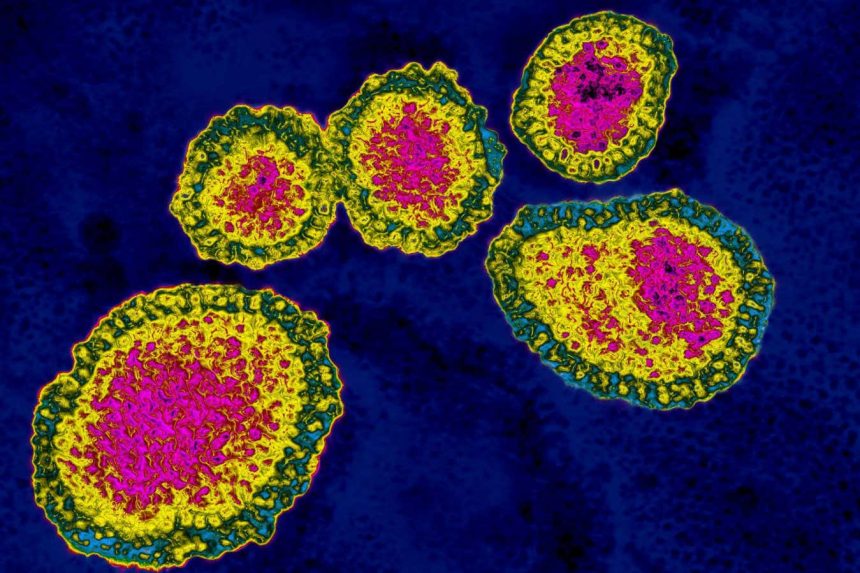
Some influenza viruses are freeloaders
BSIP SA/Alamy
Viruses, much like other organisms, have to deal with parasites in the form of cheating relatives. These “freeloader” viruses, which may be more prevalent and significant than previously believed, play a role in flu infections by outnumbering normal viruses in up to a third of cases, ultimately impacting the severity of the infections.
When a virus infects a cell, it hijacks the cell’s machinery to replicate itself. While most of this replication process relies on the cell’s existing components, certain viral proteins are crucial for successful replication. However, mutations can lead to the deletion of genes encoding these essential proteins, resulting in defective viruses that rely on complete viruses within the same cell to provide the missing proteins for replication.
These defective interfering viruses, also known as cheater viruses, have been known to exist since the 1970s. Recent research led by Asher Leeks at the University of British Columbia in Canada has shed light on the abundance of these cheater viruses in the wild. Through sequencing data from various infected individuals across different species, including ostriches, house cats, cows, and birds, Leeks and his team found that cheater viruses are remarkably prevalent, with an estimated one-third of infected individuals having these non-functional viruses as the majority in their viral population.
Studies suggest that higher levels of cheater viruses may actually reduce the severity of infections, leading to the possibility of using them to predict disease outcomes or even explore them as a potential treatment for certain viral infections like HIV.
Rafael Sanjuán at the University of Valencia in Spain notes that while the prevalence of cheater viruses may be more pronounced in influenza viruses, their impact and potential applications warrant further investigation.