The latest jobs report released today provides further evidence of the ongoing inflation concerns in the economy. Average hourly earnings saw a significant increase of 0.5%, surpassing the 0.3% rate that aligns with the Federal Reserve’s inflation target. Wage inflation has been hovering around 4.1% over the past year, slightly higher than the 3.0% to 3.5% range typically associated with 2% price inflation. Unfortunately, the fight against inflation appears to have hit a roadblock and may even be regressing, with wage inflation averaging 4.6% over the last 6 months, indicating a troubling trend towards higher inflation levels that could potentially lead to a recession.
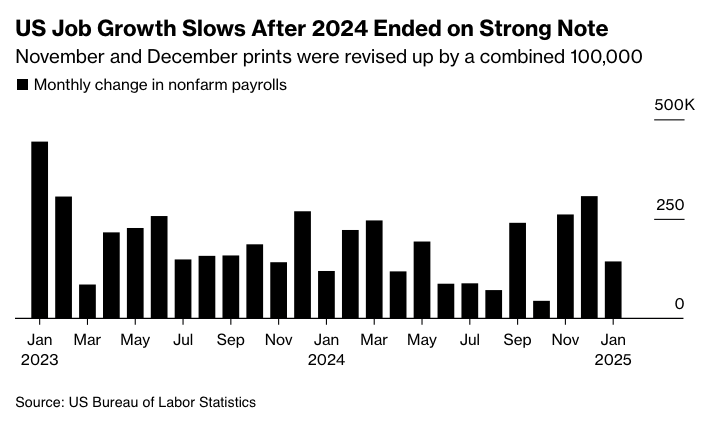
Economist Jed Kolko has pointed out signs of a cooling job market, citing revisions in the jobs data for previous months. The adjustments in the payroll survey of businesses have shown a downward trend in job growth, while the household survey used for calculating the unemployment rate has seen an upward revision. These revisions have narrowed the gap between the two series that had emerged during 2024, indicating a more balanced view of the employment situation.
While the employment figures are often used as a gauge for forecasting inflation, the correlation between wage inflation and employment is complex and influenced by various factors. For instance, recent policies such as the immigration crackdown and potential changes under the Trump administration could impact job growth and wage inflation dynamics. As such, it is crucial to monitor wage inflation closely as it plays a key role in maintaining macroeconomic stability.
Nominal wages are known to be sticky, making it challenging to assess whether wage growth is excessive until it’s too late. Real indicators such as job growth and labor force dynamics can provide insights into the economy’s health, but their interpretation is not straightforward. Amidst these uncertainties, the concept of Nominal Gross Domestic Product (NGDP) level targeting emerges as a viable monetary policy framework to ensure stability and credibility in monetary policy decisions.
As the economy navigates through the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic, the Federal Reserve faces mounting pressure to address inflation concerns and uphold its mandate. It is essential for the Fed to re-evaluate its inflation target or consider alternative strategies to align with its objectives effectively.
In conclusion, the latest jobs report highlights the ongoing challenges in managing inflation and sustaining economic growth. By closely monitoring wage inflation and adopting sound monetary policies, policymakers can steer the economy towards a path of stability and prosperity.