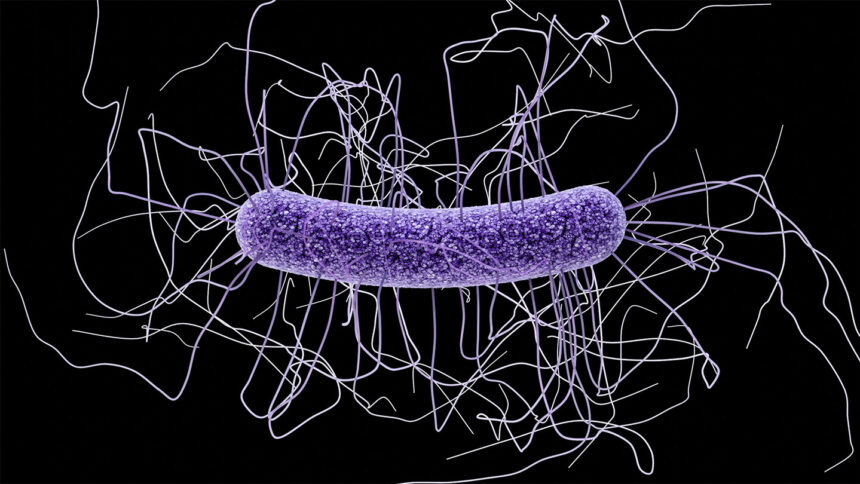
Researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery in the fight against Clostridioides difficile, a deadly intestinal infection that claims the lives of 30,000 people in the United States annually. Utilizing mRNA technology, the same technology that produced the first COVID-19 vaccines, scientists have developed a promising vaccine that has shown efficacy in mouse experiments.
The mRNA vaccine, designed to target C. difficile and its harmful toxins, successfully protected mice from severe disease and death after exposure to lethal levels of the bacterial pathogen. Published in the prestigious journal Science on October 4, the study highlights the potential of mRNA vaccines in combating infections where traditional vaccines have fallen short.
C. difficile is a resilient pathogen that often causes intestinal issues following antibiotic treatments. With around 500,000 infections reported in the US each year, the bacterium’s toxins can lead to a range of symptoms from mild diarrhea to life-threatening sepsis. Despite previous attempts at developing vaccines targeting C. difficile toxins, none have proven particularly effective.
Taking a different approach, a team of researchers at the University of Pennsylvania used mRNA technology to create a multi-faceted vaccine that targets various proteins crucial to C. difficile’s disease-causing abilities. In animal studies involving mice and hamsters, the mRNA vaccine elicited a robust immune response, generating antibodies, immunoglobulins, and T cells more effectively than conventional vaccines.
The results were remarkable. All vaccinated mice survived exposure to a highly lethal dose of C. difficile, while unvaccinated mice succumbed to the infection within days. Although vaccinated mice still got infected, they experienced mild symptoms and recovered swiftly. Furthermore, the immune protection provided by the vaccine was long-lasting, with vaccinated mice showing resilience to a second C. difficile infection six months later.
While the vaccine also triggered an immune response in rhesus macaques, further testing in more naturalistic animal models, known as “dirty mice,” is necessary before human trials can commence. The road from successful animal studies to effective human vaccines is often challenging, but the promising results of this mRNA vaccine against C. difficile offer hope for a breakthrough in the battle against this deadly infection. The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and advancements being made every day. One of the most exciting areas of development in recent years has been the field of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. It is becoming increasingly prevalent in our daily lives, from virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to self-driving cars and facial recognition technology.
One of the most promising applications of AI is in the healthcare industry. AI has the potential to revolutionize the way we diagnose and treat diseases, making healthcare more efficient and effective. For example, AI algorithms can analyze medical images like X-rays and MRIs to detect abnormalities that may be missed by human doctors. This can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, ultimately saving lives.
AI is also being used to develop personalized treatment plans for patients based on their unique genetic makeup and medical history. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI can identify patterns and trends that human doctors may not be able to see, leading to more effective treatments and better outcomes for patients.
In addition to diagnosis and treatment, AI is also being used to improve the overall patient experience. Chatbots powered by AI can provide patients with instant access to medical information and advice, reducing the burden on healthcare providers and improving communication with patients. Virtual reality technology, which uses AI algorithms to create immersive experiences, is being used to help patients manage pain and anxiety during medical procedures.
While the potential benefits of AI in healthcare are immense, there are also challenges and concerns that need to be addressed. One of the biggest concerns is the potential for bias in AI algorithms, which can lead to disparities in healthcare outcomes for different groups of people. Ensuring that AI is used ethically and responsibly is crucial to avoid exacerbating existing inequalities in healthcare.
Despite these challenges, the future of AI in healthcare looks bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of AI that will improve the quality of care and ultimately save lives. By harnessing the power of AI, we have the opportunity to transform healthcare for the better and create a healthier, more equitable world for all.