An Unusual Discovery: Non-Venomous Spider Uses Toxic Silk to Subdue Prey
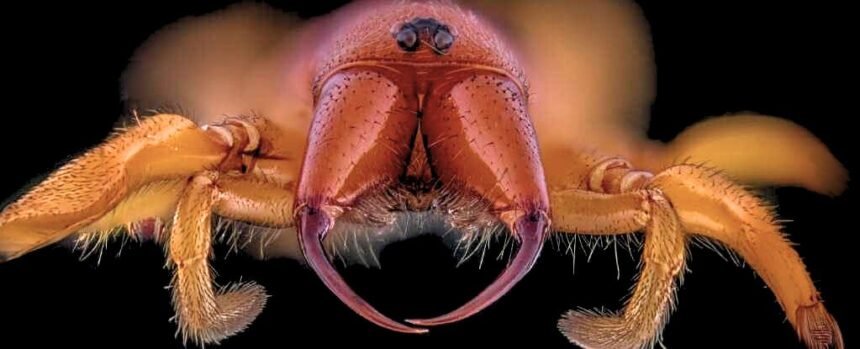
In a surprising turn of events, researchers have found that a non-venomous spider species, the feather-legged lace weaver (Uloborus plumipes), has been using a unique method to poison its victims. This spider, commonly found in Europe and Africa, was previously believed to be harmless due to the absence of venom glands on its head. However, scientists suspected that it might employ a different strategy for chemical warfare.
A recent study led by ecologist Xiaojing Peng from the University of Lausanne has revealed that lace weavers use toxins from their midgut to coat their silk-wrapped prey, incapacitating them. This discovery challenges the perception that only venomous spiders possess the ability to subdue their victims through chemical means.

Although the toxins found in lace weavers differ from those typically present in venomous spiders, they are equally effective in disabling their prey. Ecologist Giulia Zancolli, a co-author of the study, reported that these toxins were highly insecticidal, causing a mortality rate of around 50% among fruit flies within an hour of exposure.
The research also revealed that the toxic proteins in lace weavers bear resemblance to those found in the digestive fluids of other spider species, such as Parasteatoda tepidariorum, which possess venom glands. This suggests a potential evolutionary link between digestive toxins and venom components in spiders.
Unlike venomous spiders that inject toxins through specialized fangs, U. plumipes lack such structures for delivering substances. The researchers hypothesize that these spiders may have lost their venom-producing capability over time and adapted by utilizing digestive toxins for prey immobilization.
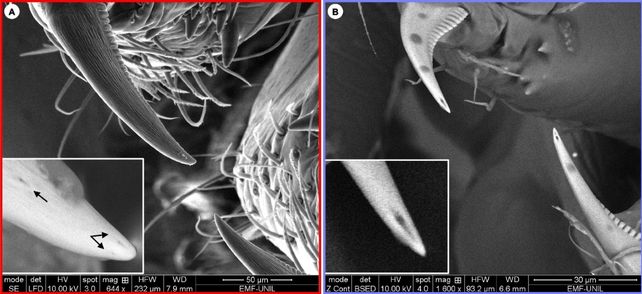
While spiders are often feared for their venomous properties, they play a vital role in ecosystems by controlling insect populations and serving as a food source for various animals, including humans. Their venoms have also shown potential for medical applications, prompting further exploration of their toxicological properties.
This groundbreaking research, shedding light on the unconventional predatory behavior of lace weavers, has been published in the journal BMC Biology.