Health
Researchers are developing mRNA vaccines that create virus-like nanoparticles, aiming to enhance immune responses while minimizing side effects compared to existing vaccination methods.
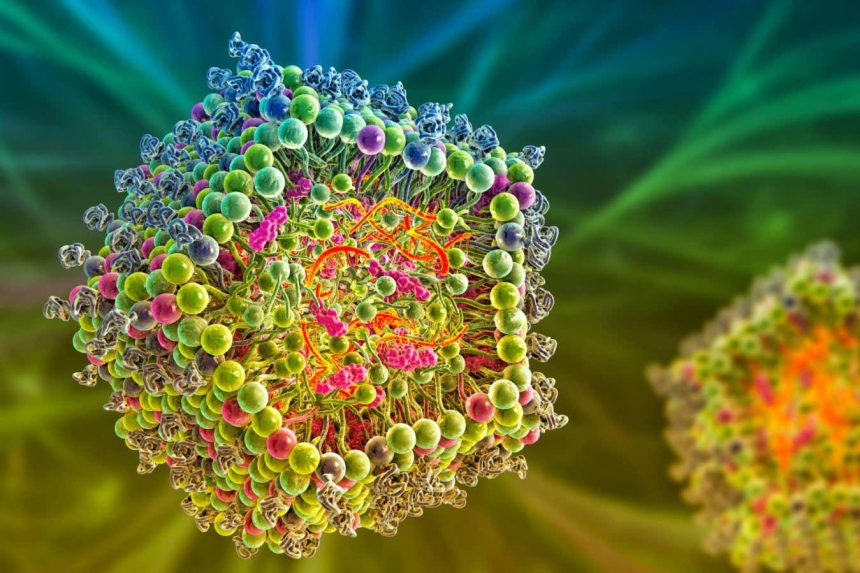
A computer illustration of a cross-section of a lipid nanoparticle carrying the mRNA of a virus (orange strands)
Science Photo Library / Alamy
Vaccines that mimic viruses typically elicit a stronger immune response, while mRNA vaccines are notably fast and cost-effective to produce. The latest innovation merges both concepts by utilizing mRNA to instruct the formation of virus-like nanoparticles, as opposed to only coding for individual proteins like current covid-19 mRNA vaccines.
Grace Hendricks from the University of Washington has demonstrated that an mRNA version of a covid-19 nanoparticle vaccine elicits an immune response in mice that surpasses standard mRNA vaccines by as much as 28 times.
According to Hendricks, some of the mild but unpleasant side effects associated with mRNA vaccines arise from the body’s immediate response to the introduced mRNAs and the lipid particles they come with. “With more effective vaccines, the dose could potentially be reduced, ensuring that the essential immune response remains intact but with fewer side effects,” she explains.
The earliest vaccines utilized weakened “live” viruses which are highly effective but could be dangerous for individuals with compromised immune systems. This was followed by inactivated vaccines comprising “dead” viruses, which, while safer, present manufacturing challenges.
Protein subunit vaccines emerged next, containing only the outer proteins of viruses. These vaccines are even safer than inactivated vaccines but often yield a weaker immune response due to the proteins floating freely.
This led to the creation of viral proteins embedded within tiny spheres, resembling spiky balls that signal to the immune system while remaining as safe as protein subunit vaccines. One method involves modifying existing proteins to self-assemble into small balls, presenting viral proteins on their surface, known as vaccine nanoparticles.
During the pandemic, Hendricks’ colleagues developed a covid-19 nanoparticle vaccine dubbed Skycovion, which received approval in South Korea in 2022, although it was overshadowed by the existing mRNA vaccines at that time, limiting its widespread use.
mRNA vaccines are easier and quicker to manufacture compared to protein-based alternatives, as they provide the genetic instructions for protein synthesis, allowing our body cells to handle the actual protein creation. The viral proteins from the initial mRNA vaccines manifest on the exterior of cells, fostering a stronger immune reaction than soluble proteins but still falling short compared to nanoparticle vaccines.
Now, Hendricks and her team have succeeded in encapsulating the strengths of both technologies by creating a vaccine comprised of mRNAs for Skycovion. The proteins generated within cells self-assemble into nanoparticles, showing early efficacy in mouse studies.
“This primarily serves as proof of concept for this genetic delivery system,” notes Hendricks. She and her team are already exploring mRNA-based nanoparticle vaccines targeting flu, Epstein-Barr (which can trigger cancer), and various other viral pathogens.
“I am very optimistic about the potential of mRNA-launched protein nanoparticles for vaccine development,” remarks William Schief from the Scripps Research Institute, involved in the design of HIV vaccines. “My associates and I have produced impressive immunogenicity results with two mRNA-launched nanoparticles in clinical trials and several in mouse models. This new study adds to the existing knowledge base on this subject.” However, despite the promising outlook for mRNA vaccines, significant cuts in US funding for their development were recently announced.
Topics: