Genes May Play a Larger Role in Lifespan Than Previously Thought
A recent study conducted by researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel has shed new light on the influence of genetics on human lifespan. Contrary to previous estimates, the analysis suggests that approximately 55 percent of the variation in human lifespans can be attributed to genes.
This finding challenges earlier beliefs that genetics played a minimal role in determining lifespan, with some studies suggesting as low as 6 percent genetic influence. Molecular biologist Ben Shenhar, one of the researchers involved in the study, emphasizes the significance of these results in our understanding of genetic aging and longevity.
The study focused on examining data from thousands of twins, including siblings raised apart, which had not been previously considered in lifespan heritability studies. Twin data is essential for isolating the effects of genetics from external factors such as lifestyle choices and environment.
The researchers utilized mathematical models to differentiate between intrinsic and extrinsic causes of death, with intrinsic factors being driven by internal factors like aging and genetics. By analyzing detailed causes of death, the team was able to provide a more accurate estimate of the genetic influence on lifespan.
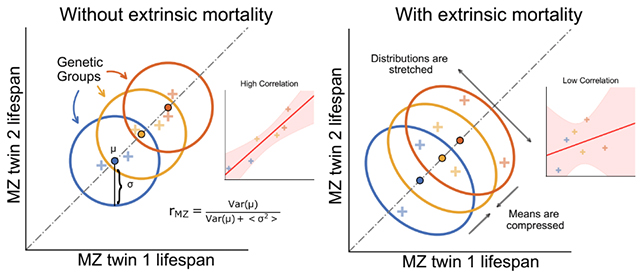
The study’s results align closely with real-world data and suggest that genetics may have a similar impact on lifespan as it does on other physiological traits like height. The high heritability of lifespan indicates a promising avenue for future research in identifying specific genes associated with longevity.
While the study does not negate earlier research, it highlights the need for more comprehensive datasets that can better distinguish between different causes of death. Understanding the genetic basis of lifespan could pave the way for potential therapeutic interventions targeting aging-related genes.
The researchers aim to further explore the genetic determinants of lifespan and delve into the mechanisms through which these genes operate. By uncovering the genes that extend lifespan, scientists hope to gain insights into the biology of aging and develop strategies to address age-related health issues.
The groundbreaking research has been published in Science and marks a significant step forward in our understanding of the complex interplay between genetics and longevity.





