Revolutionizing Biomedical Technology: 3D Printing Inside the Body Using Ultrasound
Researchers in the United States have made a groundbreaking advancement in biomedical technology by developing a method to 3D print materials inside the body using ultrasound. Initial tests on mice and rabbits have shown promising results, indicating that this technique could be used to deliver cancer drugs directly to organs and facilitate the repair of injured tissue.
Known as deep tissue in vivo sound printing (DISP), this innovative approach involves injecting a specialized bioink into the body. The composition of the bioink may vary based on its intended purpose, but essential components include polymer chains and crosslinking agents that help in the formation of a hydrogel structure.
To prevent immediate gelation of the hydrogel, the crosslinking agents are encapsulated within lipid-based particles called liposomes, which have outer shells designed to release the agents when exposed to a temperature slightly above the body’s normal temperature.
Using a focused ultrasound beam, the research team from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) was able to heat and puncture the liposomes, triggering the release of crosslinking agents and facilitating the formation of a hydrogel directly inside the body.
Unlike previous studies that utilized infrared light for in-body 3D printing, ultrasound was chosen as the activation mechanism this time due to its ability to reach deeper tissues, including muscles and organs.
Wei Gao, a biomedical engineer at Caltech, emphasized the advantages of ultrasound over infrared light, stating that “our new technique reaches the deep tissue and can print a variety of materials for a broad range of applications, all while maintaining excellent biocompatibility.”
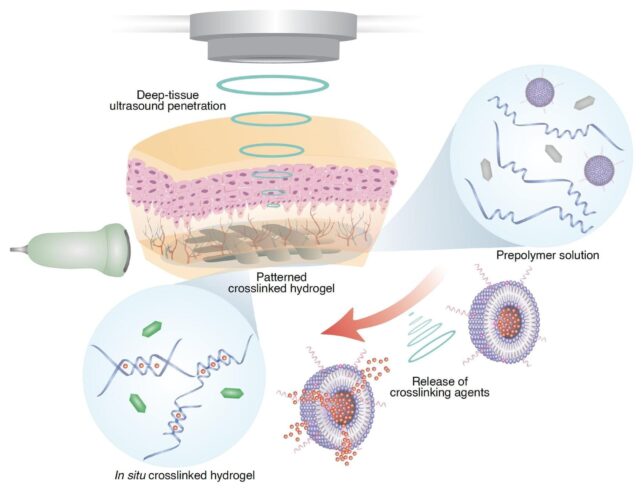
Through precise control of the ultrasound beam, the researchers were able to create complex 3D shapes, such as stars and teardrops, demonstrating the versatility of the DISP technique.
Aside from its potential as a tool for body modification, animal experiments using different formulations of the hydrogel have shown its efficacy in tissue replacement, drug delivery, and monitoring of electrical signals for applications like electrocardiography.
By incorporating tiny gas vesicles as imaging contrast agents, the researchers were able to visualize the process and confirm the successful formation of the hydrogel through ultrasound detection of chemical reactions.
In rabbit studies, the team successfully printed artificial tissue pieces at depths of up to 4 centimeters below the skin, suggesting its potential for accelerating wound healing and tissue repair, especially when combined with cell incorporation into the bioink.
In a separate experiment on 3D cell cultures of bladder cancer, the researchers administered a bioink loaded with the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin. By utilizing the DISP method to solidify the bioink into a hydrogel, the drug was released gradually over a few days, resulting in significantly higher cancer cell death compared to traditional drug injection methods.
Furthermore, the addition of various components to the bioink can expand the capabilities of DISP. The team developed conductive bioinks using carbon nanotubes and silver nanowires, which could be utilized for implantable sensors to monitor temperature or electrical signals from the heart or muscles.
Crucially, no toxicity associated with the hydrogel was observed, and any residual liquid bioink is naturally eliminated from the body within seven days, ensuring biocompatibility and safety.
While further testing in larger animal models and eventually in human subjects is necessary, the concept of 3D printing biomedical devices inside the body holds immense promise for the future of personalized medicine.
Wei Gao expressed optimism about the future prospects of this technology, stating that “with the help of AI, we would like to be able to autonomously trigger high-precision printing within a moving organ such as a beating heart.”
The research findings were published in the prestigious journal Science, marking a significant milestone in the field of biomedical engineering and 3D printing.





