significant change brought about by digital journalism is the rise of citizen journalism. With the proliferation of smartphones and social media platforms, anyone can now report on news events as they happen. This has led to a more diverse and decentralized news landscape, with everyday people playing a more active role in shaping the news cycle.
However, as with any technological advancement, there are challenges that come with digital journalism. The rise of fake news and misinformation has become a major concern, as it can be difficult to discern fact from fiction in the digital age. This has led to a growing emphasis on media literacy and critical thinking skills, as well as increased efforts by news organizations to fact-check and verify information before publishing.
Despite these challenges, digital journalism has opened up new opportunities for journalists and news organizations to reach a wider audience and engage with readers in innovative ways. From interactive multimedia stories to live video coverage, digital journalism has transformed the way we experience and interact with news.
As we continue to embrace the digital age, the future of journalism will undoubtedly be shaped by technology and the changing needs of readers. With digital journalism at the forefront, the way we consume news will continue to evolve, creating new possibilities for storytelling and engagement in the digital era.