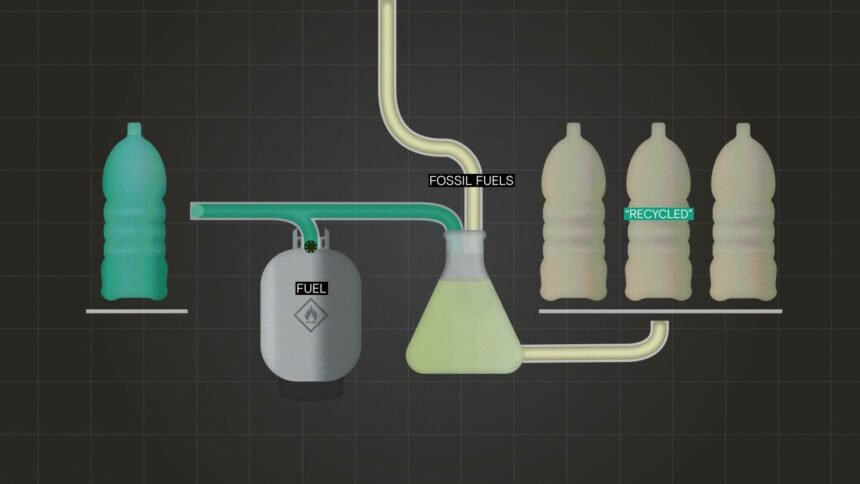
Mass balance is a system that allows companies to account for the use of recycled materials in their products without physically segregating the recycled content from the virgin material. This means that a company can claim that a certain percentage of their product is made from recycled materials even if the actual product does not contain any recycled content.
In the case of Mondelez and their Triscuit packaging, the company has announced that up to 50 percent of the plastic in the cracker boxes’ inner bags would be sourced from advanced recycling technology. However, the company has not labeled its packaging with these recycled content claims. This has raised concerns among environmental organizations and government watchdogs who argue that mass balance is not based on scientific facts or operational engineering evidence.
The California attorney general’s office has called mass balance a false and misleading marketing scheme, and the Biden administration’s Environmental Protection Agency has rejected its use in products labeled with its “Safer Choice” logo. Mondelez has become the target of a shareholder resolution demanding that the company substantiate its recycled content claims.
Chemical engineer Jan Dell, who owns Mondelez stock and filed the resolution, has criticized mass balance as a bogus scheme and a PR stunt that could lead to legal liability for the company. Dell believes that corporate funds should not be wasted on such schemes and instead returned to shareholders as dividends.
In order to understand mass balance, it is important to understand advanced recycling methods like pyrolysis, which convert plastics into their chemical building blocks using high heat and pressure. These methods offer a potential solution to the plastic recycling crisis, where only a small percentage of the world’s plastic waste is currently recycled through conventional methods.
Overall, the use of mass balance in product labeling is a controversial issue that raises questions about transparency and accountability in the recycling industry. As companies strive to meet sustainability goals and reduce their environmental impact, it is crucial that they use accurate and reliable methods to track and report the use of recycled materials in their products. This practice allows the company to claim that its products contain a certain percentage of recycled content, even if that content is minimal or nonexistent. The certificates serve as proof of sustainability, even though the reality may be quite different.
The issue with this approach is that it creates a false sense of environmental responsibility. Consumers may believe they are making a positive impact by purchasing products labeled as containing recycled content, when in fact, the majority of the material is still virgin plastic. This greenwashing tactic undermines genuine efforts to reduce plastic waste and promote true recycling practices.
Furthermore, the reliance on pyrolysis as a solution to plastic pollution raises concerns about the energy and resources required for the process. Burning pyrolysis oil for fuel, instead of converting it into new plastic products, defeats the purpose of recycling in the first place. The complex and costly nature of pyrolysis also calls into question its viability as a widespread solution to plastic waste management.
