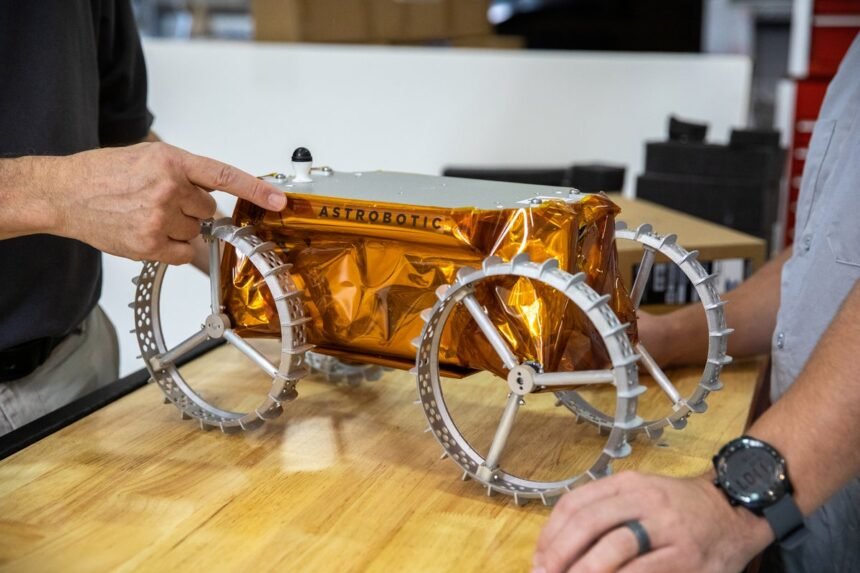
Math Enthusiasts Collaborate to Calculate Pi on the Moon Using Rover
Later this year, a small rover will embark on a unique mission on the lunar surface, involving the calculation of the mathematical constant pi.
By Emma R. Hasson, edited by Sarah Lewin Frasier

During its journey across the moon, Astrobotic’s CubeRover, which is about the size of a shoebox, will have some spare computing power that engineers at the company saw as an opportunity to engage in a unique project. They reached out to Matt Parker, a math YouTuber and comedian known for his creative approaches to calculating pi, to brainstorm ideas for utilizing this additional capacity.
Parker quickly seized upon the idea of calculating pi on the moon, a concept that intrigued him but initially made him question the legitimacy of the proposal. After confirming the authenticity of the offer, Parker began developing a plan to incorporate random numbers generated by data collected by the rover to calculate increasingly accurate approximations of pi.
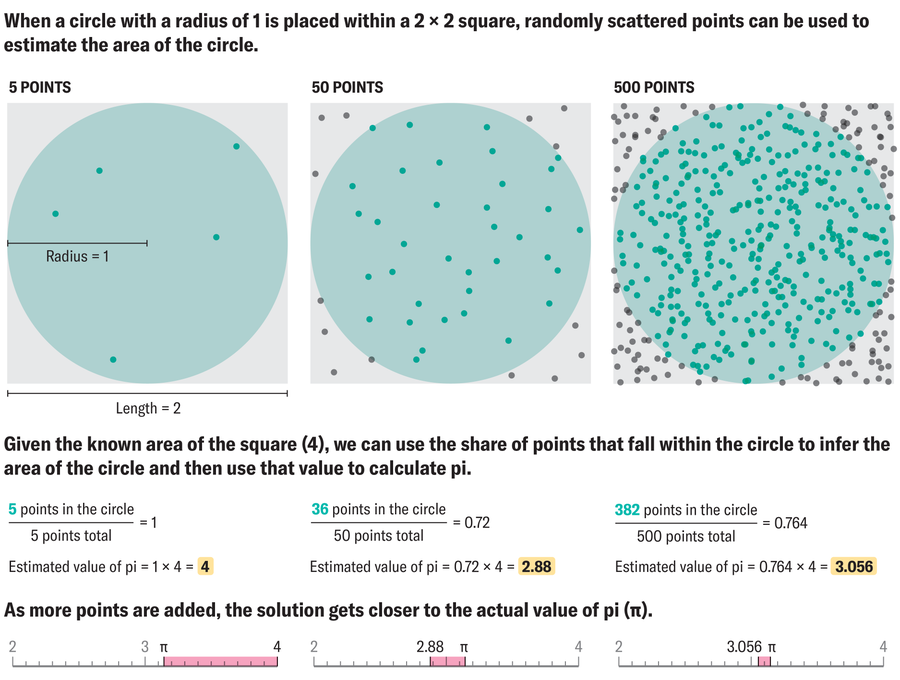
There are various methods for calculating pi using random numbers, and Parker is currently exploring different options. One approach involves using random coordinates within a 2×2 square to determine the proportion of points that fall within a circle with a radius of 1. This ratio converges towards pi/4, representing the area of the unit circle divided by the area of the square. Alternatively, Parker may explore using random points in three dimensions to estimate pi or employ a formula for the surface area of a section of a sphere, mimicking the rover’s path on the moon’s surface.
Supporting Science Journalism
If you’re enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. Your subscription helps sustain impactful stories about the latest discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Astrobotic agreed to support the project at no profit, but there were significant engineering costs associated with integrating the code into the rover without affecting its primary mission objectives. To raise the necessary funds, Parker turned to YouTube and Kickstarter, where his audience quickly exceeded the $150,000 target. The overwhelming support demonstrated the enthusiasm within the math community for such a project.
Parker emphasizes the importance of engaging in math for enjoyment and community-building rather than solely for practical purposes. While calculating pi on the moon may not lead to groundbreaking discoveries, it serves as a reminder that math is accessible and enjoyable for everyone. He plans to involve schools in the project, allowing students to participate in calculating pi and fostering a deeper appreciation for mathematics.
Andrea Davis, the project manager and lead mechanical engineer at Astrobotic, is eager to inspire students through this initiative, showcasing the potential for young minds to pursue careers in space exploration and engineering.
The field of neuroscience is a rapidly expanding and exciting area of study that seeks to understand the complex workings of the human brain. With advances in technology and research methods, scientists are able to delve deeper into the mysteries of the brain and unlock its potential.
One of the key areas of focus in neuroscience is understanding how the brain processes and stores information. This involves studying the structure and function of the brain, as well as the various processes that occur during learning and memory formation. By gaining a better understanding of these processes, scientists hope to develop new treatments for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of memory loss.
Another important area of research in neuroscience is studying the brain’s response to stress and trauma. The brain is a highly adaptive and resilient organ, but it can also be sensitive to external influences that can have a lasting impact on its function. By studying how the brain responds to stress and trauma, scientists hope to develop new therapies and interventions to help individuals cope with these challenges and improve their mental health.
Neuroscientists are also interested in understanding the neural basis of emotions and how they influence our behavior. By studying the brain regions that are involved in processing emotions, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of how emotions are regulated and how they can influence our decision-making processes. This research could have important implications for understanding and treating mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Advances in technology have revolutionized the field of neuroscience, allowing scientists to study the brain in ways that were previously impossible. Techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG) allow researchers to monitor brain activity in real-time, providing valuable insights into how the brain functions. These technologies have opened up new avenues of research and have the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the brain and how it works.
In conclusion, neuroscience is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field that holds great promise for improving our understanding of the brain and its functions. By studying how the brain processes information, responds to stress and trauma, and regulates emotions, scientists are making important strides towards developing new treatments and interventions for a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders. As technology continues to advance, the field of neuroscience will only continue to grow and expand, leading to new discoveries and breakthroughs that could revolutionize our understanding of the human brain.





