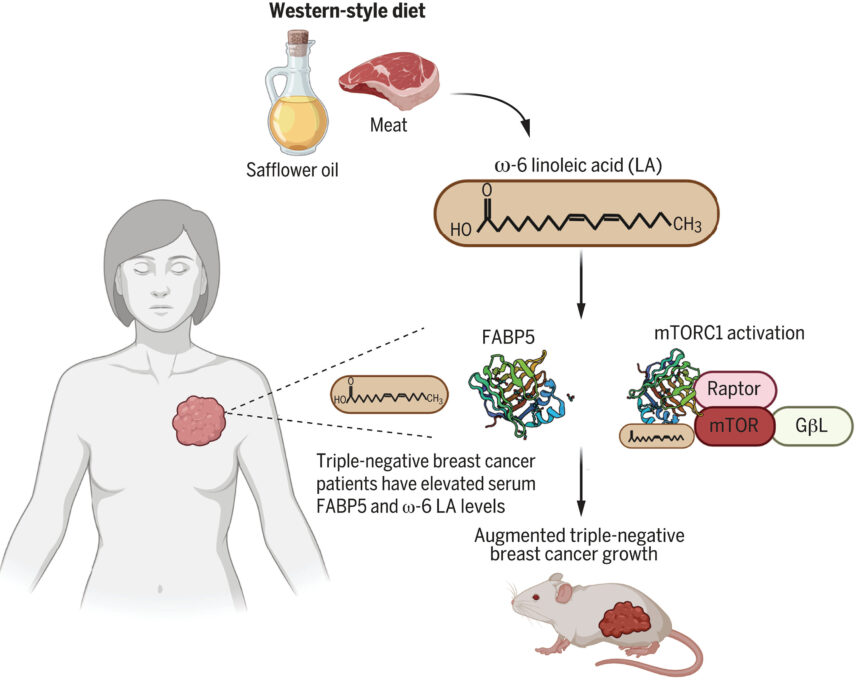
Linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid commonly found in seed oils like soybean and safflower oil, as well as in animal products such as pork and eggs, has been identified as a key factor in promoting the growth of the aggressive “triple negative” subtype of breast cancer. This groundbreaking discovery comes from a preclinical study conducted by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, opening up new possibilities for dietary and pharmaceutical interventions in the fight against breast and other cancers.
Published in the prestigious journal Science on March 14, the study revealed that linoleic acid can activate a crucial growth pathway in tumor cells by binding to a protein known as FABP5. The researchers observed that this activation occurs specifically in triple-negative breast cancer cells, where FABP5 is abundantly present, but not in other hormone-sensitive subtypes. In fact, feeding mice with triple-negative breast cancer a diet high in linoleic acid resulted in enhanced tumor growth, highlighting the impact of this fatty acid on cancer progression.
Dr. John Blenis, the senior author of the study and a renowned cancer researcher at Weill Cornell Medicine, emphasized the significance of this discovery in understanding the link between dietary fats and cancer. The research sheds light on how personalized nutritional recommendations could benefit patients based on their specific cancer subtype, paving the way for tailored treatment strategies.
While omega-6 linoleic acid is essential for various bodily processes, its overabundance in modern “Western-style” diets has raised concerns about its potential role in the rise of certain diseases, including breast cancer. Previous studies on the subject have yielded inconclusive results, but this study provides a clear biological mechanism linking omega-6 fatty acids to cancer development.
The researchers found that linoleic acid activates the mTORC1 pathway, a key regulator of cell metabolism and cancer cell growth, specifically in triple-negative breast cancer cells. This subtype-specific effect is attributed to the interaction between linoleic acid and FABP5, a protein that is highly expressed in triple-negative tumors. By elucidating this mechanism, the study not only highlights the role of linoleic acid in breast cancer but also identifies FABP5 as a potential biomarker for guiding personalized treatment approaches.
Furthermore, the study suggests that the omega-6-FABP5-mTORC1 signaling pathway may have implications beyond breast cancer, potentially influencing the growth of other cancer types like prostate cancer. Dr. Nikos Koundouros, the first author of the study, noted the broader implications of this research in understanding common chronic diseases such as obesity and diabetes.
In conclusion, the study provides valuable insights into the impact of dietary fats on cancer progression and opens up new avenues for targeted therapies in triple-negative breast cancer and potentially other cancer types. By unraveling the role of omega-6 fatty acids in cancer development, this research sets the stage for future investigations into personalized nutritional and therapeutic interventions tailored to individual patients’ needs.