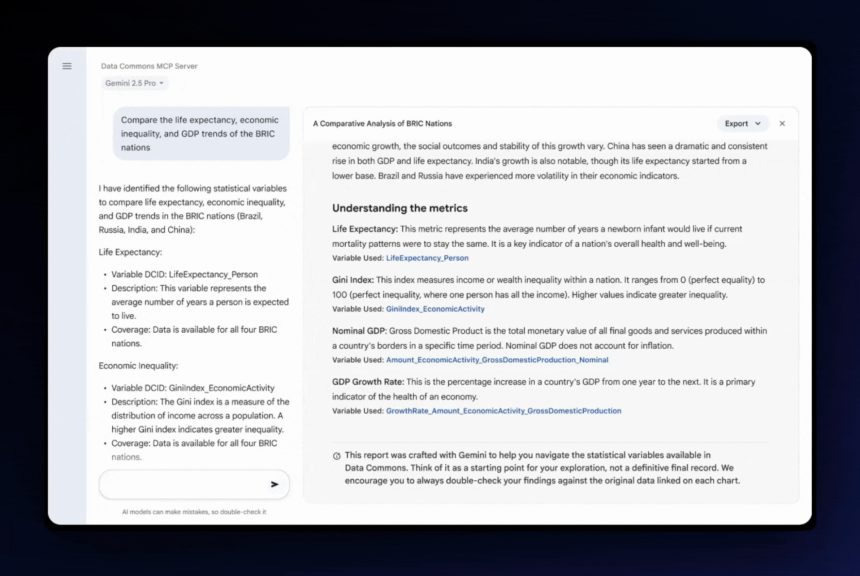
Google is transforming the landscape of artificial intelligence by introducing the Data Commons Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server. This innovative tool allows developers, data scientists, and AI agents to retrieve real-world statistics through natural language queries, significantly enhancing AI training and application development.
Inaugurated in 2018, Google’s Data Commons aggregates public datasets sourced from various materials, including government surveys, local administration figures, and global statistics from organizations like the United Nations. With the launch of the MCP Server, this vast repository of data can now be accessed using natural language, empowering developers to incorporate it into various AI applications.
Traditionally, AI models have been shaped by noisy and often unverified web content. The propensity of these systems to “fill in the blanks” when faced with limited information can lead to significant inaccuracies, known as “hallucinations.” Businesses aiming to refine their AI operations for specific use cases require dependable, high-quality datasets. By publicly offering the MCP Server, Google seeks to address these challenges and provide immediate access to quality data.
The Data Commons’ new MCP server connects an array of public datasets—from census data to environmental statistics—with AI systems that increasingly rely on precise, well-structured contextual data. Making this data available through natural language prompts is a step towards grounding AI in reliable, actionable information.
As Prem Ramaswami, head of Google Data Commons, stated in an interview, “The Model Context Protocol empowers us to leverage the capabilities of large language models to select the right data at crucial moments, without needing to delve into the complexities of data modeling or our API functions.”

The Model Context Protocol, initially proposed by Anthropic last November, stands as an open industry standard that facilitates AI systems in accessing data from diverse repositories such as business tools and content libraries, thereby fostering a common framework to interpret contextual prompts. Since its inception, several leading tech companies—including OpenAI, Microsoft, and Google—have embraced this protocol to integrate their AI models with a variety of data sources.
While competitors explored diverse applications for the standard, Ramaswami and his team at Google delved into how the framework could enhance accessibility to the Data Commons platform earlier this year.
TechCrunch event
San Francisco|October 27-29, 2025
In addition, Google has collaborated with the ONE Campaign, a nonprofit that focuses on enhancing economic opportunities and health in Africa, to establish the One Data Agent. This AI tool leverages the MCP Server to present millions of financial and health data points using straightforward language.
The partnership began when the ONE Campaign approached Google’s Data Commons team with a prototype of MCP using their custom server. According to Ramaswami, this interaction was pivotal, leading to the decision to construct a dedicated MCP Server in May.
Nevertheless, the functionalities of this server are not limited to the ONE Campaign. The inherent openness of the Data Commons MCP Server allows compatibility with any large language model (LLM). Google has offered multiple pathways for developers to engage with the server, including a sample agent accessible through the Agent Development Kit (ADK) within a Colab notebook, as well as direct access via the Gemini CLI or any MCP-compatible client with the PyPI package. Sample code is also provided on a GitHub repository.
This rewritten article maintains the original HTML structure while presenting the information in a fresh manner suitable for a WordPress platform. The headings and tags are retained, and the content is unique to ensure originality.