New Discovery Offers Hope for Alzheimer’s Treatment
Researchers from the Baylor College of Medicine in the US have made a groundbreaking discovery that could pave the way for new treatments targeting the protein aggregations implicated in Alzheimer’s disease. By studying mice with a condition similar to Alzheimer’s, the team found that increased levels of a protein called Sox9 stimulated specialized brain cells to enhance the removal of plaques associated with the disease.
Not only did the treated mice show improved performance in behavioral and memory tests, indicating a potential reversal of cognitive decline, but further investigation revealed that the benefits of Sox9 were linked to the upregulation of a receptor called MEGF10 in astrocytes – brain maintenance cells responsible for clearing amyloid-beta plaques.
Neuroscientist Dong-Joo Choi highlighted the importance of astrocytes in maintaining normal brain function and emphasized the role these cells play in aging and neurodegeneration. The researchers observed that boosting Sox9 levels rejuvenated aging astrocytes, while removing the protein had detrimental effects on memory and plaque accumulation.
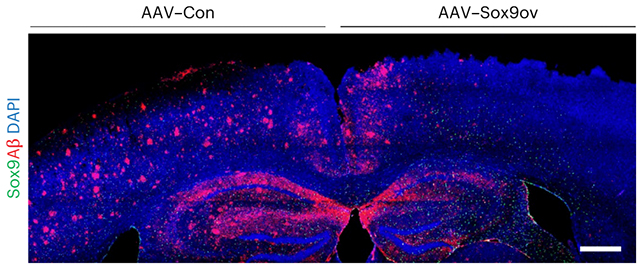
The study, published in Nature Neuroscience, underscores the potential of targeting astrocytes as a novel approach to Alzheimer’s treatment. While existing therapies mainly focus on neurons or plaque prevention, enhancing astrocytes’ natural cleaning abilities could offer a promising alternative.
Although the research was conducted in mice and not yet tested in humans, the findings provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying Alzheimer’s disease progression. By shedding light on the role of astrocytes in plaque clearance, this study opens up new avenues for developing effective interventions against Alzheimer’s.
As scientists continue to explore different strategies for tackling Alzheimer’s, the complexity of the disease remains a challenge. While efforts to target amyloid-beta plaques are ongoing, the underlying causes of Alzheimer’s and the role of protein aggregations in its pathogenesis require further investigation.
Ultimately, each study brings us closer to unraveling the mysteries of Alzheimer’s and offers hope for innovative treatments that could one day halt its progression. By focusing on enhancing astrocytes’ role in plaque clearance, researchers are paving the way for a potential breakthrough in Alzheimer’s therapeutics.





