During pregnancy, Chrastil’s hippocampus, a region crucial for memory and navigation, expanded in volume by about 7 percent. This expansion was unexpected and unprecedented, the researchers say. The change may be linked to the demands of new motherhood, such as remembering where things are in the house or recognizing the cries of a newborn.
Despite the reduction in gray matter volume in other parts of the brain, the expansion of the hippocampus could be a sign of adaptation to the demands of motherhood. This ability to adapt and change is a hallmark of brain plasticity, which allows the brain to reorganize itself in response to new experiences.
Overall, the study provides a detailed look at the changes that occur in a woman’s brain during and after pregnancy. Understanding these changes can help researchers better understand the complexities of the brain and how it adapts to different life stages.
Future research will build on these findings to further explore how pregnancy affects the brain and how these changes impact cognitive function and behavior in new mothers. By unraveling the mysteries of the maternal brain, scientists hope to gain insights into the profound transformations that occur in the brain during the journey to motherhood.
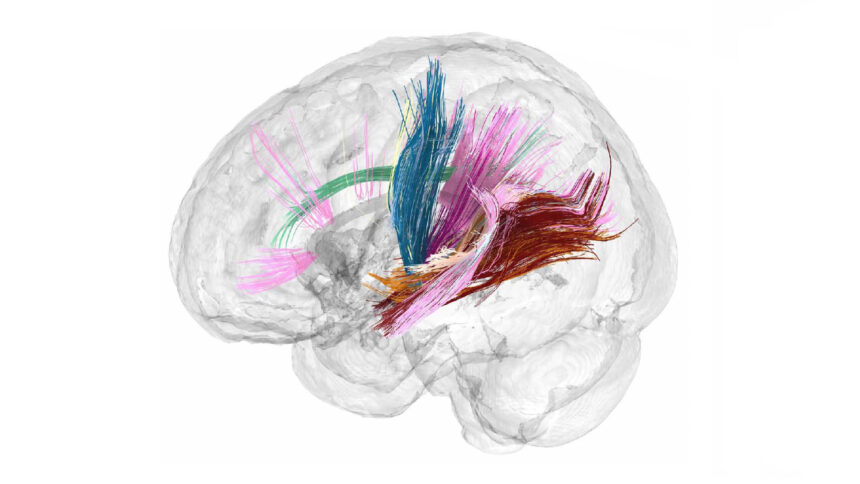
During her pregnancy, researcher Chrastil experienced changes in her brain’s white matter tracts, which grew stronger during the second trimester. White matter tracts are bundles of fibers that send information throughout the brain, and the stronger they are, the more efficiently they can carry information. By the end of Chrastil’s pregnancy, her white matter tracts had mostly returned to their pre-pregnancy strength.
However, some changes, such as reductions in gray matter, appear to be permanent, according to neuroscientist Susana Carmona from the Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Gregorio Marañón in Madrid. Research has shown that these changes can last for years after pregnancy, suggesting that they may be lifelong. This highlights the need for further research into the long-term effects of pregnancy on the brain.
Chrastil, from the University of California, Irvine, acknowledges that there is still much to learn about how pregnancy affects the brain. Women’s brains are often understudied, and there is a lack of knowledge in this area. The findings from studies like Chrastil’s raise more questions than answers, prompting the need for continued research in this field.
Chrastil’s participation in the study involved spending many hours in a scanner, contributing valuable data to advance scientific understanding. She remains open to further research opportunities, stating that if she were to have another child, she would be willing to undergo scanning once again. Her four-and-a-half-year-old son, who has a passion for volcanoes and planets, has inspired her to continue exploring the fascinating realm of brain research.
Overall, Chrastil’s study sheds light on the complex changes that occur in the brain during pregnancy, emphasizing the importance of further research to fully understand the long-term implications. By delving deeper into how pregnancy impacts the brain, scientists can gain valuable insights into the intricacies of the human brain’s adaptability and resilience.
The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new advancements and innovations being made on a daily basis. One of the most exciting developments in recent years is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is a branch of computer science that aims to create intelligent machines that can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. This has led to the development of a wide range of applications across various industries, from healthcare to finance to retail.
One of the most prominent uses of AI in recent years has been in the field of healthcare. AI has the potential to revolutionize the way that healthcare is delivered, making it more efficient, accurate, and personalized. For example, AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images and data to help doctors make more accurate and timely diagnoses. This can lead to earlier detection of diseases, better treatment outcomes, and ultimately, improved patient care.
In finance, AI is being used to streamline processes and make better investment decisions. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of financial data to identify patterns and trends that human analysts may have missed. This can help investors make more informed decisions, reduce risks, and increase returns on their investments.
In retail, AI is being used to personalize the shopping experience for customers. By analyzing customer data and behavior, retailers can create personalized recommendations and promotions that are tailored to each individual customer. This can help drive sales, increase customer loyalty, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Overall, the potential applications of AI are vast and diverse. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the years to come. From healthcare to finance to retail, AI has the power to transform industries and improve the way that we live and work. It is truly an exciting time to be a part of the world of technology. New studies have shown that regular exercise can have a significant impact on mental health and well-being. The link between physical activity and mental health has long been established, but recent research has shed light on just how important exercise is for maintaining a healthy mind.
One study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that adults who engaged in regular physical activity were less likely to experience symptoms of depression and anxiety. The study followed over 1,000 participants over a period of six years and found that those who exercised regularly were 25% less likely to develop depression compared to those who did not exercise.
Another study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine found that exercise can be an effective treatment for depression. The study reviewed over 30 years of research and concluded that exercise is just as effective as medication for treating mild to moderate depression. The researchers also found that exercise can have long-lasting effects on mental health, with the benefits continuing even after the exercise regimen has ended.
But what exactly is it about exercise that has such a profound effect on mental health? One theory is that exercise triggers the release of endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good chemicals. Endorphins are known to reduce pain and improve mood, leading to a sense of well-being and happiness. Exercise also increases the production of serotonin and dopamine, neurotransmitters that play a key role in regulating mood and emotions.
Additionally, exercise has been found to reduce levels of cortisol, the stress hormone. High levels of cortisol have been linked to anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. By reducing cortisol levels, exercise can help alleviate symptoms of stress and improve overall mental well-being.
So how much exercise is needed to reap these mental health benefits? The general recommendation is to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. This can include activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or yoga, are also beneficial for mental health.
It’s important to find an exercise routine that you enjoy and can stick with in the long term. Whether it’s going for a run in the park, taking a dance class, or practicing yoga at home, finding an activity that brings you joy and fulfillment is key to reaping the mental health benefits of exercise.
In conclusion, the connection between exercise and mental health is clear. Regular physical activity can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, improve mood, and boost overall well-being. So next time you’re feeling down or stressed, consider lacing up your sneakers and going for a walk or hitting the gym. Your mind will thank you for it.