The Mysteries of Earth’s Deep Interior
While humanity has sent probes far into interstellar space, we have barely explored the depths of our own planet. Earth’s deep interior remains a mystery, with most of our knowledge coming from geophysics.
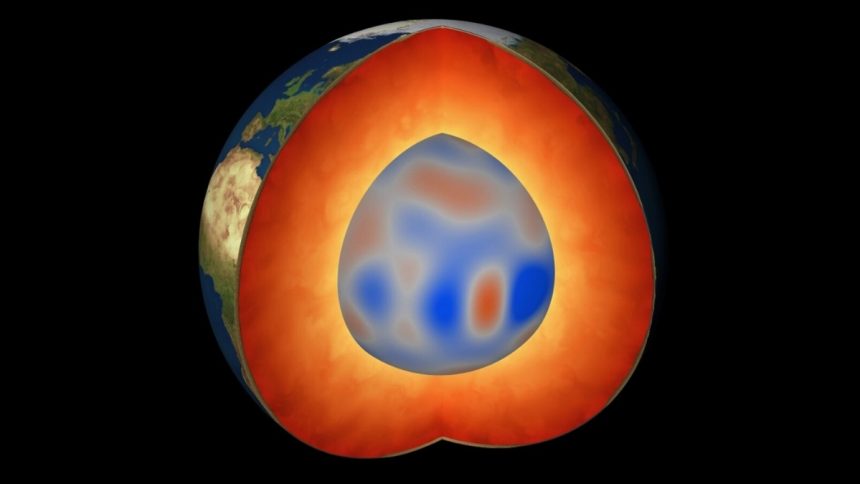
The Earth’s interior consists of a solid crust, a rocky mantle, a liquid outer core, and a solid inner core. The core-mantle boundary is a crucial interface within the Earth’s interior that plays a significant role in shaping our planet.
Located approximately 3,000 km beneath the Earth’s surface, the outer core is a vast ocean of molten iron alloy that generates the planet’s magnetic field. This geodynamo process, sustained by the heat transferred from the core to the mantle, has been protecting Earth from harmful radiation for billions of years.
Unveiling the Blobs
Recent research has shed light on the presence of massive structures known as Blobs in the lowermost part of the mantle, just above the core. These Blobs, located beneath Africa and the Pacific Ocean, are regions where seismic waves travel more slowly, indicating potential differences in temperature or composition.
By studying the magnetic fields generated by these Blobs, scientists have revealed that they are hotter than the surrounding mantle. This temperature variation has had a significant impact on Earth’s magnetic field over millions of years.
Implications for Earth’s Magnetic Field
Through advanced simulations on supercomputers, researchers have demonstrated how the presence of Blobs affects Earth’s magnetic field. The magnetic directions recorded by ancient rocks correlate with the heat flow patterns into these Blobs, influencing the stability and variability of the magnetic field.
These stagnant areas of conductive liquid beneath the Blobs act as insulators, preventing heat loss and creating unique patterns in Earth’s magnetic field. By understanding the role of Blobs, scientists can better comprehend the dynamics of Earth’s geodynamo process.
Conclusion
While the mysteries of Earth’s deep interior continue to intrigue scientists, the discovery of Blobs has provided valuable insights into the planet’s magnetic field. By unraveling the secrets hidden within the core-mantle boundary, researchers are paving the way for a deeper understanding of Earth’s geophysical processes.
Andrew Biggin, Professor of Geomagnetism, University of Liverpool
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article here.