In conclusion, while the concept of chemical recycling through pyrolysis may sound promising, the practical implementation raises significant challenges and ethical considerations. Companies must be transparent about their recycling practices and avoid misleading consumers with inflated claims of recycled content. True progress in addressing plastic pollution will require a commitment to reducing plastic production, promoting circular economy practices, and investing in sustainable alternatives. However, critics argue that the ISCC certification does not guarantee that the plastic is actually being recycled. Instead, it only verifies that the mass balance system is being used, which allows companies to make claims about the recycled content of their products without actually using recycled materials.
This controversy highlights the challenges and complexities of the recycling industry. As companies strive to meet sustainability goals and reduce their environmental impact, they may be tempted to use deceptive practices that give the appearance of eco-friendliness without actually making a significant difference.
In the case of Mondelez and other companies using mass balance systems for plastic recycling, it is essential for consumers to remain vigilant and informed. By understanding the limitations of these practices and demanding transparency from companies, individuals can make more informed choices about the products they purchase.
Ultimately, the goal should be to promote genuine recycling efforts that contribute to a more sustainable future. By holding companies accountable and advocating for truly sustainable practices, consumers can help drive meaningful change in the recycling industry. Mondelez has taken steps to make its Triscuits packaging more sustainable by using the mass balance approach developed by the ISCC. This allows the company to claim that its packaging is ISCC certified, a designation that signifies adherence to strict transparency requirements set by the organization. Other companies such as Exxon Mobil, Shell, and Chevron Phillips Chemical have also been approved to use the mass balance approach by the ISCC.
Despite these efforts, some environmental advocates like Peter Blair from the nonprofit Just Zero believe that mass balance claims may not be accurate enough. There are concerns that such claims could lead to accusations of greenwashing within the industry. A survey conducted by the Association of Plastic Recyclers found that very few adults are familiar with what mass balance means, highlighting the need for more education and transparency around this approach.
Dell, a sustainability advocate, suggests that Mondelez should focus on investing in paper-based packaging as a more sustainable alternative to plastic. Many consumer goods companies are already transitioning to paper packaging for products like candy bars, tissue packs, and coffee bags. Last September, Mondelez announced a new packaging design for its Lu cookies in Europe that reduced the need for virgin plastic by 63 percent per package, demonstrating a commitment to reducing plastic waste.
Overall, Dell believes that authentic progress in packaging sustainability involves both reducing the amount of material used and transitioning to more eco-friendly alternatives like paper. By making these changes, companies like Mondelez can make a meaningful impact on the environment and reduce their carbon footprint. The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new advancements and innovations being made every day. One of the latest breakthroughs in technology is the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize various industries and change the way we live and work.
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables machines to learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed. These technologies have the ability to analyze large amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on that information.
One of the key applications of AI and machine learning is in the field of healthcare. These technologies have the potential to improve patient care, diagnosis, and treatment by analyzing medical data and providing insights to healthcare professionals. For example, AI algorithms can analyze medical images such as X-rays and MRIs to detect abnormalities and assist radiologists in making more accurate diagnoses.
In addition to healthcare, AI and machine learning are also being used in industries such as finance, retail, transportation, and manufacturing. In finance, AI algorithms can analyze market data and make investment decisions, while in retail, they can personalize customer experiences and recommend products based on past behavior. In transportation, AI is being used to optimize routes and schedules, while in manufacturing, it is being used to improve efficiency and productivity.
Despite the numerous benefits of AI and machine learning, there are also concerns about their potential impact on jobs and society. Some fear that these technologies will lead to job displacement and inequality, as machines become increasingly capable of performing tasks that were once done by humans. There are also concerns about privacy and security, as AI systems have the ability to collect and analyze large amounts of personal data.
In order to address these concerns, it is important for policymakers, industry leaders, and researchers to work together to ensure that AI and machine learning are developed and implemented responsibly. This includes developing regulations and guidelines to protect privacy and security, as well as investing in education and training programs to prepare workers for the jobs of the future.
Overall, the development of AI and machine learning has the potential to bring about significant benefits to society, improving efficiency, productivity, and quality of life. However, it is important to approach these technologies with caution and ensure that they are developed and used in a way that benefits everyone. By working together to address the challenges and opportunities of AI and machine learning, we can create a future where technology enhances our lives in meaningful ways.