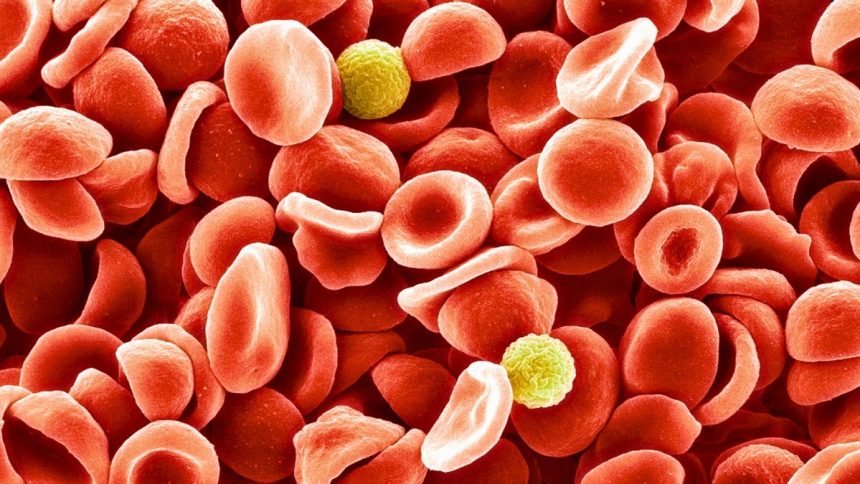
Blood Group System Discovered 50 Years After Mysterious Blood Sample
In 1972, a pregnant woman’s blood sample baffled researchers by missing a surface molecule present in all other known red blood cells at the time. Fast forward more than 50 years, and this strange absence has led to the identification of a new blood group system in humans by a team of researchers from the UK and Israel. Their groundbreaking discovery was published in a paper in 2024.
Hematologist Louise Tilley from the UK National Health Service expressed her excitement about this achievement, emphasizing the importance of offering the best care to rare patients who may benefit from this new blood group system. After nearly two decades of dedicated research into this unique blood characteristic, the team’s efforts have finally paid off.
While most people are familiar with the ABO blood group system and the Rh factor, humans actually have many different blood group systems based on the diverse proteins and sugars that coat our blood cells. These antigen molecules serve as identification markers, distinguishing ‘self’ from ‘not-self’ in our bodies.
The newly discovered blood group system, named the MAL blood group, arose from the absence of the AnWj antigen on the 1972 patient’s blood cells. This antigen is typically present on a myelin and lymphocyte protein, and its absence led to the identification of this new blood group system. Through genetic analysis, researchers found that mutations in both copies of the MAL gene result in an AnWj-negative blood type.
Further investigations revealed three additional AnWj-negative patients without the same gene mutation, suggesting that certain blood disorders can suppress the antigen. The MAL protein, responsible for maintaining cell membrane stability and aiding in cellular transport, proved to be a key player in this discovery.
By inserting the normal MAL gene into AnWj-negative blood cells, researchers were able to restore the presence of the AnWj antigen, confirming the gene’s role in this blood group system. Understanding these genetic markers can help identify whether a patient’s negative MAL blood type is inherited or the result of suppression, potentially uncovering underlying medical conditions.
The implications of these rare blood quirks are significant, as they can have devastating effects on patients in need of blood transfusions. By unraveling the mysteries of such unique blood characteristics, more lives can be saved through improved medical care.
This groundbreaking research was published in the journal Blood, marking a significant advancement in our understanding of human blood group systems. As we continue to explore the complexities of blood biology, new discoveries like the MAL blood group system shed light on the intricacies of our circulatory system, offering hope for enhanced healthcare practices in the future. The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and advancements being made every day. One of the most exciting areas of technology is artificial intelligence, or AI. AI is a branch of computer science that aims to create machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as speech recognition, decision-making, and problem-solving.
One of the most popular applications of AI is in the field of virtual assistants. Virtual assistants are AI-powered software programs that can perform a wide range of tasks, from answering questions and providing information to scheduling appointments and sending reminders. Some of the most well-known virtual assistants include Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google Assistant.
These virtual assistants use a combination of natural language processing, machine learning, and other AI technologies to understand and respond to user inputs. For example, if you ask Siri to set a reminder for a meeting, the virtual assistant will use speech recognition technology to understand your request, machine learning algorithms to determine the best time to set the reminder, and natural language processing to generate a response.
Virtual assistants are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with new features and capabilities being added all the time. For example, some virtual assistants can now carry on conversations with users, providing personalized recommendations and advice based on their preferences and behavior. Others can recognize and identify objects in images, translate languages in real-time, and even predict future events based on historical data.
While virtual assistants have many practical applications, they also raise concerns about privacy and security. Because virtual assistants are constantly listening to and recording user interactions, there is the potential for sensitive information to be compromised. Companies that develop virtual assistants must take steps to protect user data and ensure that it is not misused or shared without consent.
Despite these concerns, virtual assistants are becoming an increasingly important part of our daily lives. As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect virtual assistants to become even more intelligent and capable, helping us navigate our increasingly complex and interconnected world. Whether you’re looking for a quick answer to a question or need help managing your schedule, virtual assistants are there to help.