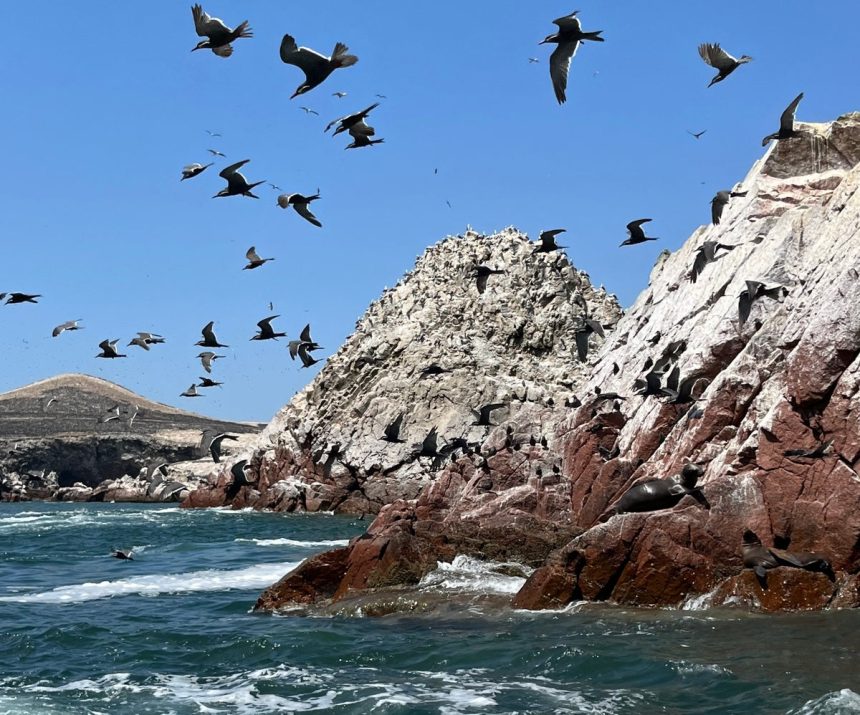
The Chincha Valley in Peru holds a fascinating history that dates back to the early 1400s, before the rise of the Inca Empire. A recent study published in PLOS One sheds light on the agricultural practices of the ancient Peruvians, revealing their innovative use of seabird guano as fertilizer for their maize crops as early as 1250.
Seabird guano, also known as “white gold,” was a valuable nitrogen deposit that played a crucial role in the agricultural success of the region. The Chincha Valley farmers understood the benefits of using guano to enrich their soil and boost crop yields. This practice not only sustained their communities but also allowed for trade and interactions with neighboring societies.
Archaeologists have long been intrigued by the mysteries of the Chincha Valley civilization. The recent findings provide valuable insights into the agricultural technologies and social dynamics of the ancient Peruvians. By analyzing isotopes in maize cobs found in the region, researchers were able to confirm the use of guano-based fertilizers in local farming practices.
The presence of seabird iconography in the Chincha Valley further supports the idea that guano was a prized resource that contributed to the prosperity of the region. The rich nitrogen content in guano made it a superior fertilizer, enhancing crop growth and increasing agricultural productivity.
Looking ahead, future research could delve deeper into the impact of guano fertilization on the economic and social structures of ancient Peruvian societies. Understanding how access to guano influenced community wealth and power dynamics could offer a more comprehensive picture of life in the Chincha Valley.
Moreover, the study highlights the importance of considering marine inputs in isotopic analyses of ancient diets. The introduction of seabird guano to terrestrial crops can create misleading chemical signatures, complicating the interpretation of ancient dietary habits. Researchers must account for these factors when studying ancient food sources to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Overall, the research on guano-based agriculture in the Chincha Valley provides valuable insights into the ingenuity and resourcefulness of ancient Peruvian civilizations. By unraveling the agricultural practices of the past, archaeologists can piece together a more comprehensive understanding of the societies that once thrived in this region. As a subscriber to Scientific American, you play a crucial role in supporting our commitment to providing in-depth coverage of meaningful research and groundbreaking discoveries. Your subscription helps us maintain the resources needed to report on critical decisions that impact labs across the United States and to champion the efforts of both aspiring and established scientists. In a time where the importance of science is often overlooked, your support allows us to shine a spotlight on the value of scientific inquiry.
In exchange for your subscription, you gain access to a wealth of essential news, engaging podcasts, visually stunning infographics, informative newsletters, compelling videos, thought-provoking games, and the finest writing and reporting in the world of science. With the option to gift a subscription to someone else, you can share the wealth of knowledge and inspiration that Scientific American has to offer.
Now more than ever, it is imperative for us to come together and demonstrate why science matters. By subscribing to Scientific American, you join us in our mission to promote the significance of scientific discovery and innovation. We hope you will stand with us in this important endeavor.
To subscribe and become a part of our community, visit our website and sign up today. Thank you for your support in advancing the cause of science and knowledge. The world of technology is constantly evolving, with new advancements and innovations being introduced every day. One of the most exciting areas of technology is artificial intelligence (AI), which is revolutionizing the way we live and work.
AI is the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. This technology has the potential to transform industries and improve efficiency in various sectors, including healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
In healthcare, AI is being used to improve patient care and diagnosis. AI algorithms can analyze medical images and data to help doctors make more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans. This technology can also help identify patterns in patient data to predict potential health issues and provide personalized treatment plans.
In finance, AI is being used to detect fraud and manage risk. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of financial data in real-time to identify suspicious transactions and prevent fraudulent activity. This technology can also help financial institutions automate processes and improve customer experience by providing personalized recommendations and services.
In manufacturing, AI is being used to optimize production processes and improve efficiency. AI-powered robots and machines can perform tasks with more precision and speed than human workers, leading to increased productivity and cost savings. This technology can also help manufacturers predict maintenance needs and prevent equipment failures, reducing downtime and improving overall performance.
While AI has the potential to bring many benefits, it also raises concerns about privacy and ethics. As AI becomes more integrated into our daily lives, it is important to consider the ethical implications of this technology and ensure that it is used responsibly.
Overall, AI is a powerful tool that has the potential to transform industries and improve the way we live and work. As this technology continues to evolve, it is important for society to embrace AI and leverage its potential for positive change. By harnessing the power of AI, we can create a more efficient and sustainable future for all.