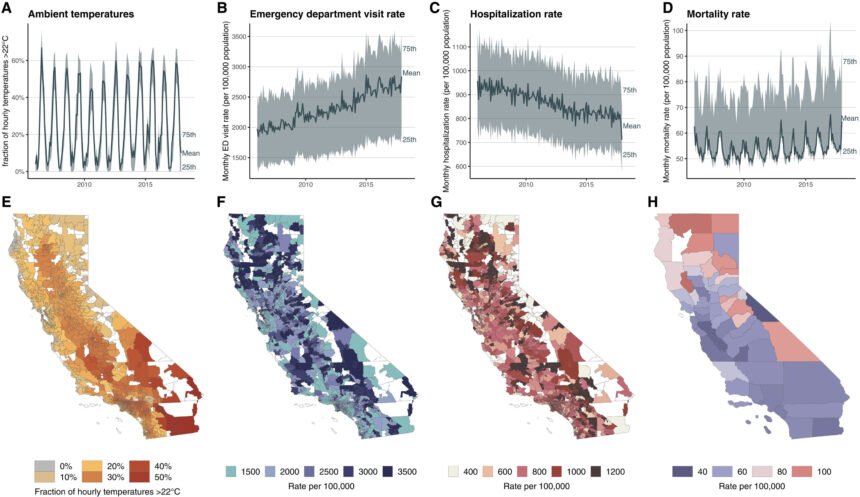
Climate change is having a significant impact on public health in California, with a new study revealing some surprising findings. As temperatures rise, the state is experiencing fewer deaths from cold temperatures, but an increase in emergency department visits due to extreme heat. This overlooked consequence of climate change could place a greater burden on the healthcare system in the coming years.
Researchers from the University of California San Diego and Stanford University analyzed data from 2006 to 2017, including all deaths, emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and daily temperatures in California. Their findings, published in the journal Science Advances, shed light on the varied health impacts of hot and cold temperatures in the state.
According to the study, emergency room visits rise sharply on hotter days, reflecting a wider range of health impacts across different age groups. Conditions like injuries, mental health issues, and poisonings show clear increases with heat, highlighting the need for a more comprehensive approach to addressing temperature-related health risks.
Older adults are particularly vulnerable to cold temperatures, while younger adults and children are more affected by heat. As California experiences fewer extreme cold days, the state may see fewer cold-related deaths. However, this benefit is offset by more trips to the emergency room as a result of extreme heat.
The economic and social burden of climate change on public health is also a concern. Health care spending in the United States on chronic diseases alone exceeds $3 trillion annually, accounting for 17.6% of the US gross domestic product. With projections based on moderate climate change scenarios through 2050, researchers estimate that California will see fewer deaths overall due to less cold weather, resulting in savings of approximately $30 billion annually. However, the state is expected to see an increase in heat-driven emergency department visits, costing an additional $52 million annually in health care spending.
The study emphasizes the importance of considering the full spectrum of health impacts when planning for the effects of climate change. Hospitals, insurers, and public health agencies must prepare for increased demand during extreme heat events and tailor warnings and resources to different age groups to protect public health.
In conclusion, understanding the health impacts of temperature extremes is crucial for developing effective responses to protect public health. Climate change is altering who is exposed to what health risks, making it essential to address these challenges proactively. By acknowledging the nuanced effects of temperature on health, policymakers can better prepare for the future and mitigate the impact of climate change on public health.