The rise in stress levels among people living in urban areas worldwide has spurred the development of various technological tools aimed at improving mental health and providing stress relief. One such innovation is smartphone applications designed to reduce rumination, foster presence, and promote positive lifestyle changes to alleviate stress. These apps are easily accessible and often more affordable than traditional therapy, making them increasingly popular among users seeking self-administered stress relief practices.
Despite the widespread use of these apps, their effectiveness in reducing stress and enhancing quality of life remains unclear. Previous studies evaluating their efficacy have primarily focused on individual apps rather than comparing a wide range of options. To address this gap, researchers from Peking University conducted a review study and meta-analysis of existing literature on mobile applications for stress management. Their findings, published in Nature Human Behaviour, provide valuable insights into the most effective self-administered practices for stress relief.
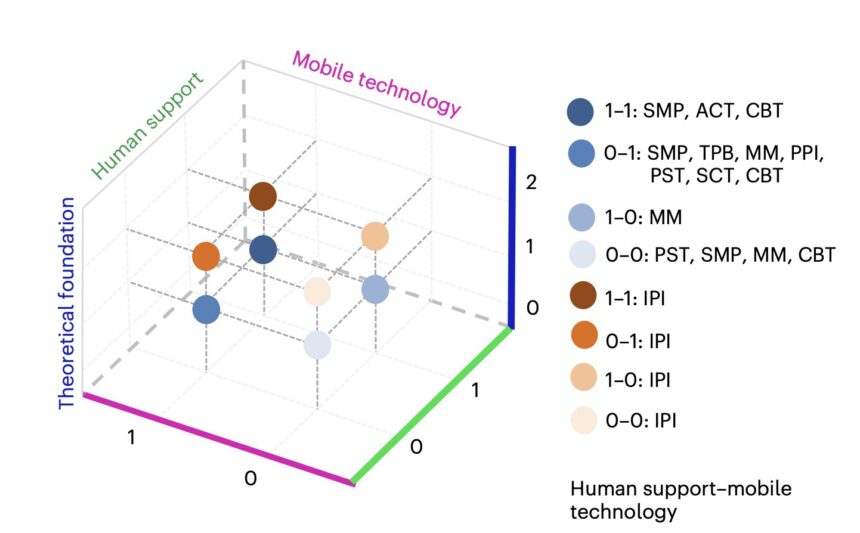
The study identified 19 mobile stress interventions, with stress management programs, problem-solving therapy, and mindfulness meditation ranking as the top performers. Interestingly, the research found no significant evidence that human support or mobile technology influenced intervention outcomes. The results highlight the potential benefits of cognitive-behavioral therapy-based applications, particularly for individuals unable to access traditional mental health services.
By analyzing data from 63 studies involving over 20,000 participants, the researchers employed Bayesian statistical techniques to compare the efficacy of different mobile apps and identify factors that could enhance their effectiveness. The study’s three-dimensional framework incorporated theoretical foundations, human support, and mobile technology to classify and evaluate stress management interventions.
Overall, the study suggests that mobile applications rooted in problem-solving therapy, stress management programs, and mindfulness meditation may offer effective stress reduction strategies for individuals seeking mental health support. These findings could serve as a foundation for future app development and enhancements, guiding the creation of new features to optimize users’ well-being and stress management.
In conclusion, the research underscores the potential of mobile interventions for stress relief and highlights the importance of evidence-based approaches to mental health support. By leveraging these insights, developers and mental health professionals can collaborate to create innovative solutions that empower individuals to manage stress and improve their overall quality of life.