Heat stroke is a serious health concern, especially in the face of rising global temperatures brought on by climate change. With the increasing frequency and intensity of heat waves, vulnerable populations are at greater risk than ever before. Detecting heat stroke risks early is crucial for timely intervention and reducing the impact of these dangerous events.
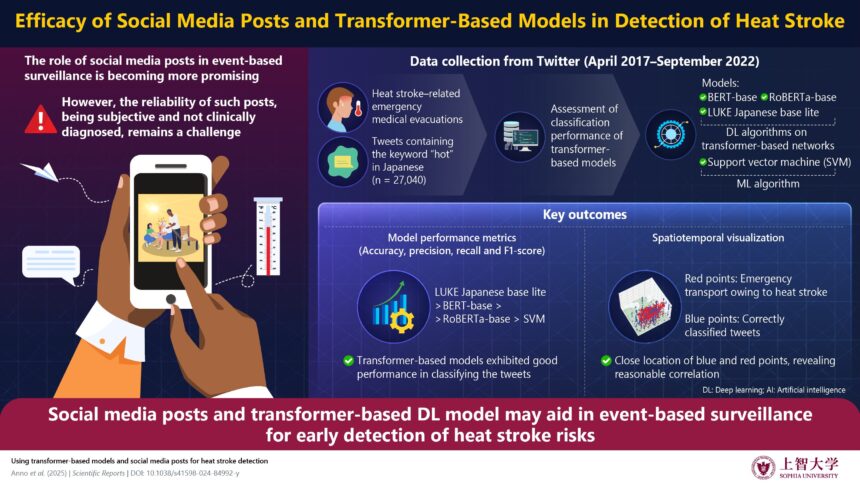
In a groundbreaking study published in Scientific Reports, researchers from Sophia University in Japan explored the use of social media posts and transformer-based deep learning models to detect heat stroke risks in Nagoya City. By harnessing the power of advanced technology and real-time data from platforms like Twitter, the team was able to identify tweets containing relevant keywords and train their models to recognize patterns associated with heat stroke events.
The results were impressive, with transformer-based models like LUKE Japanese base lite outperforming traditional machine learning approaches. These models achieved high accuracy rates in identifying heat stroke-related tweets, showcasing the potential for real-time event-based surveillance. By mapping the locations of heat stroke emergencies and correlating them with geo-tagged tweets, the researchers demonstrated how social media data can serve as an early warning system for heat stroke risks in urban areas.
Lead researcher Professor Sumiko Anno emphasized the importance of leveraging social media for public health surveillance and early detection of health risks. The study not only highlighted the effectiveness of transformer-based models in monitoring heat stroke risks but also underscored the value of integrating social media data with emergency response systems for rapid intervention.
Looking ahead, the team plans to expand their research to establish an early warning system for heat stroke in Aichi Prefecture, with the ultimate goal of creating a nationwide alert system for Japan. By collaborating with local authorities and conducting comprehensive analyses across different regions, the researchers aim to enhance public health surveillance and improve response mechanisms to climate-related health challenges.
This innovative approach to combining deep learning and social media for health monitoring sets the stage for future applications in detecting and responding to emerging infectious diseases. As the impact of climate change continues to escalate, early detection and rapid response to health risks will be critical in safeguarding public health and well-being.
In conclusion, the study from Sophia University represents a significant advancement in using technology and social media for real-time health monitoring. By harnessing the power of transformer-based models and leveraging the wealth of data available on platforms like Twitter, researchers have demonstrated the potential for early detection of heat stroke risks and paved the way for future innovations in public health surveillance.