Understanding the Resolution Limits of the Human Eye: Do Ultra-High-Def TVs Make a Difference?
Have you ever wondered about the retinal resolution of the human eye and how many pixels we can actually perceive? Is there any real benefit to investing in an expensive, ultra-high-def TV for the ultimate in-home viewing experience? These are the questions that researchers from the University of Cambridge, in collaboration with Meta Reality Labs, set out to explore.
Their recent study suggests that, at the average viewing distance between the sofa and TV in a typical UK living room, the human eye may not be able to resolve all the pixels presented by ultra-high-def 4K or 8K TVs. In fact, these high-resolution screens may not offer any noticeable advantages over a lower resolution 2K television of the same size (44 inches).
To arrive at this conclusion, the researchers conducted tests to assess viewers’ ability to perceive specific on-screen features, such as fine gradations in patterns, under various conditions. These conditions included viewing in shades of color or grey, at different distances from the TV, and when viewed straight-on or via peripheral vision.
The study involved 18 participants ranging from 13 to 46 years old. If the participants could discern the lines in the image presented to them, it indicated that their eyes could resolve detail at that level.
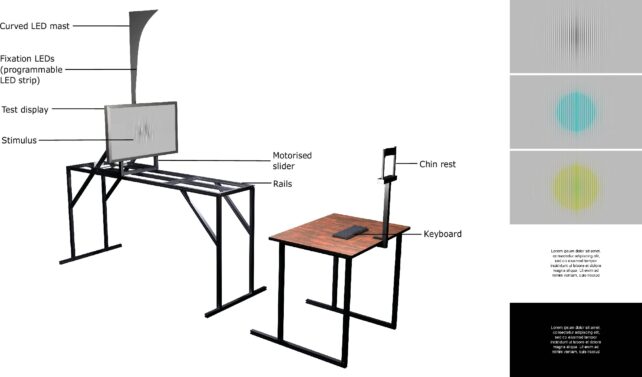
But the study didn’t stop at simple resolution measurements. The researchers also delved into pixels per degree (ppd) to determine how many individual pixels could be packed into each degree of the viewer’s field of vision.
Past assumptions had pegged the human eye’s ability to perceive details at 60 ppd based on the 20/20 vision standard from the Snellen wall chart. However, the researchers found that the human eye actually has a higher resolution limit, which varies by color. In grey, it’s 94 ppd; in green and red, it’s 89 ppd. But in yellow and violet, it drops to 53 ppd.
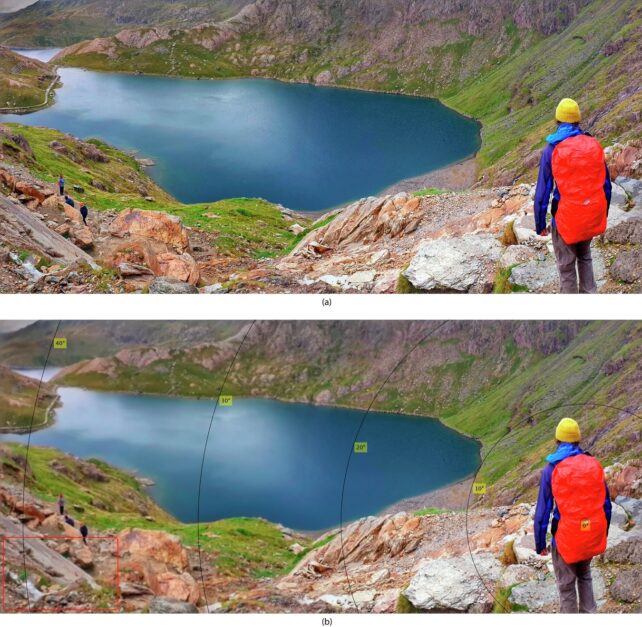

These findings suggest that TV manufacturers may be hitting a point of diminishing returns in terms of resolution. While larger TVs will always be desirable, the researchers hope that manufacturers will design displays that align with the resolution capabilities of a higher percentage of viewers, rather than assuming an average observer.
It’s worth noting that our ability to perceive visual details isn’t solely limited by our eyes but also by our brains. Human senses work in tandem, and our ocular resolution is influenced by the eyes, the brain, and their complex interactions.
Rafał Mantiuk, a computer scientist at the University of Cambridge and senior author of the study, highlights the role of the brain in processing visual information. Our brain processes data from our eyes to create the visual experience we perceive, compensating for the limitations of our eyes.
Ultimately, this study serves as a reminder that our vision has evolved to be functional rather than perfect. If manufacturers aim to captivate consumers with their screens, they should consider designing displays that cater to a broader range of visual capabilities.
This research has been published in Nature Communications.
The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and advancements being made every day. One area that has seen significant growth in recent years is the field of artificial intelligence (AI). AI has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, from healthcare to finance to transportation.
One of the most exciting developments in AI is the creation of intelligent virtual assistants. These virtual assistants, such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, are designed to provide users with personalized information and assistance. They can perform a wide range of tasks, from setting reminders and scheduling appointments to answering questions and playing music.
These virtual assistants are powered by AI algorithms that enable them to learn from user interactions and improve their performance over time. This means that the more you use your virtual assistant, the better it will become at understanding your preferences and providing you with relevant information.
In addition to virtual assistants, AI is also being used to develop chatbots, which are computer programs that can simulate a conversation with human users. Chatbots are being used by companies to provide customer support, automate tasks, and engage with users on social media platforms.
Another exciting application of AI is in the field of healthcare. AI algorithms are being developed to analyze medical data and assist doctors in making diagnoses and treatment decisions. This has the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
AI is also being used in the financial industry to detect fraud, automate trading, and personalize customer experiences. By analyzing large amounts of data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and trends that humans may not be able to see.
In the transportation industry, AI is being used to develop self-driving cars that can navigate roads and make decisions without human intervention. This technology has the potential to reduce accidents and traffic congestion, as well as provide mobility solutions for individuals who are unable to drive.
Overall, AI has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries and improve the way we live and work. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more exciting innovations in the field of artificial intelligence.





