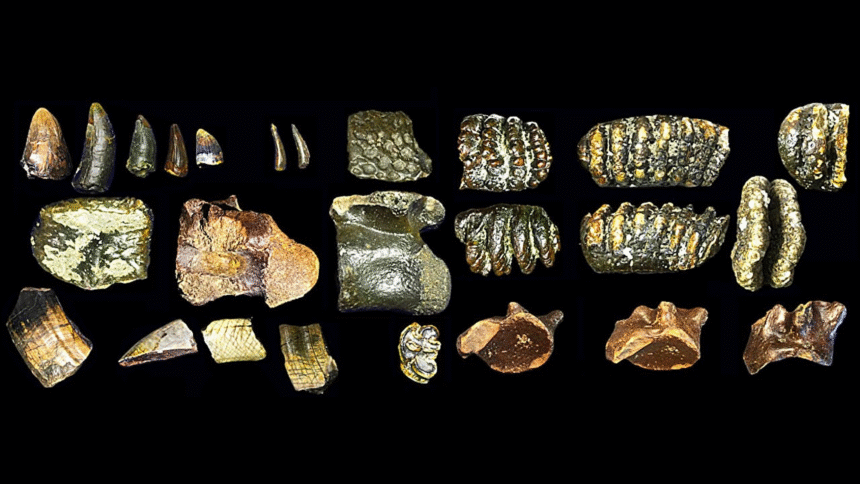
Archeologists have long believed that the ancient Homo erectus population living on Java existed in isolation from their island relatives. However, recent discoveries of fossilized skull fragments off the Javanese coast are challenging this assumption. These fossils, found around 140,000 years ago, suggest that life for the Javanese Homo erectus may not have been as solitary as previously thought.
The findings, published in the journal Quaternary Environments and Humans, shed new light on the ancient populations of Homo erectus in the region. It is now understood that these populations may have had more interactions and connections with neighboring islands than previously believed.
The discovery of these skull fragments in the Madura Strait, which separates Java from Madura, was made during a land reclamation project. Over 6,000 fossil specimens were uncovered, including remains of ancient fish, reptiles, and mammals. Among these fossils were the two unexpected Homo erectus skull fragments, providing valuable insights into the lives of these ancient human ancestors.
According to Harold Berghuis, an archaeologist at Leiden University in the Netherlands and co-author of the study, the discoveries are truly unique. The fossils, dating back to around 140,000 years ago, provide a glimpse into the penultimate glacial period when the global sea level was significantly lower than it is today.
During this time, Sundaland, the landmass that included present-day Indonesia, resembled the African savannah with dry grasslands, major rivers, and narrow strips of forests. The region offered abundant resources such as water, shellfish, fish, edible plants, seeds, and fruits year-round, sustaining the Homo erectus population.
The fossils also revealed evidence of butchery by Homo erectus, including cut marks on bones of water turtles and broken bovid bones indicating hunting and consumption of bone marrow. These practices were previously documented in more modern human species on the Asian mainland, suggesting a potential exchange of knowledge and techniques between different hominin groups.
The discoveries on Java challenge previous assumptions about the isolation of Homo erectus populations and highlight the complexity of interactions and adaptations among ancient human ancestors in the region. This new understanding of the lives of Homo erectus in Indonesia adds valuable insights to our knowledge of human evolution and migration patterns in Southeast Asia. The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and advancements being made every day. One area that has seen significant growth in recent years is artificial intelligence (AI). AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. It is used to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
One of the most exciting applications of AI is in the field of healthcare. AI has the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered, making it more efficient, accurate, and personalized. One of the key areas where AI is being used in healthcare is in medical imaging. AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as CT scans and MRI scans, to detect abnormalities and assist in diagnosing diseases such as cancer.
Another area where AI is making a big impact in healthcare is in predictive analytics. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data from electronic health records, medical imaging, and genetic information to predict the likelihood of a patient developing a certain disease or condition. This can help healthcare providers take preventive measures to reduce the risk of disease and improve patient outcomes.
AI is also being used in drug discovery and development. Drug discovery is a complex and time-consuming process that typically takes years and billions of dollars to bring a new drug to market. AI can help speed up this process by analyzing vast amounts of data to identify potential drug candidates and predict how they will interact with the human body.
In addition to these applications, AI is also being used in virtual health assistants, personalized medicine, and remote patient monitoring. Virtual health assistants, powered by AI, can provide patients with personalized health information and advice, helping them manage their health more effectively. Personalized medicine uses AI to analyze a patient’s genetic information and medical history to tailor treatment plans to their individual needs. Remote patient monitoring uses AI to track and analyze patient data in real-time, allowing healthcare providers to intervene quickly if any issues arise.
While AI has the potential to transform healthcare in many positive ways, there are also challenges and concerns that need to be addressed. One of the biggest challenges is the need to ensure that AI algorithms are accurate, reliable, and unbiased. There is also a need to protect patient privacy and data security, as AI algorithms rely on vast amounts of sensitive patient information to operate effectively.
Overall, the use of AI in healthcare holds great promise for improving patient care, enhancing medical research, and reducing healthcare costs. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of AI in healthcare in the years to come.