A recent study published in Science Advances has shed light on the earliest human ancestor that may have walked on two legs. The fossil of an ancient hominin, Sahelanthropus tchadensis, dating back seven million years ago, has been found to exhibit key features of bipedalism. This discovery challenges previous findings and adds to our understanding of human evolution.
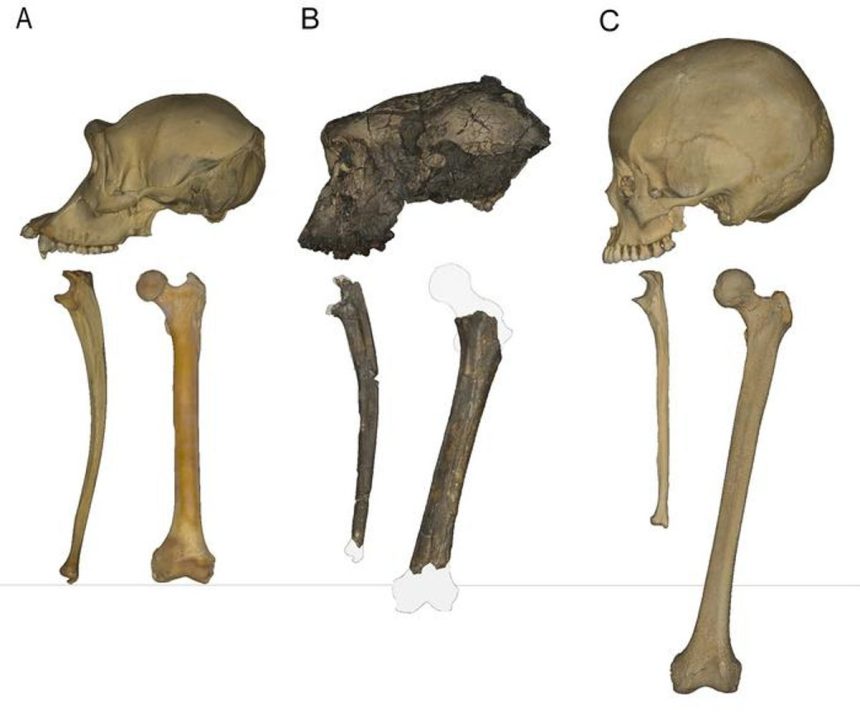
The initial discovery of Sahelanthropus tchadensis in 2001 sparked curiosity among anthropologists due to the positioning of the hole at the base of its skull, suggesting bipedalism. However, subsequent analysis of a femur found alongside the skull fragments did not initially provide evidence of bipedalism. This discrepancy led to debates within the scientific community regarding the classification of Sahelanthropus as a hominin.
The recent study, led by Scott Williams and his team, used advanced techniques to analyze the fossil and identified anatomical features associated with bipedalism. These include the inward twist of the femur and a small protrusion where the gluteus maximus muscle would have attached. Additionally, a subtle clue in the form of a femoral tubercle, where the iliofemoral ligament would attach, further supports the hypothesis of bipedalism in Sahelanthropus.
While some researchers remain skeptical of these findings, citing the poorly preserved condition of the fossil and the presence of similar features in non-bipedal primates, Williams is confident in his team’s interpretation. He suggests that Sahelanthropus may have walked on two legs while still relying on trees for foraging and safety.
The debate surrounding the bipedalism of Sahelanthropus tchadensis continues, with researchers planning to return to the original field site in search of additional remains. The discovery of new evidence could potentially resolve the ongoing discussions and provide further insights into the evolutionary history of early hominins.
Overall, this study highlights the importance of ongoing research in paleoanthropology and the need for continued exploration to unravel the mysteries of human evolution. By building on past discoveries and leveraging advanced techniques, scientists are gradually piecing together the puzzle of our ancient ancestors and their unique characteristics.